Some people worry about the risk of food poisoning, so when eating canned foods such as canned fish and canned meat, they often reheat them thoroughly. Is the Botulinum toxin hidden in canned foods (if any) still a health hazard when the food has been heated?
1. Cook canned food thoroughly before eating to prevent Botulinum poisoning?
Although Ms. Th.V's daughter (Cau Giay, Hanoi ) does not like to eat fish, canned fish in tomato sauce, tuna in oil... are her favorite dishes, so Ms. Th.V often buys them for her to eat.
Whether eating the fish directly or mixing it with rice and adding a little mayonnaise and seaweed, Ms. V. still carefully boils the canned fish thoroughly before feeding it to her child. Her husband and children wonder why they have to do that, as heating it up makes it less delicious, but Ms. V. believes that heating it up is safer.
This question is also asked by many people who have the habit of eating canned fish and canned meat. So is Ms. V's method necessary when the canned food is still within its expiration date, the can does not show signs of swelling, dents, or rust, and does heating help prevent Botulinum poisoning?
Select and store canned foods properly to prevent the risk of food poisoning.
According to Dr. Pham Thuy Duong, Lecturer of Biotechnology Department, Phuong Dong University: Canned food is a popular form of food today because of its convenience and diversity. The method of canning food allows food to be stored for a long time using a process suitable for each type of food and is divided into three stages: Processing, canning, heating. All three stages require a high level of prevention and control of infection by pathogenic bacteria.
During the heating stage - when the food is canned and sealed, people use appropriate sterilization techniques to destroy harmful microorganisms in it while ensuring that nutrients are lost to the minimum, giving the product the best quality. One of the microorganisms that often invades canned food and has a major impact on the health of users is the bacteria C.Botulinum.
Consumers heat food after opening the can to avoid toxins that may arise later, but heating canned food at high temperatures does not break down the toxins, so it is almost meaningless to prevent Botulinum poisoning if the canned food is contaminated with this toxin during storage. Because if the food is contaminated with Botulinum, this toxin has already grown and developed before the can is opened and produces toxins.
Boiling at high temperature for 8-10 minutes can destroy the spores but does not break down the existing toxin. Botulinum spores are very heat resistant and can survive for several hours at 100°C. Therefore, reheating for a few minutes before eating as Ms. Th.V did will not destroy the toxin if the food is already contaminated with Botulinum.
Although thoroughly cooking canned meat and fish before eating at high temperatures for a long time (120°C for 30 minutes) can destroy toxins, in reality, if the canned food meets the standards for shelf life, the can is not dented, swollen, rusted, and is well preserved, overcooking can cause the food to lose its flavor and deliciousness.
Store canned food in a cool, dry place with a temperature below 30 degrees Celsius.
2. Some notes when using canned food
To best preserve canned foods, store them in a cool, dry place below 30 degrees Celsius, preferably between 10 and 21 degrees Celsius, but not in a freezing environment. Do not store them in places exposed to excessive humidity such as above the stove or under the sink.
Do not store canned food in an iron container after opening, but reheat it, transfer the food to an airtight plastic or glass container and store in the refrigerator, use within 2-3 days.
Note, before using canned food, clean the top of the can to prevent bacteria from contaminating it.
