 |
| Acute pharyngitis often occurs during seasonal changes or cold weather. (Source: Shutterstock) |
Sore throat is a condition characterized by swelling, pain, and a feeling of something stuck in the throat. Most sore throats are caused by viral and bacterial infections.
Causes of acute pharyngitis
Sore throat is inflammation of the throat lining caused by viruses or bacteria. It is very common in both adults and children, especially during cold weather or changes in weather.
Sore throat can occur alone or simultaneously with other conditions such as: Adenoiditis; Tonsillitis; Rhinitis; Sinusitis; Upper respiratory tract infections: influenza, common cold, measles…
Acute pharyngitis is caused by viruses or bacteria. It usually starts with a viral infection, followed by secondary bacterial infection, often with commensal bacteria already present in the throat such as streptococci and pneumococci. The disease can be transmitted from person to person through saliva and nasal secretions.
Viruses are the most common cause of acute pharyngitis , accounting for approximately 60-80% of cases. The condition is generally benign and usually resolves within 5-7 days if there is no secondary bacterial infection. Viral pharyngitis does not require antibiotics; symptomatic treatment is sufficient. The use of antibiotics carries a certain risk of allergic reactions or other undesirable side effects such as digestive disorders.
Acute pharyngitis can also be caused by bacteria , with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus accounting for 20% of these bacteria, but it can cause serious complications such as rheumatic fever, acute rheumatic arthritis, and acute glomerulonephritis.
Acute pharyngitis caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus can occur at any age but is most common in children aged 5-15 years. The disease presents with more pronounced symptoms than other bacterial infections: high fever of 39-40 degrees Celsius; whitish, dirty pseudomembranes on the tonsils and posterior pharyngeal wall; swollen and painful submandibular lymph nodes on both sides.
Streptococcal pharyngitis, in addition to systemic complications, can also easily cause local complications and complications in adjacent areas such as: otitis media, cellulitis or abscess around the tonsils, sinusitis, meningitis, sepsis, and necrotizing fasciitis.
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis usually occurs suddenly, causing symptoms such as: sore throat, especially when swallowing; a sharp pain radiating to the ear when speaking, swallowing, or coughing; coughing fits, dry cough or cough with phlegm; moderate or high fever; chills; headache; body aches; fatigue; loss of appetite; swollen lymph nodes in the jaw area, mobile and slightly tender to the touch.
Chronic pharyngitis often recurs with colds, flu, etc., with symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and sore throat. Other symptoms include: dry throat; painful and itchy eyes; symptoms worsening in the morning; a feeling of obstruction and pain when swallowing; persistent coughing to loosen phlegm; a slightly hoarse voice; and heartburn (in cases of gastroesophageal reflux disease).
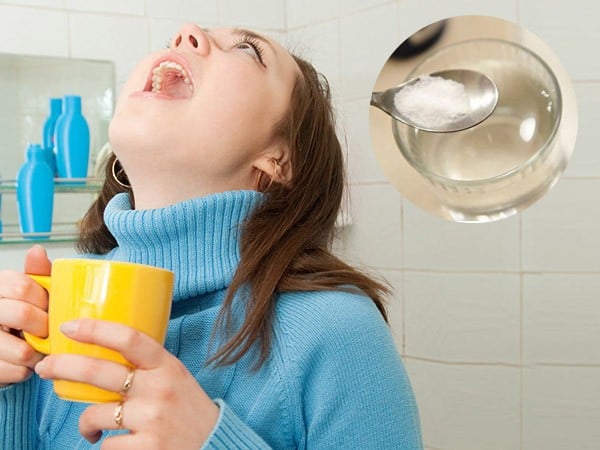 |
| Daily gargling helps prevent acute pharyngitis. (Source: Health and Life Magazine) |
What should you do if you have acute pharyngitis?
Most cases of viral sore throat are mild, with symptoms subsiding after 3-5 days. However, not all cases are benign, and some can be quite dangerous. Severe cases of sore throat are often due to bacterial superinfection, especially hemolytic streptococcus, which prolongs the illness and requires appropriate treatment.
If left untreated, a sore throat can lead to complications:
- Local complications: Inflammation or abscess around the tonsils, pharynx, and posterior pharyngeal wall. Rare but dangerous is necrotizing cellulitis of the neck.
- Nearby complications: Bronchitis, pneumonia, acute otitis media, acute rhinitis, acute sinusitis.
- Long-term complications: Nephritis, arthritis, myocarditis, streptococcal septic shock, and even sepsis.
Therefore, when experiencing symptoms of acute pharyngitis such as sore throat, fever, fatigue, cough, swollen and painful lymph nodes in the neck and jaw, etc., it is necessary to immediately go to a reputable medical facility for a thorough examination and assessment by a doctor. This will allow for appropriate diagnosis and treatment, helping to effectively treat the disease and prevent unnecessary complications.
In addition to strictly following your doctor's treatment plan, you can do the following to alleviate the symptoms of acute pharyngitis: Rest; Drink plenty of warm water; Avoid irritants such as alcohol, tobacco, sour, spicy, and fishy foods; Eat soft foods.
Preventing acute pharyngitis
Regarding prevention, it is necessary to wash hands frequently with antibacterial soap, especially after coughing or sneezing, after using the toilet, before preparing food, and before eating.
Always maintain good oral hygiene. Rinse your mouth and throat daily with antiseptic mouthwash. Keep your neck and throat warm.
Avoid consuming excessive amounts of cold foods and drinks such as ice cream or iced beverages. Quit smoking or stay away from places with cigarette smoke.
Wear a mask properly when going out.
Source


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh presides over a meeting on private sector economic development.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F20%2F1766237501876_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-40-png.webp&w=3840&q=75)







































































































Comment (0)