There are many risk factors for insomnia. In particular, certain foods and drinks can affect the quality and duration of sleep and accelerate aging.
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that makes it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get quality sleep. Insomnia can interfere with daily activities, causing irritability or daytime sleepiness.
Common causes of insomnia include age, stress, hormones, certain lifestyle habits, shift work, and certain medications. Additionally, certain foods can also cause insomnia.
1. The link between insomnia and food

Food affects the quality and duration of sleep.
What you eat can directly and indirectly affect the quality and duration of your sleep. Certain foods or food ingredients disrupt your circadian rhythm, altering your sleep habits and, if continued, can easily cause insomnia.
Additionally, diet has the potential to significantly alter gut bacteria (which help digest and absorb food), affecting other metabolic processes, including sleep. Long-term dietary factors can also cause chronic inflammation, which has also been linked to insomnia.
2. Some foods and drinks cause insomnia
Coffee
Although coffee has many health benefits, the caffeine in coffee acts as a stimulant, so it can make it difficult to sleep by disrupting the body's natural biological clock cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. Therefore, the effects of caffeine on sleep have an indirect effect on daily activities.
Other consequences of disrupted sleep cycles include the brain's inability to repair itself during sleep, which negatively impacts health. Older adults may also be susceptible to caffeine-induced sleep disturbances.
Therefore, limiting coffee intake in the late afternoon and evening can help reduce the effects of caffeine on sleep.
Tea
Although moderate tea consumption is generally good for everyone's health, drinking too much can lead to side effects such as anxiety, poor sleep, etc. Since some teas contain natural caffeine, drinking too much can disrupt the sleep cycle.
Melatonin is a hormone that signals the brain that it's time to sleep. Some studies have shown that caffeine can suppress melatonin production, leading to poor sleep quality.
Insufficient sleep has been linked to a number of mental health problems, including fatigue, memory loss, and reduced ability to concentrate. Furthermore, chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of obesity and poor blood sugar control.
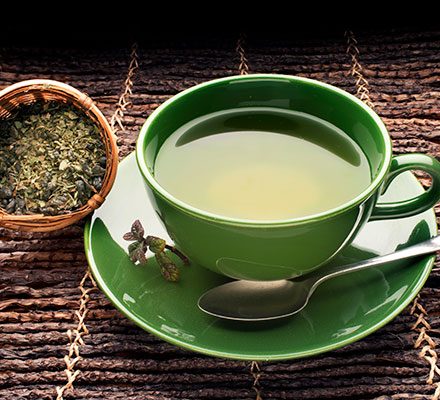

For people sensitive to caffeine, tea can cause insomnia.
People metabolize caffeine at different rates, and it’s difficult to predict exactly how it will affect everyone’s sleep. Some studies have found that even consuming as little as 200 mg of caffeine six or more hours before bedtime can negatively impact sleep quality.
If you are experiencing symptoms related to poor sleep quality and regularly drink caffeinated tea, you may want to consider reducing your intake or switching to decaffeinated or herbal teas.
High Glycemic Foods and Added Sugars
Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) raise blood sugar levels quickly. These foods include refined carbs like white bread, sweets, and foods high in added sugar.
A 2019 study that included data from more than 77,000 women found that those who followed a high-glycemic index diet were more likely to experience insomnia over a three-year follow-up period.
Research also shows that consuming a lot of sugar and refined carbs is linked to higher rates of insomnia.
Other studies have shown that diets high in sweets, sugary drinks, and refined carbs are linked to poor sleep quality.
There are several reasons why diets high in glycemic index and foods high in sugar and refined grains seem to be linked to poor sleep quality.
High GI foods cause blood sugar levels to spike and fall dramatically. This causes the body to release hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol and growth hormone, which can lead to symptoms such as anxiety, hunger and irritability.
A high glycemic index diet also causes inflammation and creates an imbalance in beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can also affect sleep.
Spicy food

