1. Geographical location
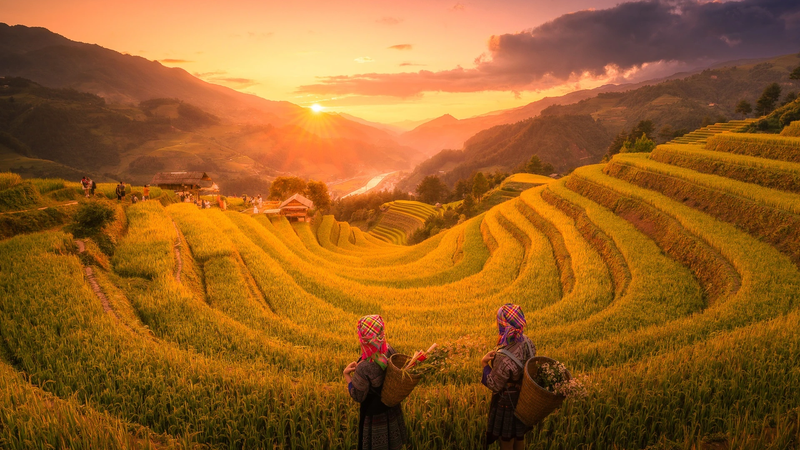
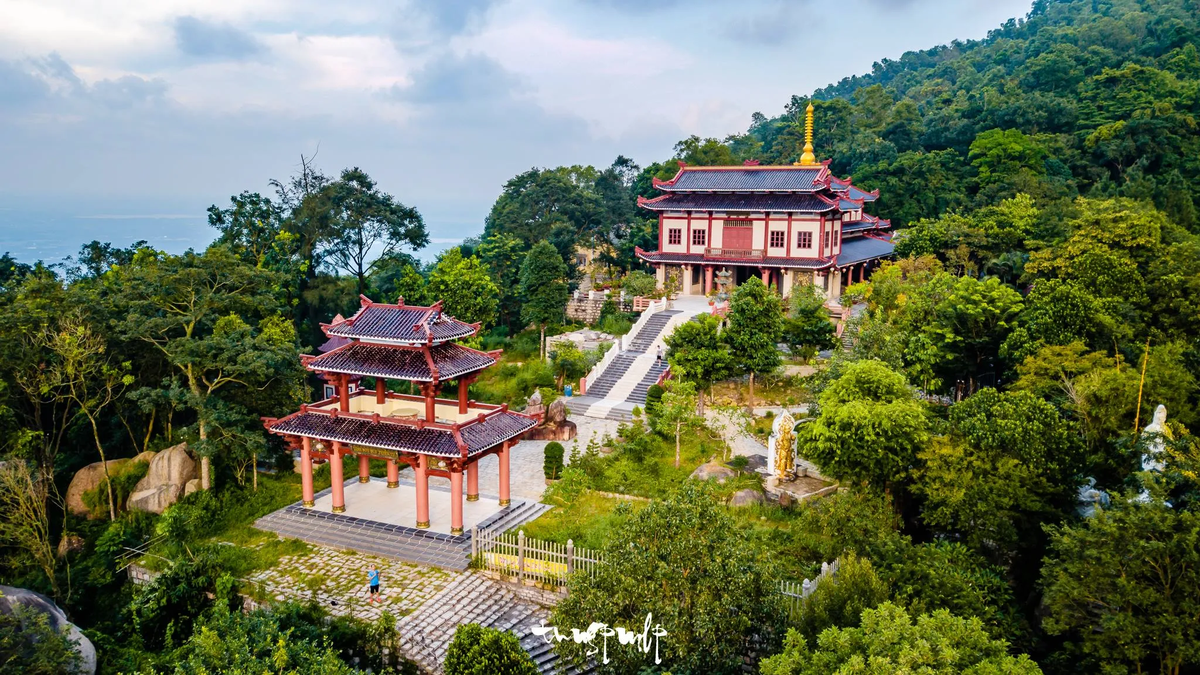
Kien Giang is located in the Northwest of the Mekong Delta and the Southwest of the country, with geographical coordinates: from 103 0 30' (calculated from Tho Chu island) to 105 0 32' East longitude and from 9 0 23' to 10 0 32' North latitude. The administrative boundaries are determined as follows: + The Northeast borders An Giang, Can Tho, Hau Giang provinces; + The South borders Ca Mau, Bac Lieu provinces; + The Southwest is the sea with more than 137 large and small islands and a coastline of more than 200 km; bordering the sea of Cambodia, Thailand and Malaysia. + The North borders Cambodia, with a land border of 56.8 km long. 2. Natural conditions - Terrain Kien Giang has a total natural area of 6,348 km 2 , a coastline of more than 200 km with more than 137 large and small islands, the largest of which is Phu Quoc with an area of 567 km 2 and is also the largest island in Vietnam. Kien Giang has a very diverse terrain, with both plains and mountains and islands. The mainland terrain is relatively flat, gradually decreasing from the Northeast (average height of 0.8-1.2 m) to the Southwest (average height of 0.2-0.4 m) above sea level. The sea and islands are mainly mountainous but there are still small, narrow plains interspersed, creating many natural landscapes of tourism value. The system of rivers, streams, canals and ditches of the province is very favorable for agricultural development, goods circulation and flood drainage. In addition to the main rivers (Cai Lon River, Cai Be River, Giang Thanh River), Kien Giang also has a dense network of canals, with a total length of about 2,054km. This topographic feature, together with the tidal regime of the West Sea, greatly influences the ability to drain water in the rainy season and is greatly affected by salinity in the dry months. Kien Giang has a 212km long sea dike, along which is a coastal protection forest strip with an existing area of 5,578 hectares. The dike is divided by 60 river mouths and canals connecting to the West Sea. The dike elevation is from 02 to 2.5m, the dike width is from 4 to 6m, up to now, 25 sluices have been invested in, the remaining 35 river mouths/canals connecting to the sea need to continue to invest in building sluices to drain floods, prevent salinity, and keep fresh water for production and people's lives. Kien Giang province is divided into 4 regions: Long Xuyen Quadrangle is the main flood drainage area of the province; The West Hau River region is affected by annual floods; the U Minh Thuong region with low terrain is often flooded in the rainy season and the island sea area. - Resources In 2006, the International Coordinating Council of the UNESCO Man and Biosphere Programme recognized the Kien Giang World Biosphere Reserve. This is the 5th recognized Biosphere Reserve (BTSQ) in Vietnam, with the largest area in the country and the largest in Southeast Asia with more than 1.1 million hectares. The Kien Giang World Biosphere Reserve contains rich, diverse and unique landscapes and ecosystems, from Melaleuca forests on flooded land, forests on rocky mountains, limestone mountains to marine ecosystems, typically seagrass beds and rare marine animals. The Kien Giang World Biosphere Reserve covers the districts of Phu Quoc, An Minh, Vinh Thuan, Kien Luong and Kien Hai. There are 3 core areas belonging to the U Minh Thuong National Park, Phu Quoc National Park and the coastal protection forest of Kien