Updated on: June 18, 2023 03:30:02
DTO - Recently, anthrax has shown signs of returning and spreading rapidly, forming epidemic points. Specifically in Dien Bien province, according to a report from the Center for Disease Control, in May 2023, 3 cutaneous anthrax outbreak points were recorded with 13 cases of the disease.
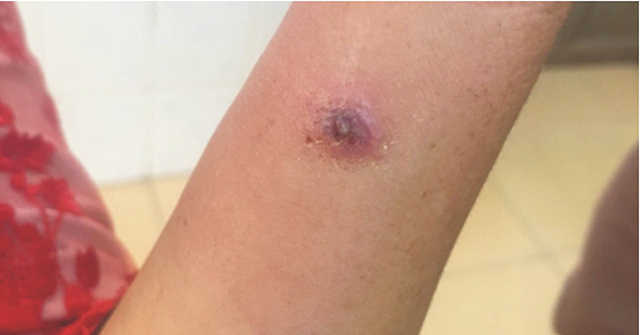
Lesions on anthrax patients (Source: SKDS)
According to the Ministry of Health, in Vietnam, anthrax is common in the northern mountainous provinces including Dien Bien, Son La, Lai Chau, Cao Bang, Thai Nguyen, and Ha Giang, with some sporadic cases of anthrax in humans still recorded. On average, in the period 2016-2022, the whole country recorded 7 cases/year and no deaths.
Anthrax is an acute bacterial infection that usually damages the skin, rarely causing damage to the mouth - throat, lower respiratory tract, mediastinum or digestive system. In the cutaneous form, the infected skin first appears itchy, then leads to lesions, papules, blisters and 2 - 4 days later develops into black ulcers. Around the ulcer there is often mild to severe edema and spreads very widely, sometimes with small secondary blisters. The mortality rate of untreated cutaneous anthrax is from 5 - 20%. If antibiotic treatment is effective, death rarely occurs.
The causative agent is Bacillus anthrasis. The bacteria are found in animals, usually herbivores, including wild animals as well as domestic animals, and spread the bacilli through bleeding and death. In the external environment, the bacilli form spores, and B. anthracis spores are very resistant and can survive in the soil for many years after the diseased animal has been killed.
The disease is transmitted through contact with tissues of animals (cattle, sheep, goats, horses, pigs and other animals) that have died of anthrax; through hair, skin, bones or products made from these materials such as drums, brushes... Transmitted through soil contaminated by infected animals or by using fertilizers made from infected animal bones for gardening. The disease is transmitted from person to person very rarely. Incubation period: from a few hours to 7 days, most cases occur within 48 hours after exposure.
To prevent the transmission and spread of anthrax, the following measures must be taken:
Maintain personal hygiene when handling contaminated objects that may transmit anthrax and care for broken skin; prevent dust and ensure good ventilation in industries with anthrax risk, especially where raw animal materials are processed.
Maintain regular health checks for workers with prompt medical attention for skin lesions suspected of infection; use protective clothing, appropriate bathrooms for bathing and changing clothes after work; use formaldehyde vapor for final sterilization in factories contaminated with B. anthracis.
Wash and sterilize feathers, skin, bone products and other foods of animal origin carefully before processing.
Do not slaughter, eat, use or trade products from sick or suspected sick livestock...
If anthrax is suspected, it is not necessary to perform an autopsy on the animal, but a sterile blood sample should be taken from the neck for bacterial culture; the carcass should be buried deep and not burned outdoors; the area where the carcass and animal waste are located should be disinfected with a 5% alkaline solution, calcium oxide (lime powder); the carcass should be covered with a layer of lime powder before burial.
Check wastewater and waste from animal processing plants that may be contaminated and factories that produce fur and leather products that may be contaminated.
My Hanh - CDC Dong Thap
Source link


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the inauguration ceremony of the Memorial Site of National Assembly Standing Committee Chairman Bui Bang Doan](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/28/6feba23492d14b03b05445dd9f1dba88)




























































































Comment (0)