 |
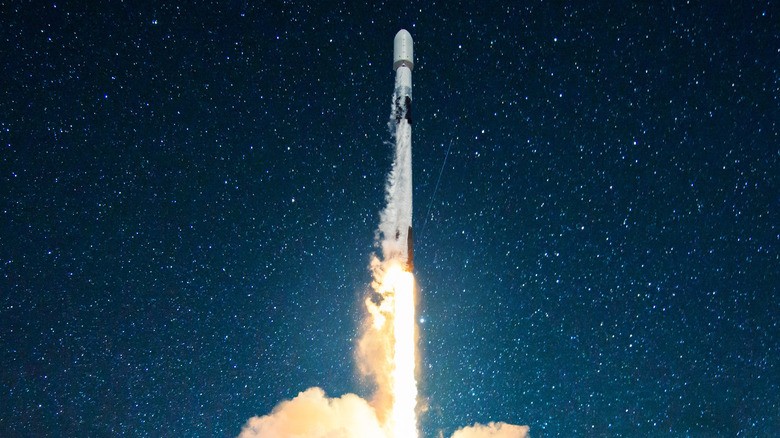
| A British design team tested a rocket that can burn its own lower body. (Source: SlashGear) |
Multi-stage rockets are currently the most efficient way to deliver cargo into orbit. Each stage is designed specifically for maximum efficiency. Splitting a rocket into multiple stages allows the rocket to shed unnecessary mass and fly faster and farther through space. When a stage of the rocket runs out of fuel, it detaches and falls into space, then the next stage's engine is started to propel the rocket forward. Because of this mechanism, multi-stage rockets often dump waste into space and Earth's orbit.
According to scientists , the risks from space debris are huge: causing damage to satellites, easily causing collisions; increasing the cost of space missions, hindering space observation activities from Earth. The cost of handling this huge amount of space debris is extremely expensive.
The design of Professor Patrick Harkness's team, which was presented at the AIAA Science and Technology Forum in Orlando, Florida (USA) last week, has attracted special attention from researchers, because this rocket model has the ability to burn its own lower body as part of the fuel to fly, thereby not having to throw these parts into space.
The team successfully designed a rocket with a thrust of 100 Newtons, and conducted a series of test launches of the rocket, called Ouroborous-3, at Machrihanish Air Force Base (USA).
Ouroborous-3 uses a shell made of polyethylene plastic. During flight, this shell is burned along with the rocket's main fuel, a mixture of oxygen and liquid propane. The waste heat from burning the main fuel melts the plastic shell, and sucks the plastic into the combustion chamber to burn with the main fuel.
Tests showed that the Ourobourous-3 rocket was capable of stable combustion (stable combustion is a key requirement for any rocket engine), with plastic parts accounting for up to a fifth of the total fuel used.
The tests also showed that the rocket's burn could be successfully controlled, as the team demonstrated the ability to throttle and restart the rocket. These capabilities could help future autonomous rockets control their flight from launch pad to orbit.
Professor Patrick Harkness, from the University of Glasgow's James Watt School of Engineering, is leading the development of a rocket engine that uses fuel from the body of a rocket. He said: "There could be many future applications for such rockets, helping to boost the UK's ambitions to become a major player in the space industry."
Source



![[Photo] Cat Ba - Green island paradise](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F04%2F1764821844074_ndo_br_1-dcbthienduongxanh638-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


























































![[VIMC 40 days of lightning speed] Da Nang Port: Unity - Lightning speed - Breakthrough to the finish line](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/04/1764833540882_cdn_4-12-25.jpeg)













































Comment (0)