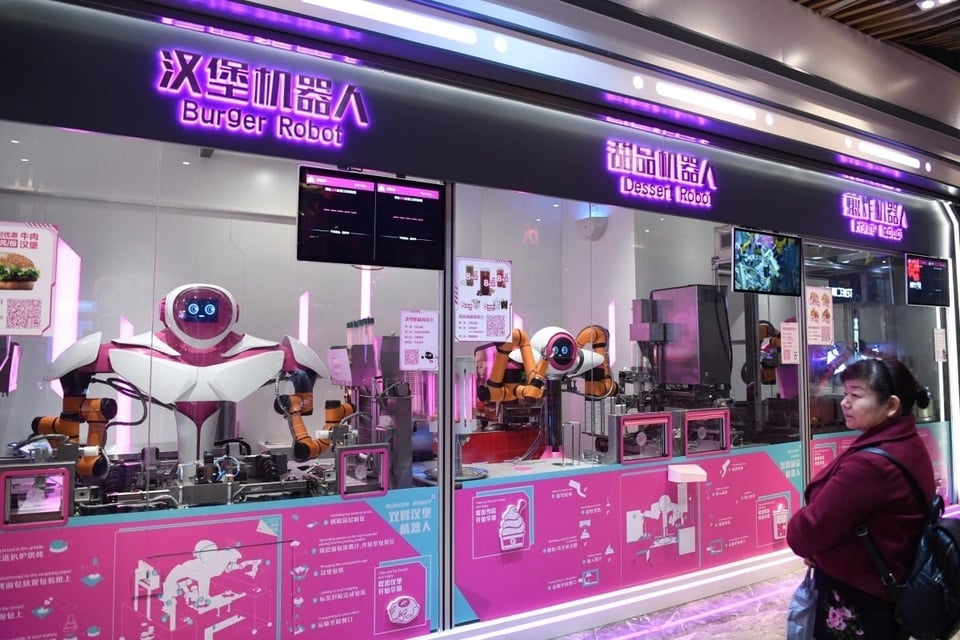
 |
Robots serve burgers and desserts at a smart restaurant in China. Photo: Xinhua . |
The Shanghai Commission of Commerce (China) and four local departments have just announced a plan to promote the city's catering industry, including a vision for the future of the culinary industry with AI restaurants, robot chefs, and data-driven menus.
According to SCMP , the boom in automation in the food industry has become a hot topic in China. As one of the most modern cities, Shanghai wants to go further in applying smart technology to local eateries and restaurants.
New opportunities for the culinary industry
As part of the plan, Shanghai aims to become a “national-leading, world- class” smart restaurant hub by 2028.
Analysts say this could bring major changes to China's food service industry, changing the way food is prepared and affecting the labor market.
“For group dining, fast food and beverage chains, more than 70% of operations will integrate smart technology into the entire value chain, while the rate of smart application in key operations at full-service restaurants will exceed 50%,” the document stated.
Shanghai also plans to set up a number of smart kitchens, build and pilot 3-5 AI-integrated dining projects, and facilitate smart solutions serving the catering industry.
The plan also encourages local restaurants to expand overseas. The city plans to support this by building smart supply chains that cover key target markets.
