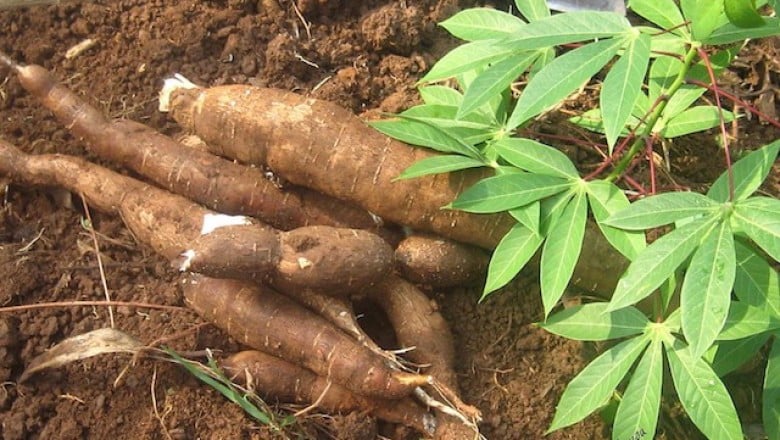
 |
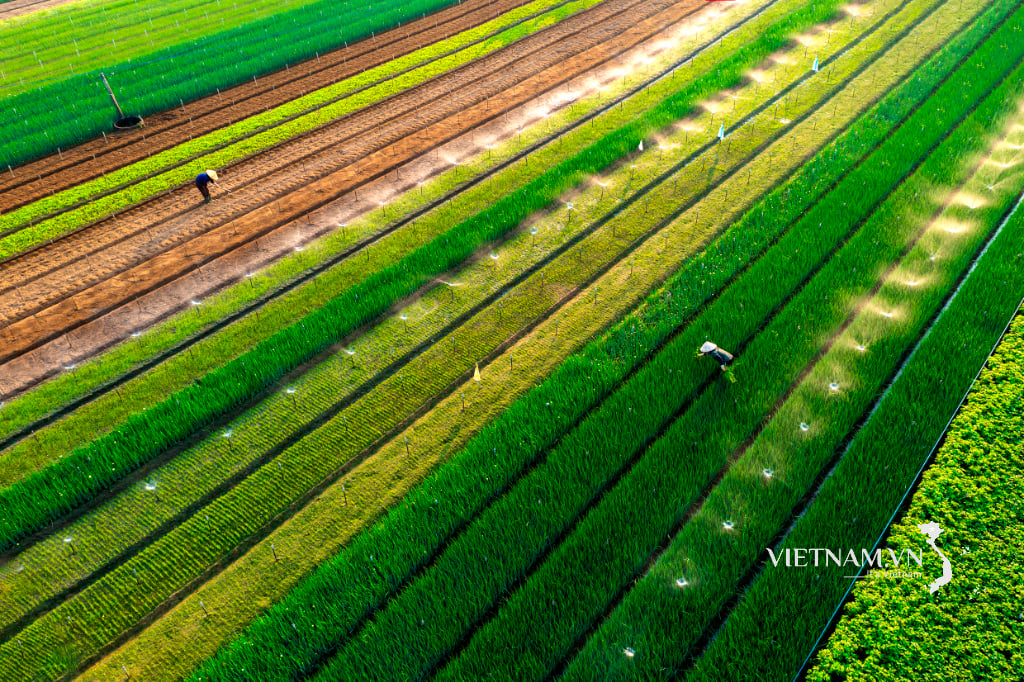
| Illustration photo. |
1. Soil
- Land for growing cassava needs to be cleared of plant residues such as grass and roots, stems, and leaves of previous crops (can be reused to cover/cover cassava roots, limiting soil erosion). Cassava should not be grown in areas with a slope > 25 degrees;
- Land preparation:
+ For flat land areas: Plow deeply, harrow thoroughly 1-2 times to ensure the soil is loose, airy and free of weeds. Make beds with a height of 20-25 cm, bed width of 0.8 m. For low-lying areas prone to flooding, dredge irrigation ditches around the field with a width of 50-60 cm and a depth of 45-40 cm. It is recommended to plow, harrow and make beds with a tractor equipped with a disc, tiller and bed making tools;
+ For hilly areas with slopes < 15 degrees: Plow deeply and harrow thoroughly 1-2 times to ensure the soil is loose, airy and free of weeds. Make ridges for gray soil, sandy soil and poorly drained soil;
+ For hilly areas with slopes of 15-25 degrees: Do not plow, just dig holes or make rows along the contour to place the seedlings directly into the holes or rows;
+ For fields with tuber rot, when preparing the land, it is necessary to clean the fields, plow and dry the soil, apply 2 tons of lime 15 days before planting, use organic fertilizer treated with Trichoderma biological products or use Trichoderma biological products mixed with decomposed organic fertilizer as basal fertilizer.
