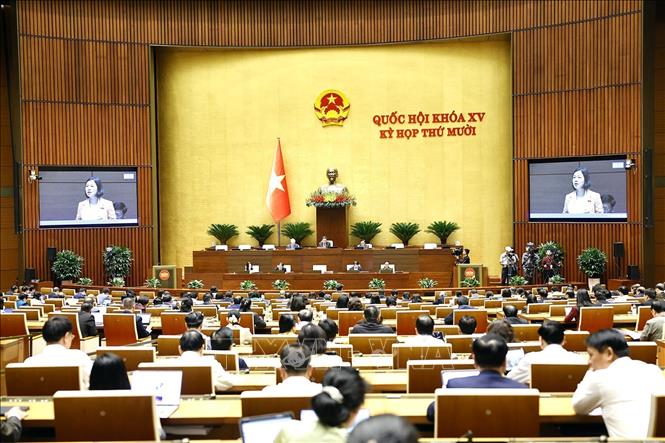

Scene of the meeting on the morning of November 12. Photo: Doan Tan/VNA
The draft Law on Civil Servants (amended) consists of 6 chapters and 43 articles (19 articles less than the current law). Notably, the draft law innovates the recruitment, use, and management of civil servants according to job positions; clearly stipulates that the recruitment, management, arrangement, and use of civil servants must be based on the requirements of the job position and the capacity and effectiveness of the civil servant's performance; and does not conduct exams or consider promotions of professional titles of civil servants.
At the same time, the draft law innovates the recruitment of civil servants in the direction of clearly defining the form of competitive examination, public and equal recruitment and the form of reception for high-quality human resources. Public service units are proactive in choosing recruitment methods suitable for the industry and field of operation, aiming at a professional and modern management model. For cases where civil servants and public employees transfer to work at a new public service unit, they must carry out job transfer procedures.
The draft law expands the rights of civil servants in the direction of regulating the conditions for civil servants to sign contracts to perform professional activities at other public service units other than the public service unit they are currently working for or at other non-public agencies, organizations, and units. Civil servants working in public science and technology organizations and public higher education institutions are allowed to contribute capital, participate in the management and operation of enterprises, work at enterprises established by such organizations or participate in the establishment to commercialize research results created by such organizations, with the consent of the head of the organization. In cases where the administrative officer is the head of a public science and technology organization or public higher education institution, the consent of the direct superior is required.
The draft law also adds provisions to encourage and protect innovative civil servants who dare to think, dare to do, dare to break through, and dare to take responsibility for the common good.
The Draft Law on E-commerce stipulates four models of e-commerce activities, including: direct business e-commerce platforms; intermediary e-commerce platforms; social networks operating e-commerce; and multi-service integration platforms.
Notably, for livestream sales activities, the draft law clearly stipulates: the platform owner must authenticate the identity of the livestreamer, publicize and implement mechanisms and measures to control livestream sales content in real time. For sellers, they are responsible for providing livestreamers with legal documents proving that they meet the conditions.
During the working session on November 13, the National Assembly will vote to approve: Resolution on the 2026 Socio -Economic Development Plan and Resolution on the 2026 State Budget Estimate.
Source: https://baotintuc.vn/thoi-su/ky-hop-thu-10-quoc-hoi-khoa-xv-quy-dinh-ro-hinh-thuc-thi-tuyen-vien-chuc-canh-tranh-20251112201143256.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends a conference to review one year of deploying forces to participate in protecting security and order at the grassroots level.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/12/1762957553775_dsc-2379-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Highways passing through Dong Nai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/12/1762940149627_ndo_br_1-resize-5756-jpg.webp)
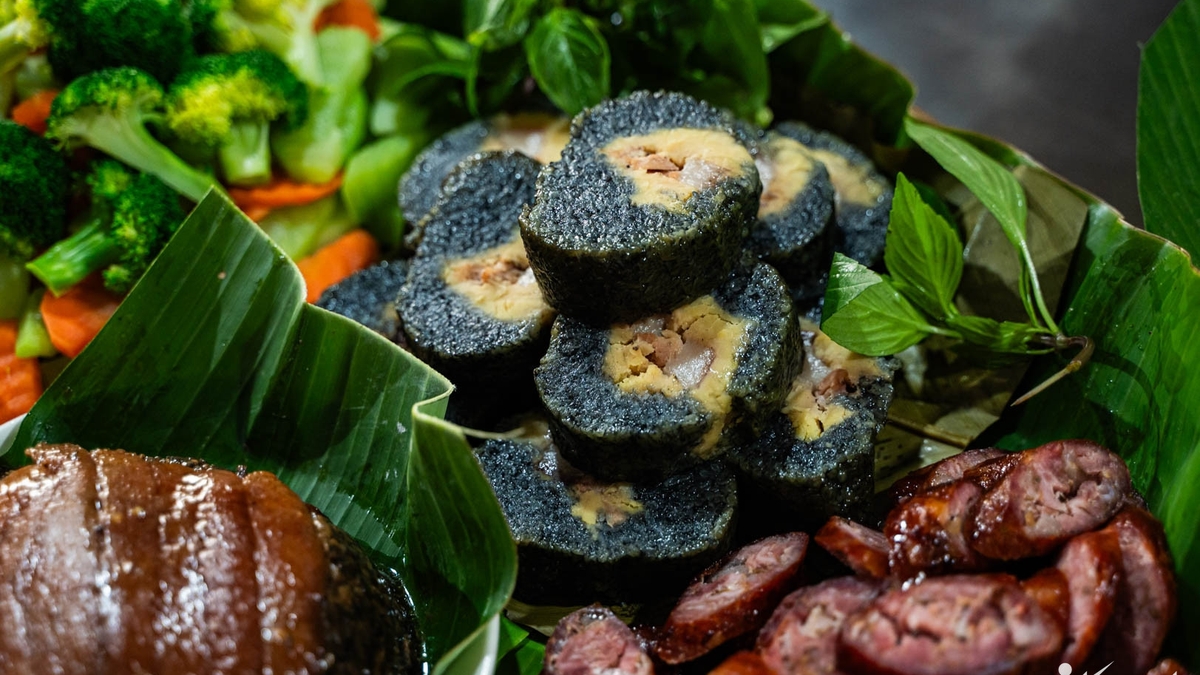



























































































