Lipomas are benign tumors that form from abnormal growth of fatty tissue under the skin.
Lipomas are benign tumors that form from abnormal growth of fatty tissue under the skin.
According to the UK National Health Service (NHS), most lipomas are harmless and usually do not require treatment. Lipomas can appear anywhere on the body where fat cells are present, most commonly on the shoulders, neck, back, chest, thighs, and armpits.
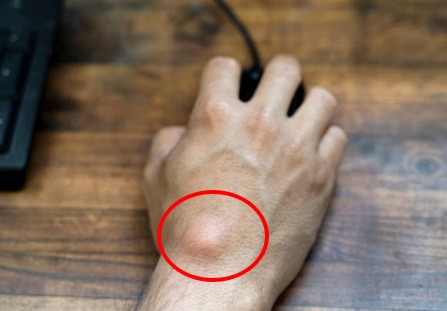 |
| Lipomas are benign tumors that form from abnormal growth of fatty tissue under the skin. |
In rare cases, lipomas can form in internal organs, bones, or muscles. Lipomas are usually soft lumps under the skin that may move slightly when pressed.
Lipomas are slow-growing tumors that can persist for months or even years, with an average size of 2-3 cm. However, some lipomas can be larger, even reaching 10-15 cm. Based on histological analysis, lipomas can be classified into the following types:
Common lipoma: The most common type.
Atypical lipomas: Contain abnormal cells.
Hibernoma: A rare fatty tumor containing brown fat cells.
Angiolipoma: A fatty tumor associated with blood vessels, often causing pain.
Spindle cell lipomatosis and pleomorphism: Rare, containing special cell types.
Middle-aged individuals (40-60 years old) are at higher risk of developing lipomas. Other risk factors include obesity, high cholesterol, diabetes, liver disease, and other metabolic disorders.
When should lipomas be surgically removed? According to Dr. Le Ngoc Vinh, Head and Neck Unit, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, most lipomas are benign and do not require surgery.
However, a doctor may recommend surgery for a lipoma in the following cases: If it is larger than 5 cm or growing rapidly; if it causes pain or discomfort; if it compresses nerves or surrounding organs; if it affects bodily function; for cosmetic reasons; if it cannot be clearly identified as a lipoma or another type of tumor; or if there are signs of infection or blood within the tumor.
According to doctors, lipomectomy is a minimally invasive and safe surgical procedure. The surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia, allowing patients to go home immediately afterward. The procedure involves making a small incision in the skin to remove the entire tumor. This method has a low recurrence rate and leaves minimal scarring.
Additionally, in some cases, liposuction may be an option. The doctor will make a small incision and use a tube to suction out the fatty tissue. However, this method has a higher recurrence rate and does not completely remove the fatty tissue.
Although generally not life-threatening, some minor complications can occur after surgery, including slight bleeding at the incision site.
Pain or bruising. Fluid accumulation, hematoma: May be due to improper wound care. Infection: Occurs if the surgical wound is not kept clean.
The doctor will provide detailed instructions on post-operative care to reduce the risk of complications. The removed tumor is usually sent to a laboratory for analysis to rule out the possibility of cancer.
Most lipomas do not require treatment if they do not affect health. However, when a lump is detected under the skin, patients should see a doctor for examination to determine whether it is a benign lipoma or has the potential to be malignant. Because some malignant tumors or cysts can resemble lipomas, specific tests are needed for an accurate diagnosis.
If you have a lipoma but are not experiencing any unusual symptoms, regular monitoring is recommended. If the tumor grows rapidly, causes pain, or affects your quality of life, consult your doctor to consider surgery. Those with a family history of skin cancer, in particular, should undergo regular screenings and health checkups.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/co-nen-phau-thuat-cat-u-mo-d229845.html
































![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives the Special Envoy of General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2026%2F01%2F30%2F1769759383835_a1-bnd-5347-7855-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




































































![OCOP during Tet season: [Part 3] Ultra-thin rice paper takes off.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F402x226%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2026%2F01%2F28%2F1769562783429_004-194121_651-081010.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)

![OCOP during Tet season: [Part 2] Hoa Thanh incense village glows red.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F402x226%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2026%2F01%2F27%2F1769480573807_505139049_683408031333867_2820052735775418136_n-180643_808-092229.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)





Comment (0)