Luong - Kien Hai. Kien Giang World Biosphere Reserve has six unique ecosystems, with about 2,340 species of flora and fauna, of which 1,480 are plant species with 116 rare species listed in the Red Book and 57 are endemic species; about 860 are animal species with 78 rare species, 36 are endemic species. This is also an area of the province containing 38 historical, cultural and scenic relics recognized at the national and provincial levels. Kien Giang World Biosphere Reserve has great potential for ecotourism development, while helping Kien Giang and coastal provinces of Vietnam enhance their ability to respond to climate change. Land resources: The total natural land area of Kien Giang is 634,852.67 hectares, of which: Agricultural land: 458,159.01 hectares, accounting for 72.17% of the natural area; Forestry land: 89,574.22 ha, accounting for 14.11% of natural area; Aquaculture land: 28,378.93 ha, accounting for 4.47% of natural area; Other agricultural land: 57.73 ha, accounting for 0.01% of natural area. Water resources: Kien Giang province has water resources including surface water, underground water and rainwater. * Surface water source: The river and canal system of Kien Giang province with a total length of more than 2000km, natural rivers including Giang Thanh River, Cai Lon River, Cai Be River, ... are large rivers with estuaries flowing into the West Sea, playing a very important role in draining excess water, releasing floods from the fields to the West Sea, in addition there is a dense canal system such as in the Long Xuyen Quadrangle area with Vinh Te, Tam Ngan, Tri Ton, My Thai, Ba The, Kien Hai, Rach Gia-Long Xuyen, Cai San canals, ... these canal sections all have a Northeast-Southwest flow direction, originating from the Hau River. Canals in the West of the Hau River include KH1 canal, Tram Bau canal, Thot Not canal, KH6, KH7 canal, O Mon canal. The Southwest region of the province has the Can Gao, Trem Trem canal, Chac Bang canal, Thu Bay village canal system, originating from the Hau River, ending at Cai Lon-Cai Be river. Canals play a very important role in providing water for irrigation and transportation in the area. * Underground water resources: In the province, through assessment, 7 different layers and water-bearing zones have been discovered: Permian - Lower Triassic fissure water zone (p-t1), upper Miocene porous water layer (n13), lower Pliocene porous water layer (n21), middle Pliocene porous water layer (n22), lower Pleistocene porous water layer (qp1), middle - upper Pleistocene porous water layer (qp2-3), upper Pleistocene porous water layer (qp3). In which, the exploitation prospects for 04 aquifers have been assessed: (qp3), (qp2-3), (qp1) and (n22). These are aquifers that can be exploited for domestic purposes and water supply today. Among the above-mentioned aquifers, the upper Pleistocene aquifer (qp3) has a narrow freshwater area (about 88km2), the area of highly mineralized, brackish and salty water accounts for the majority (about 5,603km2) of the province's area. Other aquifers: Middle - Upper Pleistocene (qp2-3); Lower Pleistocene (qp1); Middle Pliocene have good exploitation prospects. Of which, the Middle - Upper Pleistocene aquifer (qp2-3); Lower Pleistocene (qp1) is the most promising aquifer at present. The Middle - Upper Pleistocene aquifer (qp2-3) is the aquifer being exploited mainly in Kien Giang province, mainly for rural living. The total underground water exploitation reserve within the province is 1,322,417 m3/day. Of which, the static gravity