Recognize early signs of small intestine cancer
The small intestine is a part of the digestive system, connecting the stomach and colon, with the function of absorbing nutrients for the body. Small intestine cancer is divided into 4 stages:
Stage 1: Cancer has grown only in the intestinal layers and has not invaded surrounding tissue or lymph nodes.
Stage 2: Cancer grows through the intestinal wall, invading surrounding tissue. However, there is no lymph node metastasis.
Stage 3A: Cancer has spread to 1 to 3 regional lymph nodes, may or may not go beyond the muscular layer of the intestinal wall, but there is no distant metastasis.
Stage 3B: Cancer has metastasized to 4 or more regional lymph nodes, may or may not go beyond the muscular layer of the intestinal wall, but there is no distant metastasis.
Stage 4 (final stage): Cancer has metastasized to other organs in the body such as the lungs, liver, etc.
Early signs of small bowel cancer include:
- Blood in stool: Most patients have black stools, the color of coffee grounds, and a foul odor. This cancer rarely has bright red blood in the stool.
- Diarrhea: The patient has watery stools more than 3 times a day. There is a mass in the abdomen.
- Dull, vague abdominal pain, pain symptoms are rarely severe.
- Vomiting or nausea.
- Unexplained weight loss: This is a common condition in the late stages of cancer.
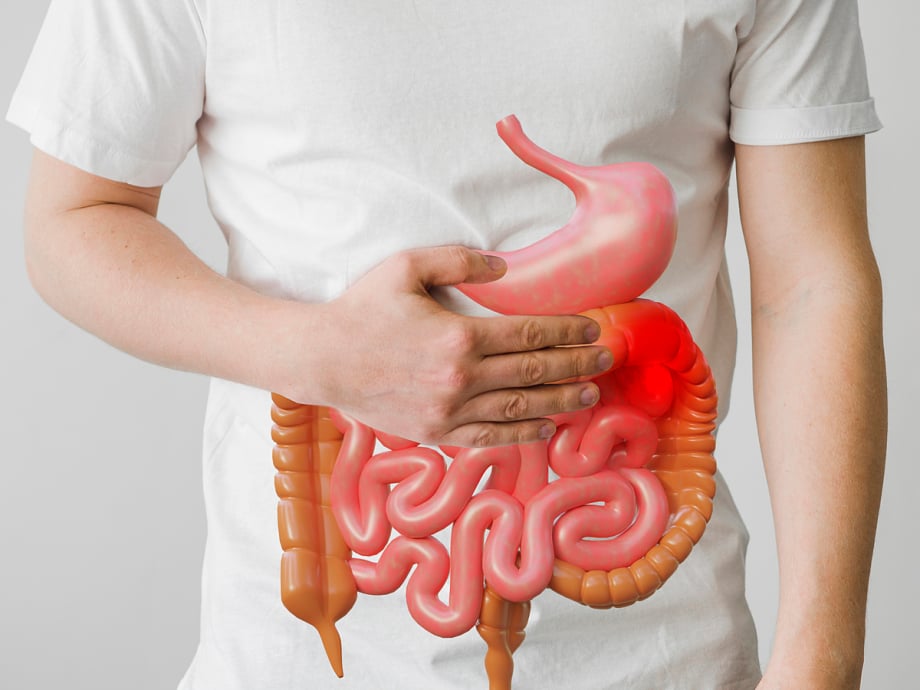
Small bowel cancer is when cells in the tissues of the small bowel mutate, grow out of control, and form tumors.
Diagnosis of small bowel cancer
To determine small intestine cancer, patients only need to do some common diagnostic tests such as:
- Blood test
- Abdominal X-ray
- Biopsy to take tissue samples for pathology
- Endoscopy to observe the mucosal surface of the small intestine.
Treatments for small intestine cancer
Some treatments for small intestine cancer:
Surgery: This is the main treatment method, performed by removing the tumor and invaded parts, ensuring digestive circulation. After surgery, some complications may occur such as bleeding, pain, postoperative infection, digestive disorders, etc.
Chemotherapy: Is a method of destroying cancer cells with drugs. Chemotherapy can cause side effects including: fatigue, vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, hair loss, diarrhea, risk of infection due to leukopenia, etc.
Radiotherapy: This method is not usually used as the main treatment. Instead, it is often indicated in the treatment of symptoms when the disease is in the late stages. Complications that can occur after radiotherapy are: fatigue, digestive disorders, mild skin reactions, etc.
Note: Symptoms in the early stages of small intestine cancer are often unclear and easily mistaken for other common digestive diseases, leading to patients being subjective and not going to the doctor. Therefore, when the disease is detected, it is already in the late stages, making treatment difficult, costly and time-consuming.
To prevent small intestine cancer, everyone needs to pay attention to the habit of regular health check-ups, not smoking, abusing alcohol, eating scientifically and healthily by: eating lots of green vegetables, cereals, fresh fruits... limit fried, grilled, processed foods...
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/dau-hieu-som-cua-ung-thu-ruot-non-172240930092436567.htm

























![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Australian Foreign Minister Penny Wong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/20/f5d413a946444bd2be288d6b700afc33)
![[Photo] Politburo works with Standing Committees of Lang Son and Bac Ninh Provincial Party Committees](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/20/0666629afb39421d8e1bd8922a0537e6)











































































Comment (0)