Most goiters are benign so there is no need to worry about them developing into cancer, but we should not be subjective. Therefore, when there are signs, we need to go to reputable hospitals and medical facilities to be examined and treated promptly by doctors.
Goiter, also known as thyroid nodule, is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes abnormally enlarged. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that produces hormones that control metabolism, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and body weight.
Although not painful, goiters can grow larger, causing coughs, sore throats, and breathing problems. There are many causes of goiters, and treatment will depend largely on the cause and the condition being treated.
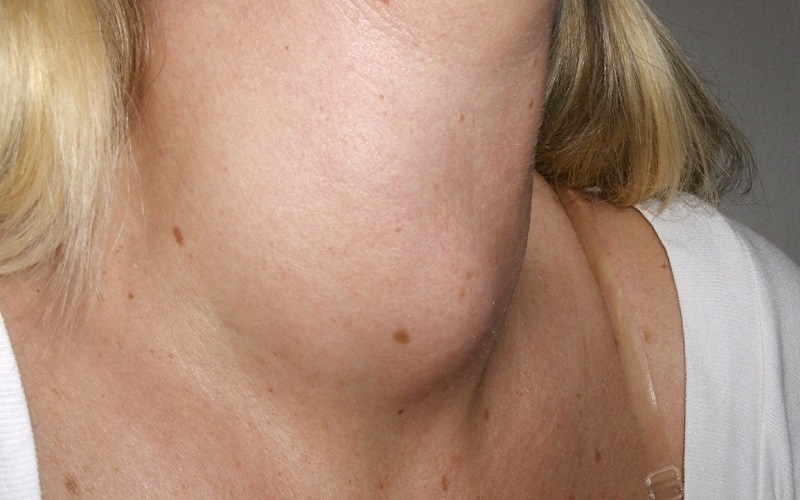
When goiter has endocrine dysfunction such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism it affects many organs in the body.
1. Does goiter affect health?
Goiter is very common in our country, most thyroid goiters are benign and do not affect health. However, if the goiter grows large, it will cause difficulty swallowing or difficulty breathing (due to compression of the airway or protrusion into the chest) or protrusion in the front of the neck, causing loss of aesthetics.
Malignant tumors will invade surrounding organs, especially the recurrent laryngeal nerve, causing hoarseness, or when the tumor metastasizes, it will damage the liver, lungs, bones, brain, etc.
When goiter has endocrine dysfunction such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, it affects many organs in the body such as causing exhaustion, weight loss or gain, chest tightness, insomnia, hair loss, hand tremors, sweating. However, many other diseases also cause these abnormalities, when examined, the doctor will determine the disease.
2. When should goiter be operated on?
The thyroid is an endocrine gland, so when it is sick, it will cause abnormalities in the neck or other parts of the body. When you see an enlarged neck or have the above signs or any changes in the body, you should go to the doctor. The doctor will examine, perform ultrasound, blood test, cell aspiration... to determine the type of goiter.
When the tumor is benign, small, and does not cause discomfort, it usually does not require any treatment and should be monitored by regular check-ups every 1-2 years. You should see a doctor immediately if there are any changes in the neck area or abnormalities in the body.
Cases requiring surgery for goiter include: Benign goiter causing difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, or loss of aesthetics, cancer or suspected cancer. Thyroid dysfunction of the hyperthyroid type.
Surgery is not required in cases of small benign tumors and surgery is not required in cases of large benign tumors that do not cause difficulty breathing or swallowing. Therefore, when you have a goiter, do not worry too much about having surgery.
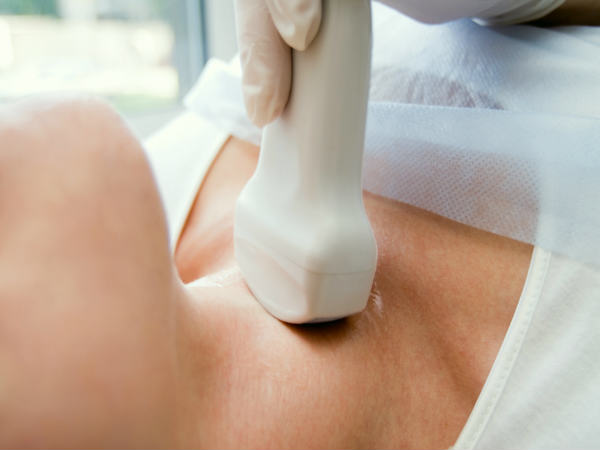
When ultrasound clearly shows thyroid tumors, thyroid cancer is clearly detected.
3. Symptoms of malignant goiter
Most thyroid tumors are benign, but about 5% are malignant (thyroid cancer). The doctor will examine, perform ultrasound, blood tests, cell aspiration... to determine the type of goiter.
In particular, when a malignant goiter first begins, it will not cause any abnormalities and will only be detected through ultrasound examination or by chance when having a CT, MRI, or PET scan of the neck for another disease.
Symptoms will appear as goiter progresses:
- Appearance of a tumor in the neck: It is necessary to monitor the condition of the tumor. We can recognize that a benign tumor will move up and down when swallowing, while a malignant tumor will not move when swallowing.
- Hoarseness: The voice becomes hoarse because the laryngeal nerve, which controls the muscles that open and close the vocal cords, is located behind the thyroid gland. As the condition worsens, thyroid tumors can spread and severely damage the voice box.
- Check for thyroid tumors that are hard, have clear edges, rough or smooth surfaces, and move with swallowing. There are lymph nodes in the neck, small, soft, mobile, appearing on the same side as the tumor.
4. Symptoms of late thyroid cancer
In the late stage, the tumor is large, hard, and fixed in front of the neck. Severe hoarseness, difficulty breathing. The patient will have difficulty swallowing, difficulty swallowing, and pain due to tumor compression.
The skin in the neck area is dark, bruised, even ulcerated and bleeding. When ultrasound clearly shows thyroid tumors, thyroid cancer is clearly detected. Patients can see a large and hard tumor in front of the neck.
5. Goiter treatment
Treatment will depend on the cause of the goiter. If the goiter is due to a lack of iodine in the diet, iodine supplements will be given orally. This will reduce the size of the goiter, but often the goiter will not disappear completely.
If the goiter is caused by Hashimoto's thyroiditis and hypothyroidism, the person will be given thyroid hormone supplements in the form of daily pills. This treatment will restore thyroid hormone levels to normal, but it usually does not make the goiter disappear completely. Although the goiter may shrink, sometimes there is so much scar tissue in the gland that it becomes too small.
Treatment with thyroid hormones will usually prevent it from getting larger.
Surgery is not usually a routine treatment for thyroiditis. If the goiter is due to hyperthyroidism, treatment will depend on the cause of the hyperthyroidism.
For some causes of hyperthyroidism, treatment can cause the goiter to disappear. For example, treatment of Graves' disease with radioactive iodine often reduces or eliminates the goiter. Many goiters, such as multinodular goiter, are associated with normal levels of thyroid hormone in the blood. These goiters usually do not require specific treatment once the appropriate diagnosis is made.
If no specific treatment is recommended, the person may develop hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in the future. However, if there are problems related to the size of the thyroid gland, such as a goiter that becomes large enough to narrow the airway, the doctor may recommend surgical removal of the goiter. Regardless of the cause, it is important to have regular (yearly) follow-up visits once a goiter is diagnosed.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/5-dieu-nhat-dinh-phai-biet-khi-bi-buou-co-172240614212819297.htm


































































































Comment (0)