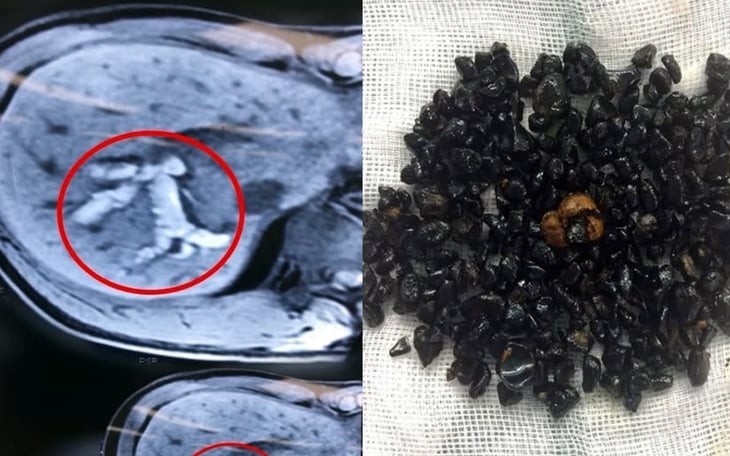
From left to right: image of gallstones in the liver of patient NTH on abdominal CT scan. Gallstones were removed from the patient's liver - Photo: HA TUONG
Gallstones in the liver are more likely to cause complications than stones in other locations in the bile duct, such as bile duct infection, hepatitis, cirrhosis, intrahepatic bile duct cancer, sepsis...
When parasites enter the bile duct
Patient NTH (70 years old) often feels pain in the right subcostal region after meals, the short pain usually goes away after about 10-20 minutes. The patient subjectively did not go to the doctor, until the pain became severe and high fever, dark yellow skin... the patient went to the emergency room at Phu Tho General Hospital and was diagnosed with gallstones in the liver.
MSc. Le Van Loi, Department of Hepatobiliary-Pancreatic Surgery, 108 Central Military Hospital, said that 108 Central Military Hospital has received and treated many cases of gallstones in the liver.
A typical case is a gallstone in the right hepatic bile duct. The patient was admitted to the hospital with symptoms of abdominal pain in the right hypochondrium accompanied by a fever of 39 degrees Celsius. The diagnosis was cholangitis due to gallstones in the right hepatic bile duct...
According to Master Loi, intrahepatic bile duct stones (often referred to as liver stones) are common in Asian countries, including Vietnam. The nature of intrahepatic bile duct stones is gallstones, but their location is in the hepatic ducts (right hepatic duct or left hepatic duct).
Gallstones in the liver are usually pigment stones, with the main component being bilirubin. The main cause of the disease is intestinal parasites that enter the bile duct, carrying bacteria that change the solubility of bilirubin, combining eggs and worm bodies to form stones.
Liver dysfunction such as cirrhosis, drug-induced hepatitis, viral hepatitis, hepatitis B... causing imbalance of components in bile, or reduced bile duct motility commonly found in obese people, sedentary people... is also the cause of gallstones in the liver.
Doctor Tran Thanh Tung, head of the general surgery department, Phu Tho General Hospital, recommends: In Vietnam, gallstones in the liver are mainly pigment stones composed of compounds such as calcium bilirubinate, cholesterol, calcium palmitate, apatite...
And parasites (roundworms, tapeworms...) play an important role in the formation of gallstones.
In the early stages, the patient feels pain in the right subcostal region after meals. The short pain usually goes away after about 10-20 minutes.
Fever due to inflammation of the bile ducts and gallbladder, if there is no inflammation then there is no fever, if there is fever it is usually a sudden high fever lasting for several hours; fever and pain in the right hypochondrium go together (if there is severe pain then the fever is high); fever usually occurs after the pain (sometimes at the same time or before). Fever can last for several weeks, months, sometimes a mild fever of 37.5 - 38 degrees.
When bile accumulates in the liver, the yellow bilirubin affects the blood, causing the patient to become jaundiced.
Easily transformed into cancer, sepsis...
MSc. Le Van Loi analyzed that the liver is responsible for producing bile to digest fat, while also helping to detoxify and remove waste from the body. Bile is secreted from liver cells, flows through the liver ducts into the large and small bile ducts, then through the main bile duct into the gallbladder and down into the intestines.
Gallstones in the liver are often detected when the stones cause dangerous complications such as cholangitis, liver abscess, cirrhosis, intrahepatic bile duct cancer...
In the early stages, patients may notice some symptoms such as bloating and indigestion after eating. When the stones cause complications, patients may experience one of three typical signs, called Charcot's triad.
Liver colic pain often appears after a full meal, is severe and sudden, can spread to the right shoulder, makes it difficult for the patient to move, lasts from 15 minutes to several hours and is cyclical.
High fever: the patient has a high fever, may have chills and sweating.
Jaundice: When bile stagnates in the liver, bilirubin (a yellow bile pigment) seeps into the blood, causing the skin and sclera to turn yellow. In particular, gallstones in the liver are more likely to cause complications than stones in other locations in the bile duct.
Biliary tract infection is the most dangerous complication of gallstones. High fever accompanied by chills, severe infection and biliary obstruction, and hemodynamic disorders often push the patient into a state of shock and fatigue.
Hepatitis, long-term stagnation of bile is a condition for bacteria to attack and cause hepatitis, they can also form pus pockets, forming liver abscesses.
Cirrhosis is a complication after the liver is infected, causing irreversible damage to liver tissue. This condition, if prolonged, can lead to cirrhosis.
About 3-10% of cases of gallstones have intrahepatic bile duct cancer. This is the most dangerous complication, patients usually only live a few months to a few years after the disease is detected.
Sepsis is an emergency complication, especially serious, if not treated promptly can be life-threatening.
Treatments
Treating gallstones in the liver is difficult, because the gallstones are often deep and scattered in the liver. Not to mention that gallstones cause bile stagnation, which can narrow the bile ducts in sections, making it difficult to perform interventional procedures.
* Stone dissolving drugs are mostly ineffective against gallstones (pigment stones, main component bilirubin), because the drugs only work against cholesterol stones.
* Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: this method is only suitable for patients with extrahepatic stones. For intrahepatic stones, this method requires expensive equipment. In Vietnam, very few facilities apply this method.
* Open surgery to remove gallstones or resect the liver, the patient must undergo a major surgery, post-operative pain, slow recovery, especially for the elderly.
* The best method currently chosen is laparoscopic surgery to remove stones or percutaneous transhepatic laparoscopic surgery to remove stones, which is a minimally invasive method.
How to prevent gallstones in the liver
Gallstones in the liver are a dangerous disease. However, there are ways to prevent the risk of recurrence of stones and minimize complications caused by stones, specifically: do not drink alcohol, do not use stimulants, and do not smoke.
Limit foods high in fat, cholesterol, fried, and canned foods.
Ensure hygienic eating, avoid eating raw or undercooked food to prevent food-borne worm infections. Eat plenty of green vegetables, fruits and drink plenty of water.
Deworming every 6 months to prevent infection caused by worms. Annual health check-ups will help detect early risks of this disease.
Regularly exercise every day such as walking, jogging, cycling, yoga to increase bile duct movement and avoid cholestasis in the liver.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/ky-sinh-trung-chui-len-duong-mat-nguy-hiem-ra-sao-20250520082328904.htm


































































































Comment (0)