Every year in the cold season, many cases of CO poisoning are recorded due to burning coal for heating in closed rooms, causing serious effects on health and even leading to death.
Warning of CO poisoning in winter
Thach Ha District Medical Center (Ha Tinh) received 4 people from a family in Viet Tien Commune (Thach Ha District) in a state of difficulty breathing, drowsiness and vomiting. According to the initial diagnosis, the patients were suffering from CO poisoning.
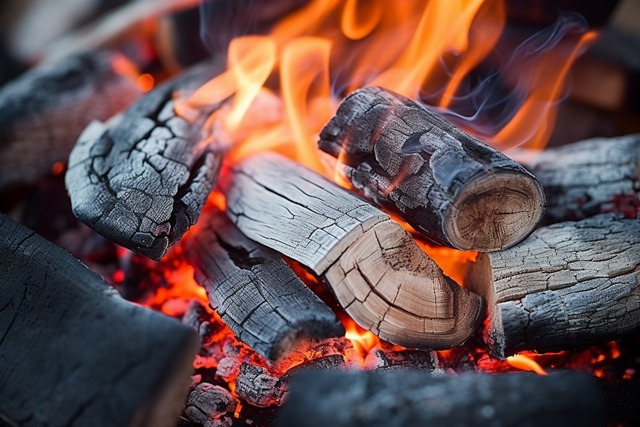 |
| In economically disadvantaged areas that are not equipped with modern machinery, people should not use charcoal or honeycomb coal to burn and heat in closed rooms. |
According to information from the patients' families, on the evening of December 15, because his wife had just given birth, the husband burned charcoal, put it in a clay pot and placed it in the bedroom, about 15 square meters wide, to keep warm.
However, the next morning, when they woke up, both the couple and their 6-year-old daughter felt headaches, tiredness and drowsiness. The newborn also kept crying, making the family worried. They quickly contacted relatives to take the whole family to the hospital.
According to doctors at Thach Ha District Medical Center, burning coal in a closed room with a narrow space will cause all the oxygen in the room to be burned, producing CO (carbon monoxide), a colorless, odorless, toxic gas that is very difficult to detect, especially when people are sleeping.
Every year in the cold season, Ha Tinh records many cases of CO poisoning due to burning coal for heating in closed rooms, causing serious health effects and even leading to death. Although authorities have warned many times, this situation continues to occur.
Previously, talking about the risk of CO poisoning, according to Dr. Nguyen Trung Nguyen, Director of the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital, burning coal, firewood or using gas in a closed room will burn all the oxygen and form more and more CO gas, causing poisoning.
CO gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, making it difficult to recognize and detect, especially when sleeping. CO poisoning occurs very quickly. When inhaled, CO gas quickly enters the bloodstream and deprives the victim of oxygen, causing headaches, dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, chest pain, and confusion.
When the patient begins to feel abnormal, he or she is no longer able to resist and gradually faints. In case a person inhales a large amount of CO gas, he or she may be severely poisoned, causing unconsciousness and rapid death, especially in pregnant women, young children, and the elderly with chronic heart and lung disease.
40% of people who are suffocated by CO gas have sequelae such as memory loss, decreased concentration, facial paralysis, abnormal movement, difficulty walking, stiff and trembling hands and feet, hemiplegia...
To prevent CO poisoning, according to the Department of Environmental Management, Ministry of Health, people need to equip themselves with safe heating devices instead of burning coal or firewood for heating.
In economically disadvantaged areas that are not equipped with modern machinery, people should not use charcoal or honeycomb coal to burn and heat in closed rooms.
If the weather is too cold and coal must be used, it should only be used for a short time, the door should be left open to ensure ventilation and only heating when people are awake; do not use heating overnight and keep the room door closed.
In case of regularly using charcoal stoves for cooking, people should place the stoves in well-ventilated areas; do not burn coal or firewood indoors, in tents, and do not run motorbike or car engines in the room, even when the door is open, it is very dangerous to ensure safety.
In case of detecting a victim of carbon monoxide poisoning, family members need to urgently ventilate the air by opening the doors.
People must wear a wet mask and quickly move the victim away from the dangerous area. If the patient has weak breathing or stops breathing, immediately perform artificial respiration and take the patient to the nearest medical facility.
For more modern heating methods, without coal, caution should also be exercised. When using infrared heaters such as fan heaters, heating lamps, fireplaces, etc., they should not be placed near children and the elderly. The heater should be placed 1 to 2 meters away, in rotation mode, and not exposed to direct heat.
When using an electric blanket, you must also check carefully before use, turn on the warm mode, when warm enough, turn it off before use, do not wash it wet.
Signs of autoimmune encephalitis
The National Hospital for Tropical Diseases (Hanoi) said it had just treated a 20-year-old female patient, residing in Da Nang, suffering from a rare disease – autoimmune encephalitis.