reserve is 1,317,474m3/day, the static elastic reserve is 4,944m3/day. * Rainwater source: Rain in Kien Giang is relatively large compared to the average rainfall in the Mekong Delta and is unevenly distributed over time, the total average annual rainfall is from 1800mm-2200mm, forming 2 seasons: rainy season and dry season. Rain is extremely important in agricultural production and in the lives of rural people in Kien Giang province, especially in coastal areas far from freshwater. Storing rainwater during the rainy season to enrich domestic water and drinking water during the dry months is almost a very common habit of people in the river delta region of the West. Marine resources: Kien Giang is a province with a sea area of about 63,290km2, with 5 archipelagos, including 09 coastal districts, towns, and cities (including 2 island districts: Phu Quoc, Kien Hai and 07 coastal district-level administrative units) with 51/145 communes, wards, and towns having islands or coastline; with more than 200km of coastline, about 137 large and small islands/islands, with national boundaries at sea, bordering Cambodia, Thailand, and Malaysia, is a coastal province with a rich and diverse coastal mangrove ecosystem, with great potential for developing agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism... especially with rich resources with potential of land, mountains, minerals, primary forests, islands, and many rare animals in the forest and under the sea; Our province also has a very important position in socio -economic development, is a bridge connecting the provinces of the Southwest, trade exchange and national defense and security in the region and internationally. Mineral resources: It can be said that Kien Giang is the province with the most abundant mineral resources in the Mekong Delta. Through investigation and survey, 237 mineral mines were identified (including 167 mineral mines for common construction materials and peat). Of which, 86 mines are planned for exploration and exploitation (construction stone: 21 mines, construction sand: 01 mine, brick and tile clay: 19 mines, filling materials: 32 mines and peat: 13 mines); 45 mines are located in areas prohibited from mineral activities. The reserve of mineral deposits for common construction materials and peat will meet the province's needs until 2025. Construction stone: 2,550,000 m3, construction sand: 1,050,000 m3, brick and tile clay: 500,000 m3, filling materials: 13,500,000 m3, peat: 400,000 m3. 3. Population Kien Giang is the second most populous province in the Mekong Delta with 1.76 million people in 2015, after An Giang (2.2 million people). The main ethnic groups include Kinh, Hoa, and Khmer. The urbanization process has attracted people to urban areas, so the population density in Rach Gia is 8.3 times higher than the average density of the whole province, and 32.9 times higher than the population density in Giang Thanh district. The urban population rate also increased from 21.9% in 2000 to 27.1% in 2010 and 27.4% in 2015. 