Eating spicy food close to bedtime can cause insomnia.
Eating spicy foods close to bedtime can make it difficult to sleep for a number of reasons. Spicy foods are known to cause indigestion, worsening symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux.
Lying down to sleep can make these spicy food-related symptoms worse because the acid can travel up into the esophagus, causing irritation. This can cause sleeplessness at night and lead to sleep disturbances.
Therefore, if you have heartburn after eating spicy food or acid reflux, you should avoid spicy food before going to bed. Eating very spicy foods such as chili peppers, slightly increases body temperature and body surface.
High fat foods
Eating fatty foods like fried chicken and fatty meats contributes to poor sleep. Research shows that higher fat intake, especially saturated fat, has a negative impact on sleep.
A 2016 study in 26 adults found that higher saturated fat intake may lead to lighter and less restorative sleep.
Another study including 459 women found that the more fat and saturated fat participants consumed, the lower their total sleep time.
A 2015 study of 211 men showed that men with insomnia had higher saturated fat intakes than men without sleep disorders.
Additionally, eating a lot of fat at night can also affect your ability to fall asleep. This may be because your digestive system slows down during sleep, so eating a high-fat meal overloads your digestive system, leading to discomfort that can cause insomnia at night.
Furthermore, fatty foods are known to aggravate acid reflux symptoms, keeping you up at night.
Fast food and other processed foods
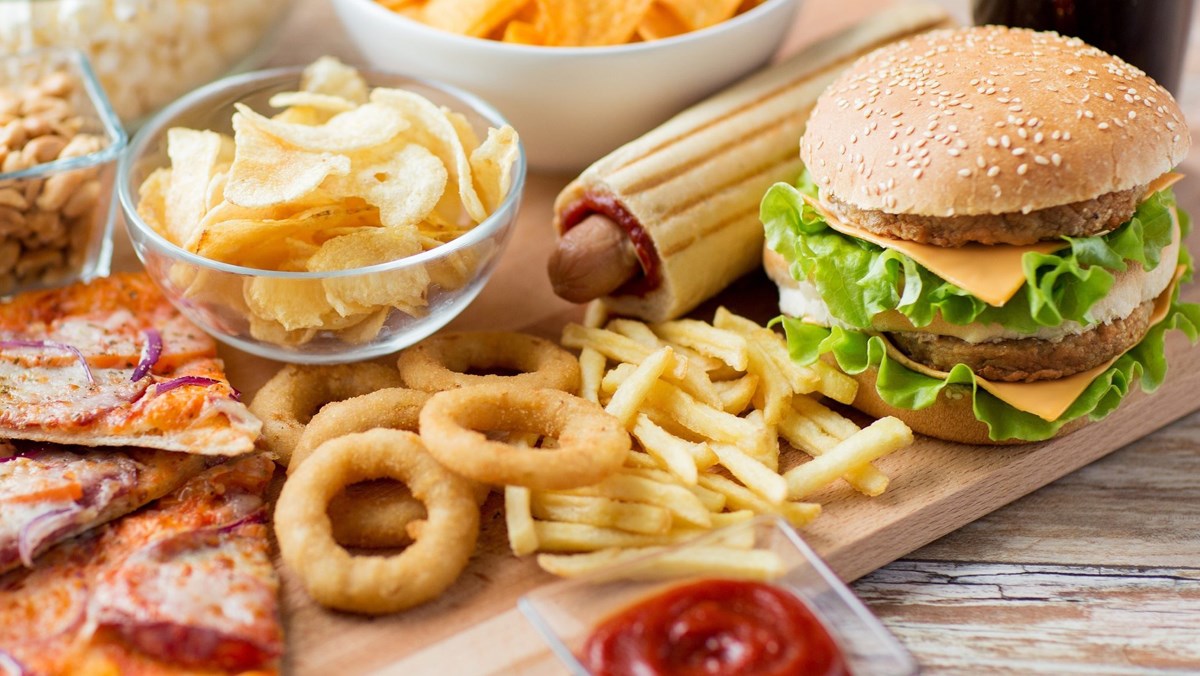

People who consume a lot of fast food and processed foods often have poor sleep quality.
Processed foods like fast food and packaged snacks may not be the best choice for a good night's sleep.
A 2018 study that included data on 118,462 adolescents aged 12–18 found that shorter sleep duration and poor sleep quality were associated with higher intakes of fast food, instant noodles, and sweets.
A 2020 study investigating the sleep habits of Brazilian adolescents linked poor sleep quality to eating a lot of processed foods.
The results of the 2020 study are not surprising given the nutritional makeup of ultra-processed foods. These foods tend to contain many ingredients linked to sleep disturbances, including refined carbs, added sugars, saturated fats, and trans fats.
Additionally, diets high in processed foods can lead to weight gain. Studies show that people who are overweight or obese tend to have more sleep problems than those who are not.
Obesity can lead to obstructive sleep apnea, a health condition that makes it difficult to breathe at night, leading to sleep loss.
Alcoholic beverages
Many people like to have a glass or two in the evening to relax and unwind. before bed. But studies show that drinking alcohol can disrupt sleep and cause insomnia at night.
Alcohol may help you fall asleep faster but then significantly disrupts sleep at night due to the drop in blood alcohol concentration.
A 2020 study in 11,905 people found that higher alcohol consumption was significantly associated with poorer sleep and shorter sleep duration. Another 2019 study found that consuming high amounts of alcohol significantly reduced total sleep time and sleep quality.
Because alcohol is closely linked to insomnia, doctors and nutritionists often recommend avoiding alcohol before bed as part of insomnia treatment.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/7-thuc-pham-gay-mat-ngu-lao-hoa-nhanh-172241108090449679.htm

































































































Comment (0)