Hoarseness can be a sign of laryngitis, gastroesophageal reflux, vocal cord paralysis, or cancer.
Hoarseness is a change in the quality or pitch of the voice, causing it to sound rough, raspy, or weak. It is caused by abnormalities in the vocal cords, which are responsible for producing sound as air passes through them. Below are some conditions that can cause hoarseness.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is one of the most common causes of hoarseness, and it can be acute or chronic. Acute laryngitis is often caused by upper respiratory infections, influenza, or overuse of the voice such as shouting, speaking loudly, singing loudly, talking for too long without rest, or speaking at too high a pitch.
Patients should rest, limit talking, and drink plenty of water to help the larynx recover. In cases of hoarseness caused by smoking or exposure to chemicals that irritate the larynx, these factors should be avoided, and excessive alcohol consumption should be limited.
If a viral infection causes hoarseness, the symptoms may resolve on their own, or the patient may need to take antiviral medication as directed by a doctor.
Laryngeal fold hemorrhage
Laryngeal fold hemorrhage occurs when blood vessels on the surface of the vocal cords rupture. This can quickly lead to hoarseness, requiring the patient to stop talking and seek medical attention.
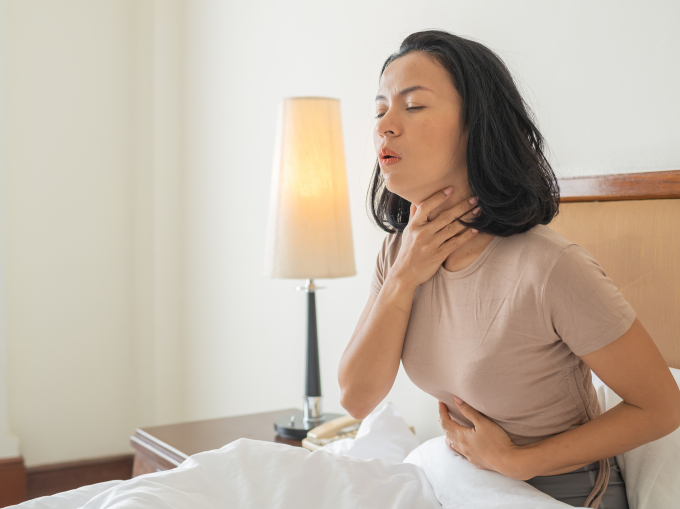

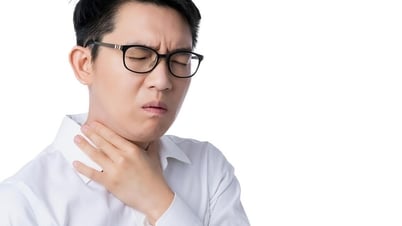
Hoarseness is an abnormal change in the pitch and volume of the voice. (Image: Freepik)
Laryngeal nodules, cysts, and polyps
Laryngeal nodules, cysts, and polyps are benign growths that can appear along the laryngeal folds. Excessive talking and shouting can lead to pressure, friction, and disruption of vocal cord vibration, resulting in hoarseness. Patients should rest and may undergo surgery or voice therapy as directed by their doctor.
Vocal cord paralysis
Vocal cord paralysis occurs when one or both vocal cords are unable to open or close properly. Causes may include head, chest, or neck injuries; tumors in the base of the skull, neck, and chest; lung cancer; and thyroid cancer.
At this stage, the vocal cords are paralyzed and unable to move normally, leading to hoarseness. Treatment methods include voice therapy and surgery.
Acid reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, leading to throat irritation. This irritation can affect the function of the vocal cords and contribute to hoarseness. In some people, it can negatively impact the larynx, leading to laryngopharyngeal reflux with the symptom of constant throat clearing.
To reduce symptoms and prevent the disease from recurring, everyone should maintain a healthy weight, eat a healthy diet (avoiding spicy, greasy, or acidic foods), not smoke, and take medication as prescribed.
Neurological disorders
Conditions such as Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, or stroke can affect the coordination and control of the muscles involved in speech, leading to hoarseness. People with Alzheimer's disease often have a raspy, unclear voice, with an "umm" sound following each utterance.
Laryngeal cancer
Malignant tumors developing in the vocal cords can affect their function and cause hoarseness. The main symptoms of laryngeal cancer are hoarseness lasting more than three weeks, changes in voice, sore throat, or a persistent cough. Treatment may include surgery to remove part or all of the larynx.
Huyen My (According to Medical News Today )
| Readers can ask questions about ear, nose, and throat diseases here for doctors to answer. |
Source link






![[Photo] Head of the Central Propaganda and Mass Mobilization Department visits and congratulates the Ministry of Health and the Military Traditional Medicine Institute.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/24/1771938483290_img-2682-3562-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] White pear blossoms bloom across the border of Pho Bang](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/24/1771927665653_a8-8280-jpg.webp)
![[Image] A dreamy "livable city" under pink clouds](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2026/02/24/1771930060937_tp4-jpg.webp)




































































































Comment (0)