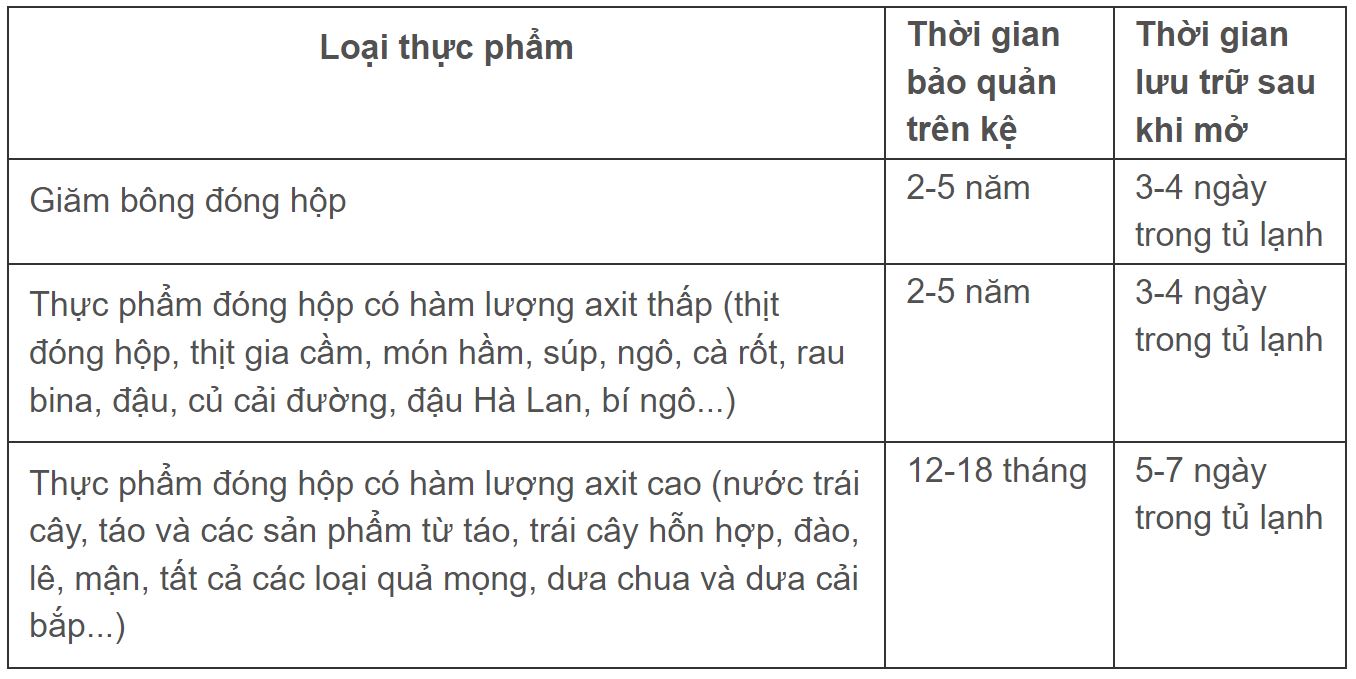
Rotate foods so that the oldest foods are used first, and don't use canned foods past the expiration date printed on the can. Canned foods with high acid content, such as tomatoes, fruits, and pickles, have a shorter shelf life and tend to stay at their best for 12 to 18 months. Meanwhile, canned foods with low acid content, such as meats and vegetables, can last from 2 to 5 years. However, nutritionists say it's best not to keep canned foods for more than 1 year.
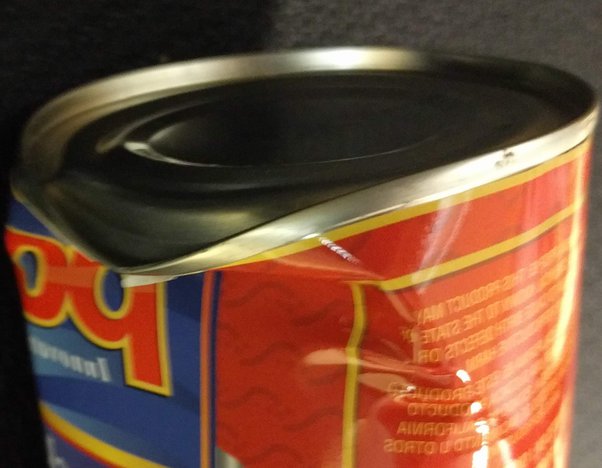
Absolutely do not use canned products that are expired, swollen, flattened, deformed, rusty, not intact, or have unusual odors or colors.
3. Recommendations for preventing Botulinum poisoning from the Department of Food Safety, Ministry of Health
1. In production and processing, raw materials that ensure food safety must be used and hygiene requirements in the production process must be strictly followed. In canned food production, strict sterilization must be followed;
2. Only use food products and food ingredients with clear origin and source. Absolutely do not use canned products that are expired, swollen, flattened, deformed, rusty, not intact, or have unusual odors or colors.
3. Eat cooked food and drink boiled water. Prioritize eating freshly prepared and cooked foods.
4. Do not pack food tightly and leave it for a long time without freezing. For fermented foods, pack or cover them tightly in the traditional way (such as pickles, bamboo shoots, pickled eggplants...) to ensure they are sour and salty. When the food is no longer sour, it should not be eaten.
5. When symptoms of Botulinum poisoning appear, go to the nearest medical facility immediately for timely diagnosis and treatment.
According to SK&DS
Source





































































































Comment (0)