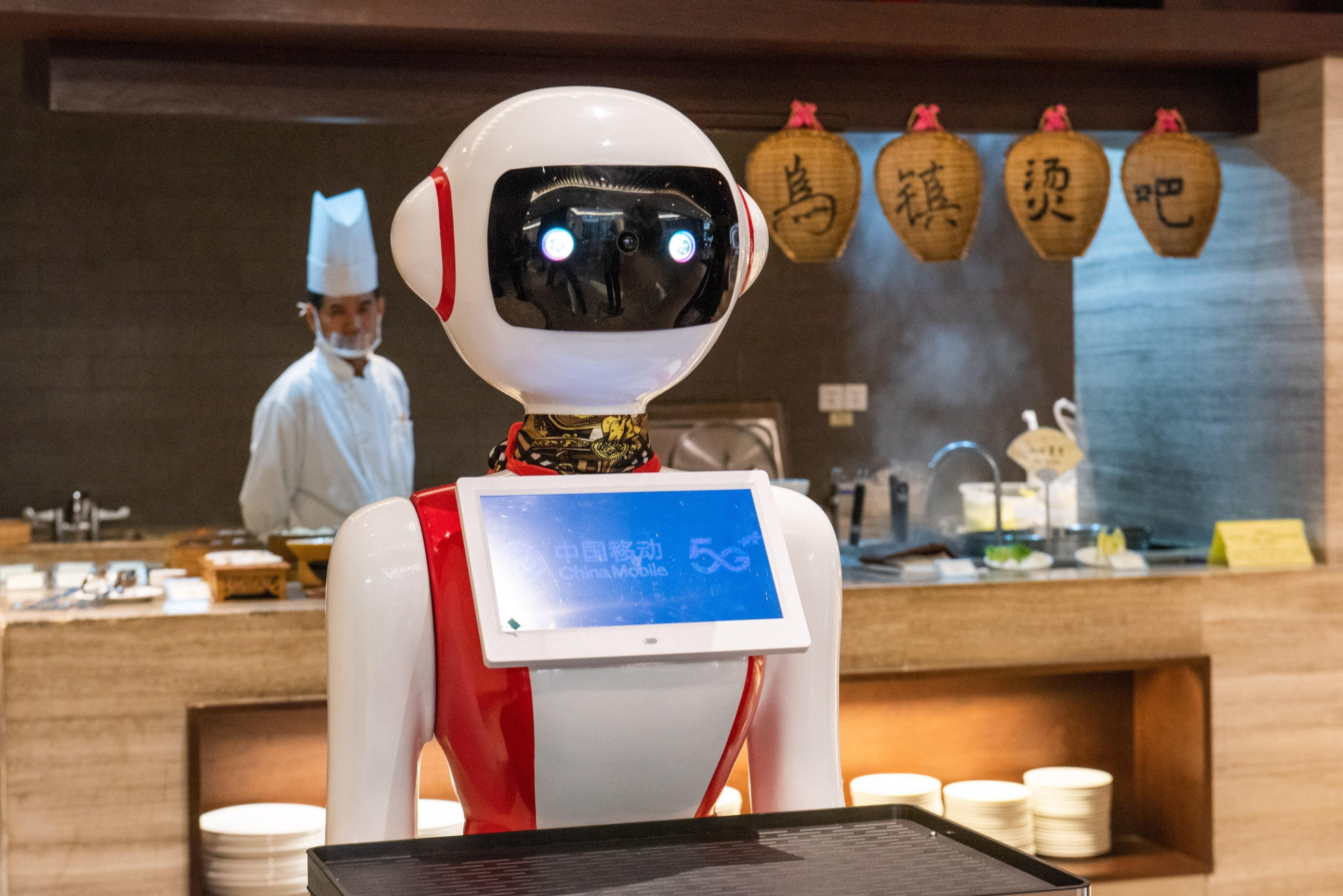 |
Robot serving at a restaurant in China. Photo: SCMP . |
Analysts say the strategy could accelerate the reshaping of China’s restaurant industry, with family-owned establishments at risk of being pushed out of the market.
“Large brand chains with good finances and resources to invest in smart technology help them quickly gain cost advantages and expand scale.
However, small eateries run by families or single members, lacking digital capabilities, may find it difficult to survive,” said Li Yingtao, an analyst at consultancy MCR.
However, Li believes the change could present new opportunities for technology providers willing to help large-scale restaurant restructuring.
The strategy also affects millions of workers in China's food service industry, with Shanghai calling on businesses with standardized menus, such as fast food and beverage chains, to shift to “operating with zero or fewer staff.”
The risk of creating a "machine flavor"
Under the plan, stores are encouraged to use smart drink makers, frying and rice cooking robots and burger stackers to increase efficiency.
In addition, the government will “support large restaurant chains and food service providers in building smart kitchens, integrating automatic washing, cooking and packaging systems.”
The plan aims to preserve and innovate culinary skills in the face of automation, helping to maintain flavor while improving efficiency, while also encouraging the use of AI-enabled menus and nutrition tools.
However, analysts say the robot-driven dining trend may not be suitable for a country where diners value human contact.
