 |
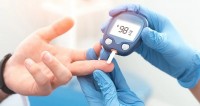
| Basically, people with diabetes should not use honey as a sugar substitute. (Source: iStock) |
If you have type 2 diabetes or are at high risk for it, you may have heard that honey is better than other sweeteners.
In fact, while honey has some health benefits, it is still a source of sugar and simple carbohydrates.
Therefore, if you have diabetes or are taking medications such as insulin, you need to calculate your daily carbohydrate intake before consuming honey.
Here is some useful information for you before deciding to add honey to your diet.
How is honey different from sugar?
Honey is also a sweetener. It is also called an “added sugar” on food labels because it is not a natural component of other foods.
Honey is a source of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates come mainly from glucose and fructose, which are simple sugars.
One tablespoon of honey contains 64 calories, 17 g of sugar, 17 g of carbohydrates, 0.06 g of protein, and 0.04 g of fiber.
Honey contains vitamins and minerals such as potassium, calcium, zinc, vitamin C and antioxidants. However, these minerals are not present in significant amounts, so honey should not be considered a main source.
Honey is different from white sugar because sugar does not contain any vitamins and minerals. Honey also has a lower glycemic index (GI) than sugar.
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly carbohydrates raise blood sugar levels. Honey has a GI of 58 and sugar has a GI of 60.
This means that honey (like all carbohydrates) will also raise blood sugar levels quickly, but not as quickly as sugar.
If you have diabetes, using honey instead of sugar will not provide any benefits, as they affect blood sugar levels in similar ways.
If you choose to eat honey, make sure you know how much you're getting.
Foods or sauces may contain more honey and carbohydrates than you realize. This can negatively affect your blood sugar levels and your ability to properly absorb insulin.
Can diabetics eat honey?
Experts used to advise people with diabetes to avoid all foods with added sugar. But now some experts say it is OK to eat small amounts of honey as part of a healthy diet.
However, if you have to take insulin (which inhibits the conversion of glycogen into glucose into the blood), always keep track and calculate the amount of carbohydrates (including honey) you take each day. This will help you determine the correct dose of insulin to take.
Maintaining your carbohydrate and fiber intake can also help keep your blood sugar from getting too high. It's important to note that even if you take insulin, high blood sugar can lead to health problems over time.
That is why it is best to limit your honey intake. Talk to your doctor or diabetes dietitian to find out how much honey is safe for you.
Is honey good for diabetes?
Research shows that honey has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may be important for people with diabetes, as they often have higher levels of inflammation in their bodies.
However, there are many foods that provide antioxidants without raising your blood sugar levels.
So you absolutely don't need honey to get those nutrients and can look for better options.
A study from Turkish scientists found that people with type 2 diabetes who consumed 5-25g of honey daily for 4 months had a reduction in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) - a measure of blood sugar control.
But people who consumed more than this amount each day showed increased A1c levels.
However, this study only involved 64 people, and half of them consumed honey every day, so it is difficult to know whether the results would be widely replicated.
Another study including 48 people with type 2 diabetes, half of whom took a dose of honey for 8 weeks, found that eating honey daily increased A1c levels.
A 2016 study from Egyptian researchers also found that people with type 2 diabetes experienced increased blood sugar levels when consuming honey.
Because trials on honey and diabetes have shown mixed results, more research is needed to know what amount of honey is safest for people with diabetes.
 | Eating guava helps treat diabetes and has weight loss effects. For fruits, guava is one of the reasonable choices, bringing many health benefits such as reducing ... |
 | New treatment research method: Diabetic patients only need 2 injections/day Diabetes is a heterogeneous metabolic disease characterized by increased blood sugar levels in the body ... |
 | Diabetic Diet to Avoid 537 million people worldwide have diabetes (2021 statistics). Every 5 seconds, one person dies from the disease... |
 | People with diabetes should avoid these 5 products People with diabetes need to avoid foods that tend to spike blood sugar, such as these 5 foods... |
 | Fruits and how to eat them to help control blood sugar levels in diabetics Cherries, peaches, oranges, and kiwis are suitable choices to help diabetics supplement nutrition and control blood sugar levels. |
Source





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to deploy overcoming consequences of storm No. 10](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/3/544f420dcc844463898fcbef46247d16)

![[Photo] Students of Binh Minh Primary School enjoy the full moon festival, receiving the joys of childhood](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/3/8cf8abef22fe4471be400a818912cb85)
























































































Comment (0)