2. Planting season
Choose the appropriate planting season, only plant cassava when air temperature >20 degrees Celsius; soil humidity >75%, specific planting season for each ecological region is as follows:
- Northern midland and mountainous region: Plant from February 15 to early April, when the weather is warm, rainy, and the soil layer is moist enough (>75%). In Son La province, due to late rain, the crop season may be delayed until late April - early May;
- North Central region: Plant from January and finish before the beginning of Spring so that the cassava plants can grow well before the Lao wind. For dry mountainous areas without irrigation, cassava should be planted in late April - early May when it rains and the soil is moist enough;
- South Central Coast region: Concentrated planting from December to March of the following year; For hilly land bordering the Central Highlands, the planting season is around April - May after rain, when the soil is moist enough;
- Central Highlands: Planting is concentrated at the beginning of the rainy season from April to May after rain, when the soil is moist enough; can also be planted in September to October (end of the rainy season);
- Southeast region: Summer-Autumn crop is planted in April - May after rain, when the soil is moist enough; Winter-Spring crop is planted in September - October for areas with proactive irrigation.
3. Seedling varieties and quality
3.1. Similar
Use cassava varieties that have been announced for circulation. Depending on the cultivation conditions, you can choose varieties that can withstand intensive cultivation such as: KM140, HN1, KM7, BK, 13Sa05, HL-S14... or varieties that can withstand poor soil conditions such as KM94, KM98-7, bamboo leaf cassava. For areas infected with cassava mosaic disease, choose varieties that are resistant to cassava mosaic disease such as: HN1, HL-RS15.
3.2. Quality of cuttings
- Seedlings used for cuttings must be 8-10 months old, free from pests and diseases (especially cassava mosaic and broom disease), with no eyes, no crushed or scratched, and the best storage time is no more than 60 days from harvest. Commercial seed lots must be produced by facilities that meet production conditions and must be inspected, tested or certified to meet requirements by certification organizations;
- Harvesting and preserving seedlings
+ After cutting, the seedlings are tied into bundles of 20 trees and placed with the roots in contact with the ground, stored in a cool place in small piles, about 20-30 bundles/pile;
+ Regularly check seedlings during storage. In case the plants are infected with harmful organisms such as aphids or fungi, they need to be controlled with appropriate pesticides.
- Collecting cuttings: cuttings are taken from the middle of the stem, 30 cm from the base and 1/3 of the plant height from the top; use sharp tools or a cassava cutting machine to cut cuttings to avoid mechanical damage to cassava cuttings (such as bruising, scratches, etc.), the length of cuttings for horizontal planting is 10-15 cm; vertical or diagonal planting is 15-20 cm and has at least 6 nodes/cutting.
Note:
+ Aphids often appear during the process of preserving seedlings, so it is necessary to check regularly. If aphids appear, pesticides must be sprayed to prevent them. Use pesticides containing one of the active ingredients Acetamiprid, Imidacloprid, Profenofos, Buprofezin with dosage according to the manufacturer's instructions.
+ It is recommended to treat cuttings before planting with lime water or plant protection drugs according to the instructions of specialized units in cultivation and plant protection to limit fungal diseases.
4. Planting and care techniques
4.1. Planting density
- Nutrient-rich soil: The planting distance between two rows of cassava is 1.0 m (including furrows in the case of raised beds) and the distance between plants is 1.0 m, corresponding to a density of 10,000 cuttings/ha;
- Soil with average nutrient content: Planting distance between two rows of cassava is 1.0 m (including furrows in case of raised beds) and 0.8 m between plants, corresponding to a density of 12,500 cuttings/ha;
- Poor soil: The planting distance between two rows of cassava is 1.0 m (including furrows in the case of raised beds) and the distance between plants is 0.7 m, corresponding to a density of 14,200 cuttings/ha or 0.8 m between rows and 0.8 m between plants, corresponding to a density of 15,600 cuttings/ha.
4.2. How to plant
- Planting steps
Mix all types of base fertilizers evenly → Make a furrow in the middle of the bed (with the bed planting method) or dig a hole (with the hole planting method) with a depth of about 15 cm → Spread the base fertilizer evenly in the furrow or hole → Cover with a thin layer of soil from 2 - 3 cm on top of the fertilizer → Place the cuttings in the furrow or hole with the distance (plant to plant) as above → Cover with soil after placing the cuttings.
- Method of placing cuttings
+ For well-drained soil, place the cuttings horizontally and cover the cassava cuttings with soil 2-3 cm thick;
+ For poorly drained soil, place the cuttings upright or at an angle of 30-45 degrees and cover 2/3 of the length of the cassava cuttings with soil. Place the base down, with the top of the cuttings tilted towards the hillside (when planting cassava on sloping land) and facing the same direction.
