The British male patient (about 30 years old) had allergic rhinitis. At the time of the incident, he was driving and suddenly wanted to sneeze. In order to concentrate on driving, he covered his nose and closed his mouth to suppress it. He sneezed, but this caused severe pain in his neck. The male patient immediately went to the emergency room for treatment.
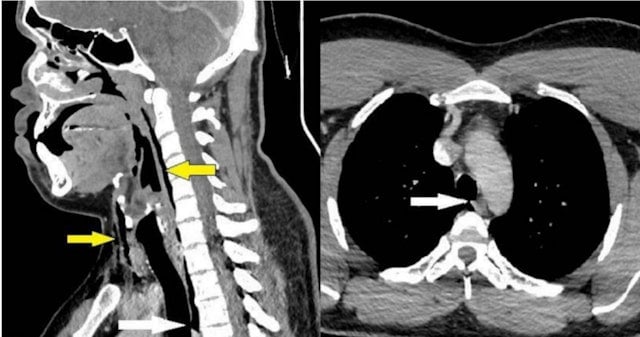
Illustration photo
After palpating the man, the doctor discovered that his throat was making a cracking sound and his movement was restricted, so he immediately arranged for a CT scan. The results showed that the man had a 2x2x5mm tear in his trachea, along with pneumothorax.
Medical staff at the hospital pointed out that tracheal injuries are often caused by trauma, such as by sharp or blunt objects, and the man's condition, known as "spontaneous tracheal perforation," has not been found to date.
Medical staff concluded that the injury was caused by the trachea closing when sneezing, causing pressure in the trachea to increase rapidly "equivalent to an explosion".
Fortunately, the injury was not life-threatening. The doctor determined that surgery was not necessary. However, he was not allowed to do strenuous exercise for two weeks. In a recent check-up, the man had made a full recovery.
Health care professionals advise people not to pinch their nose to suppress a sneeze while closing their mouth as this can lead to a punctured windpipe.
What happens when you hold in a sneeze

Illustration photo
- During a sneeze, all the air pressure that has built up in your lungs escapes through your nose. When you block the air passage by pinching your nose or mouth while sneezing, the air is forced into your ears. The air pressure can enter your middle ear and damage your eardrum.
- Holding in a sneeze will not clean the nasal cavity and harmful agents will have the opportunity to penetrate deeper, causing illness in the body.
- When we try to hold in a sneeze, intracranial pressure increases significantly. Blood flow to our brain is disrupted and blood vessels and nerve tissues are compressed. This can lead to headaches and even affect hearing.
- The pressure of holding in a sneeze can also seriously affect the eyes.
- The diaphragm (the muscle located under the rib cage, responsible for controlling breathing) is also at risk of injury because of the sudden increase in pressure.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/nguoi-dan-ong-bi-thung-khi-quan-do-lam-viec-nay-trong-luc-hat-hoi-172240920233238864.htm


![[Photo] Da Nang residents "hunt for photos" of big waves at the mouth of the Han River](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/21/1761043632309_ndo_br_11-jpg.webp)




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh received Mr. Yamamoto Ichita, Governor of Gunma Province (Japan)](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/21/1761032833411_dsc-8867-jpg.webp)















![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Speaker of the Hungarian National Assembly Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760970413415_dsc-8111-jpg.webp)











































































Comment (0)