However, if detected early, thyroid cancer is one of the most treatable forms of cancer, with a 5-year survival rate of nearly 100%. Therefore, early detection is extremely important.
Early symptoms of thyroid cancer
The earliest signs of thyroid cancer are swelling in the neck or the appearance of unusual lumps and lymph nodes in the neck. The lumps are usually quite hard, have clear borders and move with the patient's swallowing rhythm. Meanwhile, the lymph nodes are soft, mobile and located on the same side as the tumor.
Other symptoms of thyroid cancer include:
- Tired
- Hoarseness, voice changes
- Swollen glands in the neck
- Persistent cough that is not due to a cold
- Neck pain, pain may be located in the front of the neck or radiate behind the ear
- Difficulty breathing or other respiratory problems
- Difficulty swallowing
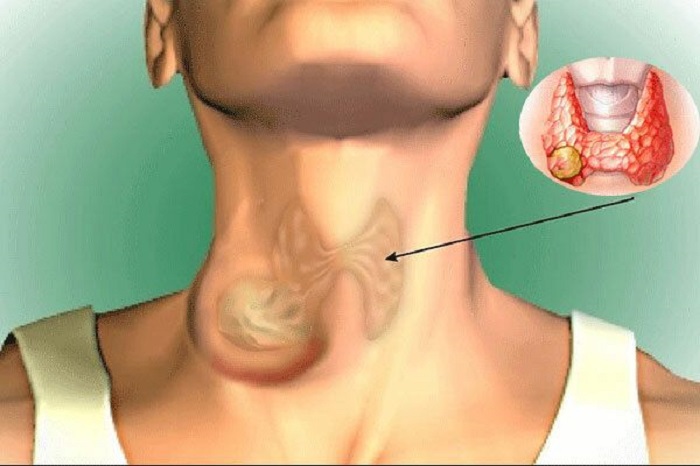
When there are symptoms of suspected thyroid cancer, you need to see a doctor early for accurate diagnosis and timely and proper treatment.
Symptoms of thyroid cancer when it develops
Late-stage thyroid cancer can have serious symptoms, including:- The tumor is large, hard and fixed in the front of the neck.
- The tumor gradually enlarges, compressing the trachea and vocal cords, causing difficulty breathing, wheezing, and hoarseness.
- Feeling of choking in the throat
- Having trouble swallowing
- The skin on the neck is red and even bleeding.
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer
In addition to clinical manifestations, doctors may order a variety of tests to help diagnose the disease, including:
Diagnostic imaging in which ultrasound is most commonly used. Ultrasound is a method that uses sound waves to recreate images of organs in the body, including the thyroid gland. From there, doctors can assess the level of malignancy through ultrasound images.
Fine needle aspiration – the doctor will use a small needle to puncture the thyroid tumor to remove a small sample of the tissue, then observe it under a microscope for diagnosis. This is a very valuable method to diagnose benign or malignant tumors.
Thyroid Cancer Treatment
The decision to choose a treatment method depends mainly on the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, the age and other health conditions of the patient.
When diagnosed with suspected or confirmed thyroid cancer by cytology, the patient should not be too worried. Thyroid cancer treatment has the following possibilities:
- Only remove the lobe and isthmus of the thyroid gland that have cancer. If the tumor is less than 1cm in diameter, or even less than 1.5cm in one lobe (one side) of the thyroid gland, the tumor in the isthmus of the thyroid gland is less than 1cm in diameter, when performing surgery, the tumor has not invaded much into the thyroid capsule or neighboring organs, and has not metastasized to the lymph nodes (roughly understood as not metastasized), and at the same time the other side of the thyroid gland has no other accompanying lesions, then the doctors will only remove one lobe of the patient's thyroid gland.
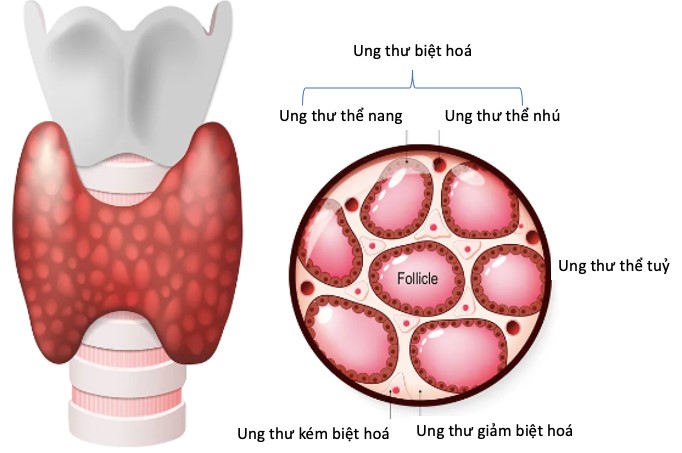
Types of thyroid cancer.
- Total thyroidectomy without radioactive iodine treatment. If the tumor is large or involves both thyroid lobes with minimal invasion of the thyroid capsule, but has not invaded neighboring organs and has not metastasized to the neck lymph nodes, the surgeon will consider total thyroidectomy and neck lymph node dissection (if any).
Patients will be evaluated after surgery and given thyroid hormone replacement. These cases may not require post-operative radioactive iodine treatment, but consideration of radioactive iodine treatment will be assessed in detail by nuclear medicine and radiation specialists such as whether there are any remaining thyroid cancer cells, whether they have metastasized, etc.
Symptoms of recurrent thyroid cancer
Signs and symptoms of thyroid cancer recurrence may include:
- Swelling or a lump in the neck. This lump usually tends to grow rapidly.
- Pain that begins in the front of the neck, sometimes radiating to the ear
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing
- Hoarseness, voice changes
- Cough that is persistent and not related to a cold.
According to research, the recurrence rate of thyroid cancer is about 30%. Of which, the recurrence rate of cancer only in the neck area accounts for about 80%. The rest are diagnosed with distant metastatic recurrent thyroid cancer. Metastatic cancer is a condition in which tumors form in other locations in the body, such as the lungs, liver, and bones.
Summary: Primary and recurrent thyroid cancer are completely treatable if detected early. For people who have been treated for thyroid cancer, regular monitoring of the disease and attending all follow-up appointments are extremely important. This helps patients detect early signs of thyroid cancer recurrence to prevent the possibility of the cancer returning and becoming more serious.
Source

























































![[Maritime News] Treasury Department Targets Diverse Networks Facilitating Iran's Oil Trade](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/14/43150a0498234eeb8b127905d27f00b6)










































Comment (0)