4.3. Fertilizers and application methods
- Amount of fertilizer for 01 hectare
+ For nutrient-rich soil: 10 tons of decomposed manure (or 2 tons of organic microbial fertilizer) + 90 kg N + 60 kg P2O5 + 120 kg K2O, equivalent to 195 kg of Urea + 375 kg of superphosphate + 200 kg of potassium chloride;
+ For average nutrient soil: 10 tons of decomposed manure (or 2 tons of organic microbial fertilizer) + 120 kg N + 60 kg P2O5 + 120 kg K2O, corresponding to the finished product of 10 tons of decomposed manure (or 2 tons of organic microbial fertilizer) + 260 kg of Urea fertilizer + 375 kg of superphosphate fertilizer + 200 kg of Potassium chloride fertilizer;
+ For poor, nutrient-poor soil: 10 tons of manure (or 2 tons of organic microbial fertilizer) + 160 kg N + 80 kg P2O5 + 160 kg K2O, equivalent to 350 kg of Urea fertilizer + 500 kg of Superphosphate fertilizer + 270 kg of Potassium chloride fertilizer.
- Time and amount of fertilizer
+ Apply all organic fertilizers (manure or organic microbial fertilizers) and phosphate fertilizers;
+ First top dressing with ½ nitrogen fertilizer and ½ potassium fertilizer 30-40 days after planting;
+ Apply the second top dressing with the remaining ½ nitrogen fertilizer and ½ potassium fertilizer 80 - 90 days after planting.
- Fertilization methods and techniques
+ Fertilize when the soil is moist enough. Do not fertilize when it is sunny or raining heavily;
+ Apply basal fertilizer when plowing in furrows or holes when planting;
+ Fertilize by digging holes about 15-20 cm from the base or cassava cuttings, spreading fertilizer evenly in the holes and covering with soil after fertilizing.
4.4. Planting and pruning trees
After 15-20 days of planting, check the field and replant in places where cassava cuttings did not grow. After the cassava plants grow, are strong and not bitten by cutworms, prune the plants to maintain 2-3 plants/hole. If the germination rate is below 70%, plow and replant.
4.5. Weed control
- 1-3 days after planting, use pre-emergence herbicides that are allowed to be used. For example, drugs containing active ingredients Acetochlor, S-Metolachlor...;
- If the grass is still growing well, carry out additional control after 30-40 days by manual method or using non-selective herbicide containing active ingredient Glufosinate ammonium; spray the herbicide at the base, avoiding contact with green leaves.
4.6. Water irrigation
For active irrigation areas, supplementary watering of cassava plants is required to achieve high yields. Water when soil moisture falls below 60% using the following methods:
- Furrow irrigation;
- Economical irrigation: Drip irrigation around the base or sprinkler irrigation to optimize productivity and limit red spider damage in the dry season.
Note:
Cassava cannot withstand being submerged in water for 6-10 hours, so when encountering prolonged heavy rain, appropriate drainage measures must be taken such as clearing the flow and opening drainage ditches around the field.
5. Intercropping and crop rotation
5.1. Intercropping
Encourage intercropping of some short-term legumes such as peanuts, green beans, soybeans, black beans, red beans, white beans, etc. to prevent erosion, limit weeds and keep soil moist, and utilize biomass as a source of green forage for livestock. Intercrops are sown at the same time as cassava cuttings; 25-30 cm apart from cassava rows.
For land with slope >15 degrees: it is recommended to plant additional green strips such as pineapple, Vetiver grass, Elephant grass, Paspalum grass, Guatemala grass, Achyranthes, Plover... along the contour lines. The distance between 2 green strips is from 8-10 m.
5.2. Crop rotation
- After 2-3 cassava cultivation seasons, it is recommended to rotate with short-term upland crops such as peanuts, green beans, soybeans, black beans, red beans, white beans, sesame, corn, sorghum, etc. Do not rotate with crops that are hosts of cassava mosaic disease and witches' broom disease such as tobacco, cotton, nightshade, cucurbit, etc.;
- In suitable weather conditions, short-term cassava varieties can be used for early harvest and supplementary planting with crops recommended above.
According to khuyennongvn.gov.vn
Source: https://baonamdinh.vn/kinh-te/202506/quy-trinh-canh-tac-san-khoai-my-ben-vung-cho-cac-vung-trong-san-trong-diem-470719c/


































































































Comment (0)