4. History of formation and development Since 1757, Kien Giang was a province in Rach Gia area belonging to Ha Tien town established by Mac Thien Tich. In 1808 (7th year of Gia Long), Kien Giang province was changed to Kien Giang district. During the Minh Mang dynasty, Kien Giang belonged to An Bien prefecture, Ha Tien province. From June 15, 1867, it was changed to Kien Giang Inspectorate. On August 16, 1967, it was renamed Kien Giang district, belonging to Rach Gia province. In 1956, according to Decree No. 143-NV, Ha Tien province was abolished and 4 districts (including Chau Thanh, Hon Chong, Giang Thanh, Phu Quoc) were merged into Rach Gia province to establish Kien Giang province. By May 1965, Ha Tien province was re-established. In 1957, according to Decree No. 281-BNV/HC/ND, the administrative units of Kien Giang province included 6 districts (Kien Thanh, Kien Tan, Kien Binh, Kien An, Ha Tien, Phu Quoc); 7 cantons; 58 communes. According to Decree No. 368-BNV/HC/ND dated December 27, 1957, supplementing Decree No. 281-BNV/HC/ND, the administrative units of Kien Giang province were determined. Article 1 of this Decree clearly stated that Kien An district included Vinh Tuy commune. On June 13, 1958, the government of the Republic of Vietnam issued Decree 314-BNV/HC/ND on amending the administrative units of Kien Giang province. Article 1 of this Decree stipulated that Kien Binh district was divided into 2 districts: Kien Binh and Kien Hung. Thus, in 1958, Kien Giang province had 7 districts and 7 cantons. According to the 1971 Administrative Yearbook of the Republic of Vietnam, Kien Giang province included 7 districts: Kien Thanh, Kien Tan, Kien Binh, Kien An, Kien Luong, Ha Tien, Phu Quoc; 42 communes; 247 hamlets. In 1973, Kien Giang province had 8 districts (Kien Thanh, Kien Tan, Kien Binh, Kien An, Kien Luong, Ha Tien, Phu Quoc, Hieu Le). Today, Kien Giang province has 15 districts, towns, and cities (Rach Gia city, Ha Tien town, An Bien, An Minh, Chau Thanh, Giong Rieng, Go Quao, Hon Dat, Kien Hai, Kien Luong, Phu Quoc, Tan Hiep, Vinh Thuan, U Minh Thuong) and 145 communes, wards, and towns. 5. Cultural and tourism potential Kien Giang has many famous landscapes and historical relics such as: Hon Chong, Hon Trem, Hon Phu Tu, Mo So mountain, Mui Nai beach, Thach Dong, Mac Cuu Tomb, Dong Ho, Hon Dat, U Minh forest, Phu Quoc island... To effectively exploit the potential for tourism development, Kien Giang has built 4 key tourist areas such as: * Phu Quoc: Has a unique terrain including a mountain range running from North to South of the island, has a primeval forest with rich flora and fauna, has many beautiful beaches such as Bai Truong (20 km long), Bai Cua Lap - Ba Keo, Bai Sao, Bai Dai, Bai Hon Thom... and around there are 26 different large and small islands. According to the Government's policy, Phu Quoc island is built into a high-quality international resort tourism center. Phu Quoc and the two archipelagos of An Thoi and Tho Chau are ideal areas for developing sea and island tourism such as: sightseeing, camping, swimming, relaxation, eco-tourism, and various types of water sports . Phu Quoc has a long-standing cultural tradition and many famous specialties, such as: Phu Quoc fish sauce, pepper, pearls, sim wine, herring, melaleuca mushrooms... Due to the richness and diversity of Phu Quoc, the number of tourists to Phu Quoc increases rapidly every year. * Ha Tien - Kien Luong area: Many sea and mountain landscapes of Ha Tien - Kien Luong such as: Mui Nai, Thach Dong, To Chau mountain, Da Dung mountain, Dong Ho lagoon, Binh San mountain cultural and historical relic, Hang pagoda, Phu Tu island, Duong beach, Mo So mountain, Trem island, Hai Tac archipelago and Ba Lua island are very suitable for developing sightseeing and relaxation tourism. Landscapes such as To Chau mountain, Dong Ho lagoon, Giang Thanh river, and Den mountain tourist area are being officially put into tourism exploitation. Ha Tien has a long tradition of history, culture, literature and art, with traditional festivals