![Dong Nai OCOP transition: [Article 3] Linking tourism with OCOP product consumption](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/10/1762739199309_1324-2740-7_n-162543_981.jpeg)
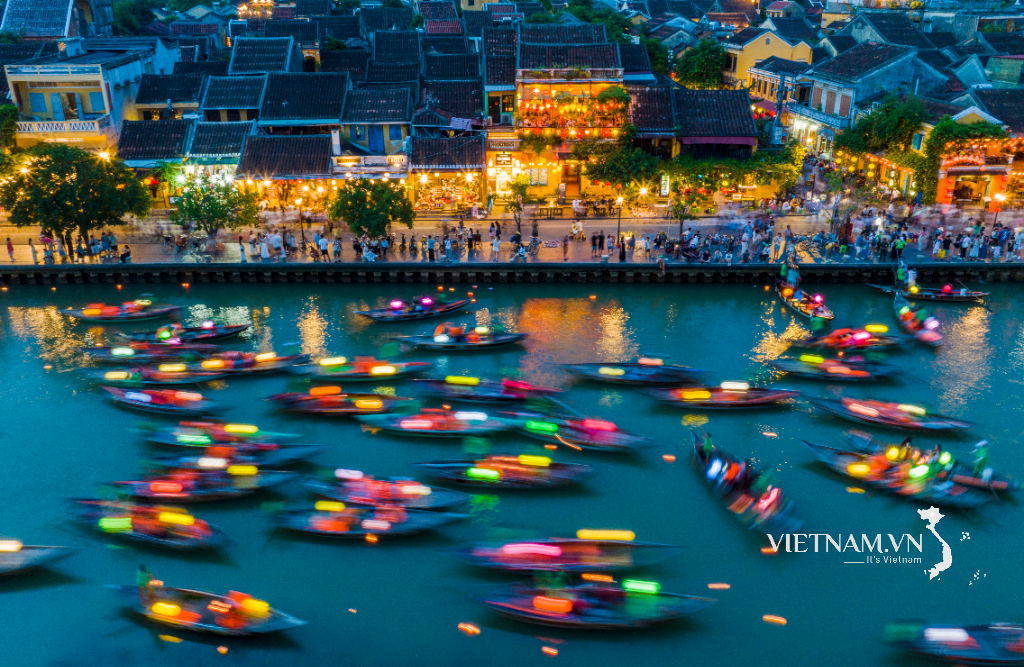







Comment (0)