Joint pain, lower back pain, muscle stiffness... are common conditions in the elderly and can be controlled by exercising and eating healthily.
Aging increases the risk of musculoskeletal pain and injury. Joint pain and lower back pain are two common types of musculoskeletal conditions in people 55 and older. In addition, aging can make movement more difficult, increasing the risk of falls and fractures. Below are common musculoskeletal conditions in older adults, prevention methods, and treatments.
Joint pain
Some common causes of joint pain in older adults include: rotator cuff tears (shoulder joint injuries); joint stiffness and pain that occur when ligaments and tendons become dehydrated, or when cartilage (the cushion between bones) is damaged; autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis; gout; osteoarthritis...
Treatment for joint pain depends on the cause and the individual. Older adults may only need to rest, lose weight, and maintain a regular, gentle exercise routine such as walking, cycling, or swimming. More severe cases may require medication, physical therapy, or surgery.
Lower back pain
Although low back pain can occur at any age, the risk increases as you get older. According to studies, up to 75% of people over the age of 60 have low back pain, which can interfere with daily life and even lead to disability. The most common cause is osteoarthritis, which occurs when the joints in the spine deteriorate over time. Other causes of lower back pain in older adults include: lumbar spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal); osteoporotic fractures (fractures due to osteoporosis, a condition in which bones become weak and brittle); spinal infections; tumors.
Treatment for lower back pain depends on the cause of the pain, but your doctor may recommend pain medication combined with physical therapy, exercise... or surgery in severe cases.
![[Caption]. Photo: Freepik](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/1/20/3da7220cc2fa4d59813dcc4e6f393cd0)
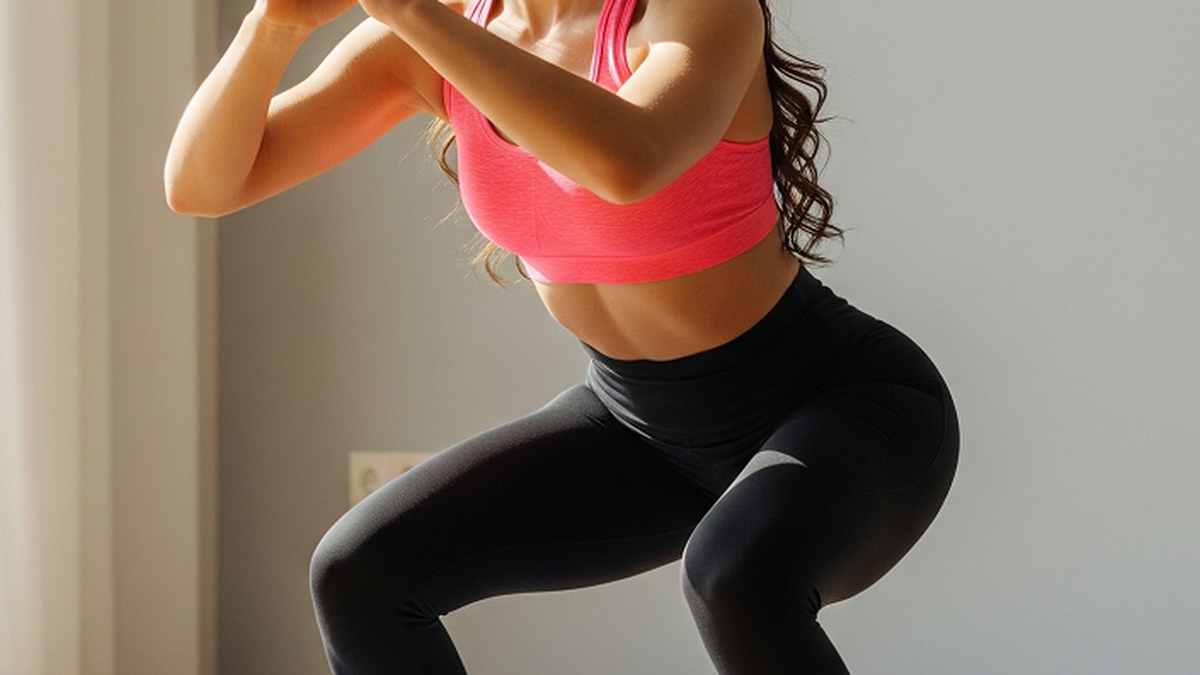
The elderly are susceptible to injuries and osteoarthritis leading to knee pain. Photo: Freepik
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve in the wrist (the main nerve that runs from the armpit to the hand) becomes pinched or compressed. Older adults, especially those over 65, are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome than younger people. Treatment includes wearing a splint, avoiding movements and activities that worsen symptoms, taking medications to reduce swelling and pain, surgery, or yoga.
Knee pain
Injuries and wear and tear on the joints can cause knee pain. Osteoarthritis, being overweight or obese can also affect the knees in older adults, making pain worse. Knee pain can be treated with medication, surgery, physical therapy or weight loss (if overweight or obese).
muscle stiffness
As people age, the tissues that connect muscles to bones lose water, causing stiffness and pain. Aging also makes it more difficult to do physical activity, leading to stiffness and pain. Physical therapy and a slow, careful increase in physical activity can help treat stiffness.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is also a common condition among older adults. Treatment includes rest, ice, support, and avoiding movements and activities that aggravate symptoms.
Pain management becomes more complex with age due to the increased likelihood of multiple diseases and medication use in older adults. If pain occurs, older adults should seek care from specialists to find ways to relieve symptoms, treat pain, and improve quality of life.
Fracture
Every year, millions of older adults fall and break bones, affecting their long-term mobility and overall health. In fact, people over the age of 70 are at higher risk of death after a fall. Experts advise people to stay calm and prevent further injury after a fall by taking deep breaths, staying still, assessing their condition, and checking for injuries before moving. Next, if there are no injuries and they can still move, they can move on their hands and knees, moving to a chair. If they cannot move, they should call for help or emergency services.
Even if you can stand up after a fall, you should still see a doctor to check for injuries and broken bones (if any). Treatment for broken bones includes wearing a splint, cast... depending on the location of the break and the severity.
The best way to limit falls leading to fractures in the elderly is to use assistive devices such as canes, walkers, handrails... in daily activities. In addition, some ways to help strengthen bones include: following a balanced diet, supplementing calcium and vitamin D; exercising appropriately; staying away from cigarettes...
Hai My ( According to Very Well Health )
Source link


































































































Comment (0)