such as Tet Nguyen Tieu, the anniversary of the founding of Tao Dan Chieu Anh Cac, the death anniversary of Mac Cuu, Phu Dung Pagoda, Thanh Hoang Temple... Currently, Kien Giang has a tour to neighboring Cambodia via Ha Tien International Border Gate. This is the door that opens for the Kien Luong - Ha Tien region to connect with Southeast Asian countries; at the same time, opening a tourist route across three countries, from Phu Quoc to Shianouk Ville (Cambodia) and Chanthaburi province (Thailand) by sea and road. * Rach Gia City and surrounding areas: Rach Gia City is the administrative center of Kien Giang province, with a 7 km long coastline, very convenient water, road and air transportation. Rach Gia has good infrastructure, many historical and cultural relics, is a stopover to continue to Ha Tien, Phu Quoc and other areas in the province. Therefore, there are advantages in developing services such as: accommodation, food and beverage, night entertainment services; there are 04 large-scale supermarket systems to ensure the shopping needs of city residents and tourists. Rach Gia city is the first place in Vietnam to reclaim land to build a new urban area. The reclaimed land area expands the city into one of the largest new urban areas in the Southwest region. Some neighboring areas of Rach Gia such as Kien Hai island district, Hon Dat, U Minh Thuong also have great potential for tourism development. Kien Hai is exploiting day tours to explore the islands. This is a scenic sea - island area with traditional occupations of going to sea, making fish sauce, processing seafood, creating a unique cultural lifestyle. Hon Dat tourist area is completing and finishing cultural works at the grave of Heroic Martyr Phan Thi Rang (Ms. Su), building an exhibition area for some war relics at the provincial television broadcasting area on Hon Me peak... * U Minh Thuong area: With the ecological characteristics of flooded Melaleuca forests on peat soil, U Minh Thuong National Park - a revolutionary base, a world biosphere reserve, has opened its doors to serve eco-tourists. U Minh Thuong National Park tourist area serves eco-tourists combined with learning about the culture and humanity of the rivers of the Ca Mau peninsula and research tourism at the archaeological site of Oc Eo - Phu Nam (Canh Den, Nen Vua, Ke Mot). The U Minh Thuong revolutionary base relic complex with relics of Nga Ba Cay Bang, Nga Ba Tau, Thu Muoi Mot, Ban Bien Phu Melaleuca Forest, the 200-day assembly area of Chac Bang canal, is a place to attract tourists to learn about revolutionary history... At the same time, the province has just started construction of a number of works according to the Project to restore the Provincial Party Committee Base during the resistance war in Vinh Thuan district. In addition to the four key tourist areas, Kien Giang currently has a Biosphere Reserve with an area of over 1.1 million hectares. Kien Giang Biosphere Reserve contains rich, diverse and unique landscapes and ecosystems, which are of great value in terms of research as well as tourism. Kien Giang Biosphere Reserve covers the districts of Phu Quoc, An Minh, U Minh Thuong, Vinh Thuan, Kien Luong and Kien Hai, including three core areas of U Minh Thuong National Park, Phu Quoc National Park and coastal protection forests of Kien Luong and Kien Hai.
According to kiengiang.gov.vn




![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)




































































































Comment (0)