About 2 weeks before being admitted to the hospital, the patient began to show symptoms of mental disorder and delirium, causing the family to take him to a psychiatric hospital for examination.
After 6 days of outpatient treatment, the patient continued to have convulsions in her hands and face, lasting about 30 seconds, every few minutes to several hours. She was hospitalized for treatment immediately after that.
However, after 3 days of treatment in the hospital, the patient's condition did not improve. The patient continued to have seizures and her consciousness was slow. She was transferred to a general hospital and diagnosed with encephalitis. A brain MRI showed lesions in the brain, and the patient was treated for viral encephalitis.
After 3 days of treatment without any signs of improvement, the patient was transferred to the Central Hospital for Tropical Diseases in a state of mental disorder, agitation, screaming and not responding to calls.
She still had seizures in her face, arms and right side of her body. Here, the patient was assigned to do screening tests for autoimmune encephalitis and viral encephalitis.
Test results confirmed that the patient had autoimmune encephalitis. At the same time, abdominal ultrasound detected an ovarian tumor measuring 4×10 cm.
The patient was scheduled for surgery to remove the tumor, but during the surgery, the actual tumor was much larger, up to 20×20 cm. Doctor Pham Thanh Bang, Emergency Department, said this was the cause of autoimmune encephalitis.
After tumor resection and plasmapheresis, the patient had no more seizures, no more screaming urges, and improved consciousness, although not yet fully recovered.
Dr. Bang said that the initial symptoms of autoimmune encephalitis are easily confused with signs of depression or autism.
In the early stages, patients may not have fever, no seizures, and often have psychological problems due to stress in life. If the disease is not detected early, brain damage can become more severe and cause serious sequelae, such as impaired consciousness, prolonged seizures or epilepsy.
Autoimmune encephalitis is a rare acute brain inflammation caused by the body's immune system producing antibodies against glutamate receptors in the brain. It is common in young women and is often associated with tumors, especially ovarian, uterine, or female reproductive cancers.
Notably, ovarian tumors can recur after treatment and cause a new episode of autoimmune encephalitis. Therefore, doctors recommend that young women should be screened for cancer, ovarian tumors, uterus and parasitic diseases periodically to detect potential risks early.
How dangerous is excess vitamin D?
Vitamin D toxicity (hypervitaminosis D) occurs when vitamin D levels in the body are too high, leading to a buildup of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia).
This condition is not usually caused by prolonged sun exposure or a diet rich in vitamin D, but is mainly the result of taking high doses of vitamin D supplements over a long period of time.
Although vitamin D is fat-soluble and stored in the body, too much vitamin D can disrupt normal physiological processes, causing serious health risks.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of vitamin D varies depending on age, gender, and health status. While the RDA for most adults is 600–800 IU/day, the tolerable upper intake level is 4,000 IU/day. However, taking vitamin D supplements above 10,000 IU per day for several weeks or months can lead to toxicity.
The risk of vitamin D toxicity increases when vitamin D supplements are combined with a calcium-rich diet or calcium supplements. This can raise blood calcium levels to dangerous levels, causing serious health complications.
Vitamin D poisoning is often manifested through symptoms mainly due to hypercalcemia, including: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, thirst, frequent urination and weakness.
If poisoning progresses, more serious manifestations may appear: Hypercalcemia can lead to kidney stone formation, impaired kidney function, or calcification of kidney tissue.
High calcium levels can also cause calcification of the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Excess vitamin D can weaken bones, interfere with calcium regulation, and increase the risk of fractures.
Hypercalcemia can cause confusion, irritability, or in severe cases, seizures.
Vitamin D is an important nutrient that helps regulate calcium and phosphate levels, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone problems such as rickets in children and bone pain in adults due to osteomalacia.
Vitamin D is found in a number of foods, including: Oily fish such as salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel. Red meat, liver (however, pregnant women should avoid eating liver). Egg yolks and fortified foods (such as breakfast cereals).
Autumn and winter are ideal times to supplement vitamin D, as lack of sunlight can affect the body's production of vitamin D. However, before supplementing vitamin D, people should consult a doctor to avoid the risk of toxicity due to excess vitamin D.



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh inspects and directs the work of overcoming the consequences of floods after the storm in Thai Nguyen](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/08/1759930075451_dsc-9441-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the World Congress of the International Federation of Freight Forwarders and Transport Associations - FIATA](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/08/1759936077106_dsc-0434-jpg.webp)




















































































Comment (0)