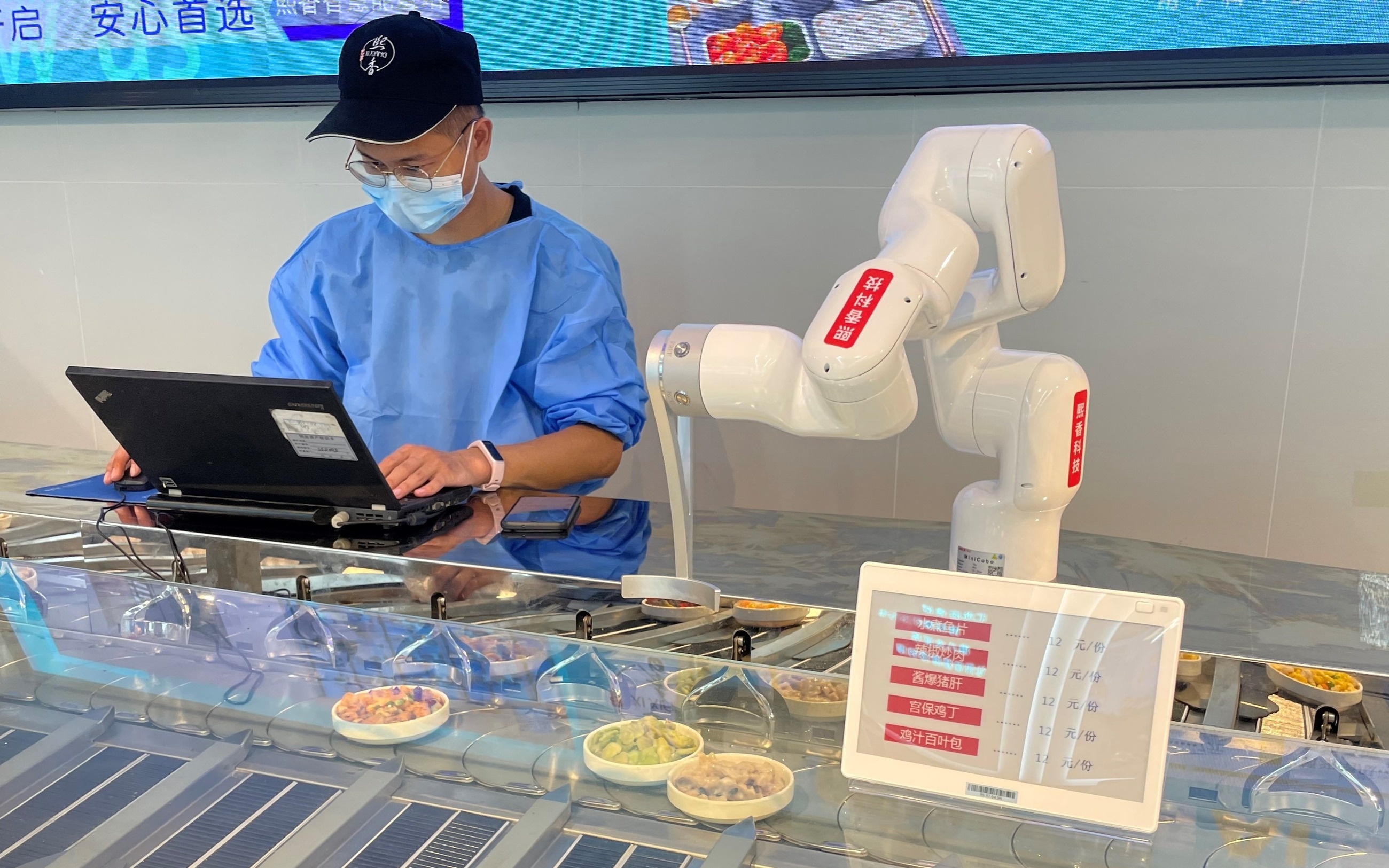 |
Robots serve in an "AI canteen" in China. Photo: Nikkei . |
Chinese cuisine is associated with the term “wok hei” (wok breath), which refers to the distinctive flavor and aroma of a cast iron wok imparted to food during stir-frying at high temperatures.
This is considered the soul of good food, and restaurants have faced harsh criticism for serving processed food.
According to Li Yingtao, the customer experience will play an important role as restaurants deploy AI and robotic solutions in the kitchen.
“In the short term, service robots can bring a new experience, which is generally positive, but challenges will soon come.
“If automation leads to a loss of pure taste or creates a ‘machine taste’, this could cause resistance and affect plans to adopt smart dining,” Li stressed.
Zhao Zhijiang, a researcher at consultancy Anbound, said the trend of adopting AI kitchens could tilt the industry towards fully processed food, which tastes very similar, reduces regional identity and makes it less human.
If that happens, diners may be hesitant to use food services, thereby reducing consumption, Zhao added.
