Kidney stones are a common condition. In the United States, an estimated 12% of the population has had a kidney stone at least once in their lifetime. Both men and women can get kidney stones, but men are more likely to get them, according to the Times of India .
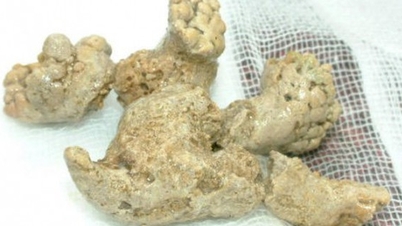
Types of kidney stones, causes and formation mechanism
The kidneys play an important role in filtering waste from the body through urine, and also regulating essential minerals such as sodium, potassium and calcium in the blood. Kidney stones form when these minerals and salts crystallize due to over-concentrated urine, forming solid masses that can appear anywhere in the urinary tract.

Underlying medical conditions involving the digestive or urinary system can increase the risk of kidney stones recurring.
PHOTO: AI
There are four main types of kidney stones, each associated with different causes:
Calcium stones: The most common type, usually occurring as calcium oxalate stones.
Struvite stones: Often associated with urinary tract infections, stones can grow large but initial symptoms are unclear.
Uric acid stones: Common in people who are rapidly or severely dehydrated, such as due to chronic diarrhea, a high-protein diet, or malabsorption disorders.
Cystine stones: Occur in people with the genetic disease cystinuria, which causes the kidneys to excrete too much of a certain amino acid.
Correctly identifying the type of kidney stone is an important step in finding the root cause and preventing recurrence.
Common causes of kidney stones recurrence and preventive measures
Many factors contribute to the formation and recurrence of kidney stones. Lifestyle and diet play a big role, especially not drinking enough water; eating too much protein, salt, or sugar; and not getting enough calcium, potassium, or magnesium in your diet.
Certain medications and supplements can also increase the risk of stone formation, such as calcium-containing antacids, some medications for migraines or depression, laxatives, and high doses of vitamin C.
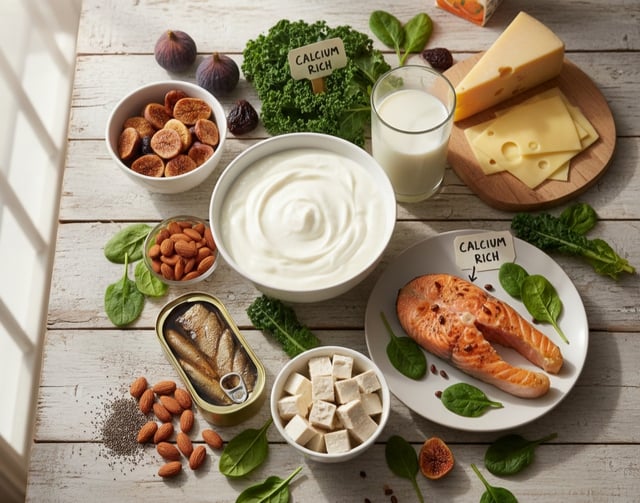

Foods such as milk and dairy products can help limit stone formation.
PHOTO: AI
In addition, underlying diseases related to the digestive or urinary system can also increase the risk of kidney stones recurring.
Therefore, to help prevent kidney stones from recurring, people should apply the following measures:
Drink enough water : Drinking plenty of water during the day helps dilute urine, reducing the risk of mineral crystallization.
Add calcium-rich foods : Foods such as milk and dairy products can help limit stone formation.
Limit animal protein intake : Avoid eating too much meat, poultry and seafood as this can increase uric acid.
Reduce oxalate-rich foods : Limit spinach, nuts, and chocolate, as these are foods that can contribute to calcium oxalate stones.
Review your medications : Some medications or supplements can increase your risk of stones. However, talk to your doctor before changing your medication.
Specialist visit : Work with a urologist for personalized advice and a tailored treatment plan to prevent stones from recurring.
How to recognize early warning signs of kidney stones
Kidney stone symptoms vary widely, depending on the size and location of the stone and whether there is an infection. Common signs include:
- Severe, stabbing pain in the back or sides, below the ribs; the pain may radiate to the lower abdomen or groin.
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating.
- Urine is pink, cloudy, or has a foul odor.
- Frequent urination, nausea, vomiting; in some cases may be accompanied by fever and chills.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/soi-than-tai-phat-nguyen-nhan-va-cach-giam-nguy-co-18525120822162209.htm



![[Photo] Urgently help people soon have a place to live and stabilize their lives](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F09%2F1765248230297_c-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)









































































![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam works with the Standing Committees of the 14th Party Congress Subcommittees](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/09/1765265023554_image.jpeg)


































Comment (0)