It is the largest and most powerful rocket and spacecraft system ever built, standing at 400 feet (120 meters) tall, with the lofty goal of taking humans to the Moon and Mars in the future.
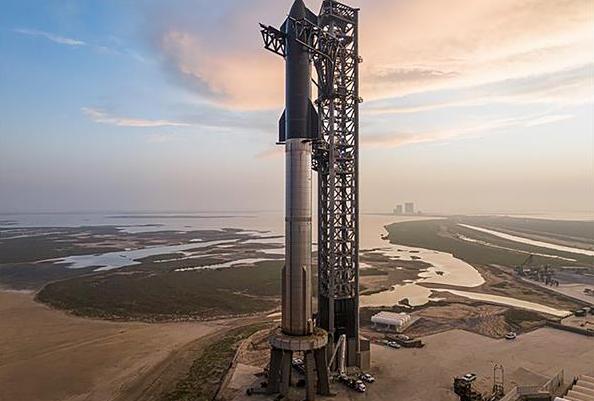

SpaceX's Starship. Photo: TI
Monday’s launch attempt was aborted due to a stuck valve in the first-stage booster, and the rocket is likely to be tested again this week from South Texas. Mr Musk’s company received approval from the US Federal Aviation Administration last Friday to test-launch its largest rocket yet.
The rocket will not carry astronauts on the test launch. The top stage, which has a sci - fi-like design, was launched into the stratosphere a few years ago, before finally landing vertically in 2021.
The rocket's booster, dubbed Super Heavy, will be tested for the first time. It is not expected to land, but to fall into the sea.
Here's what we should know about Starship:
Super large size
The stainless steel Starship has 33 main engines and 16.7 million pounds of thrust. Of those, 31 methane-fueled engines performed smoothly during a launch pad test in January, good enough to get the rocket into orbit, Musk noted.
Starship can lift up to 250 tons and carry 100 people on a trip to Mars. The six-engine spacecraft is 50 meters tall. Mr. Musk predicts that Starship will be used to launch satellites into low Earth orbit, including Starlink, before carrying out crewed missions.
Starship is far superior to NASA’s moon rockets, such as the Apollo-era Saturn V and the Artemis program’s Space Launch System (SLS), which made its first test trip to the moon late last year. It also outclasses the former Soviet Union’s N1 moon rocket.
Schedule
The test flight will last an hour and a half, orbiting the Earth. If Starship reaches the three-minute mark after launch, the booster will be commanded to detach and fall into the Gulf of Mexico. The spacecraft will continue east, passing over the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans before landing near Hawaii. Starship is designed to be fully reusable.
“It would be a huge step forward for space travel if Starship were fixed and operational,” said Harvard astrophysicist and spacecraft watcher Jonathan McDowell.
Launch pad
The spacecraft will launch from a remote site in the southernmost tip of Texas near Boca Chica Beach. It’s located just below South Padre Island and about 25 miles from Brownsville. Across the road from the launch pad is the complex where SpaceX has been developing and building Starship prototypes for the past several years. The complex, called Starbase, is home to more than 1,800 employees.

Compare Starship to the Statue of Liberty and the two spacecraft Space Shuttle and SLS.
The launch pad in Texas is equipped with giant robotic arms to catch a rocket booster as it lands back down.
Success rate
As usual, Mr. Musk has been very candid about his chances, even putting the odds of Starship reaching orbit on its first flight at best. He estimates an 80 percent chance that one of the Starship rockets currently being built will reach orbit by the end of the year. He expects it will be several years before the rocket can be fully and quickly reused.
Client
With Starship, California-based SpaceX is now focused on the Moon, with a $3 billion NASA contract to send astronauts into lunar orbit in 2024 and land on the Moon in early 2025 as part of the Artemis program.
This will be the first time astronauts have landed on the Moon in more than 50 years. Astronauts will leave Earth via NASA’s Orion space shuttle and Space Launch System rocket, then transfer to Starship in lunar orbit to land on the surface, and then return to Orion. To get to the Moon and beyond, Starship will first need to refuel in low Earth orbit.
But Starship isn’t just for NASA. A private crew will be the first to fly Starship around Earth. Two private flights will then circle the moon without landing.
The Rivals
There are other companies that are also aiming to launch space tourism by rocket. Billionaire Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin is readying its New Glenn rocket for an orbital launch from Cape Canaveral, Florida, next year. NASA will use New Glenn to send a pair of spacecraft to Mars in 2024.
United Launch Alliance hopes to make its first launch of its new Vulcan rocket later this year, sending a private lander to the moon on NASA’s orders. Europe’s Arianespace is about to launch its new Ariane 6 rocket from French Guiana in South America.
Quoc Thien (according to AP)
Source


































































































Comment (0)