Labor market impact
Since Shanghai is a hub for innovation in China, Zhao said the initial plan to “develop a more efficient culinary ecosystem” could be replicated across the country if successful.
“The results here will be evaluated and tested, and then applied to other areas. However, differences in technological capabilities and needs mean that the same cannot be applied everywhere.
Other cities can pick up some of Shanghai's successful strategies and improve AI adoption in the local food industry,” Zhao said.
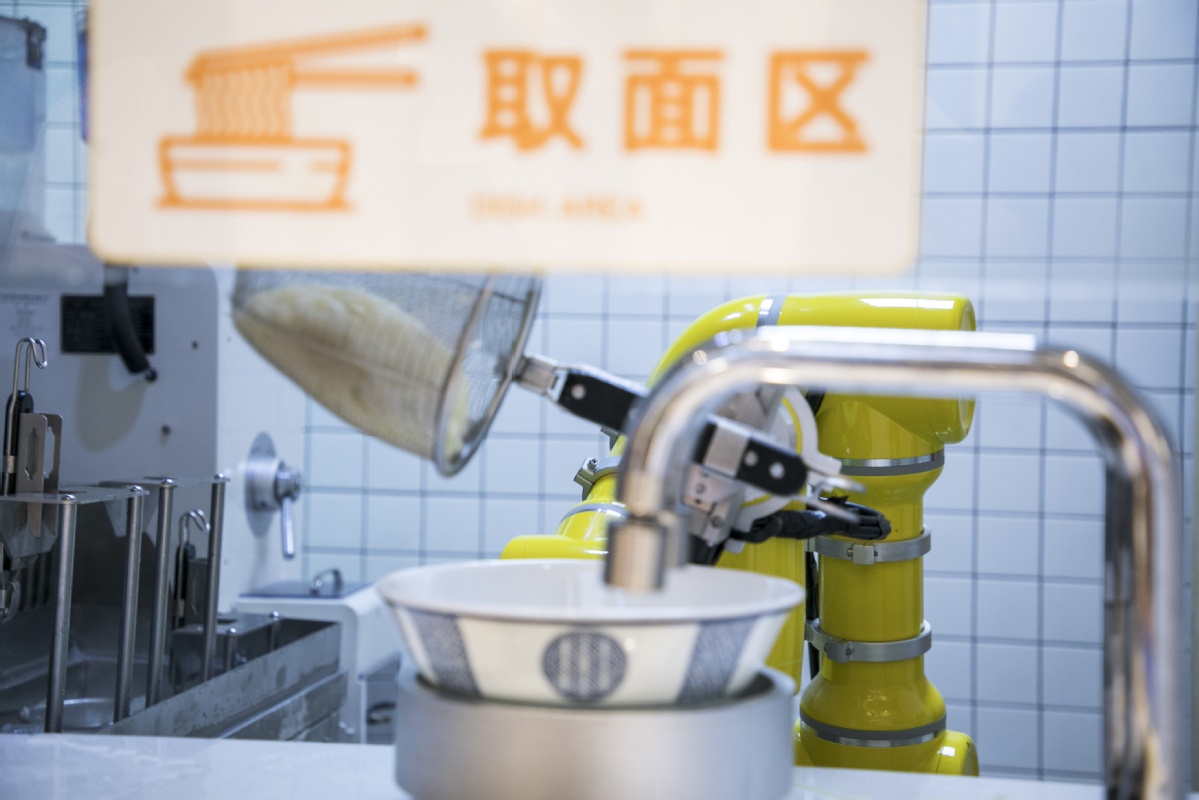 |
A robot puts noodles into a bowl at a smart restaurant in Shanghai. Photo: IC . |
In terms of jobs, analysts say the shift to automation will lead to market restructuring, rather than just layoffs.
Workers with repetitive jobs such as waiters, dishwashers, prep cooks and some chefs could be replaced by robots.
However, new jobs will emerge such as equipment maintenance, data analysis, digital system operations and AI-based management, creating a need for a more highly skilled workforce.
Source: https://znews.vn/ai-sap-xam-chiem-nha-hang-tai-thuong-hai-post1603736.html


































































































Comment (0)