A recent study from North Carolina State University (USA) surprised scientists when it discovered that protein from egg whites - a popular food because of its high nutritional content and low fat content - can cause negative effects on the intestinal microflora.
Egg white discovery from mouse study
In a study published in Scitech Daily , scientists tested the effects of different protein sources on the gut microbiota of mice.
Each mouse was fed a single high-protein diet for one week. Protein sources included: egg whites, brown rice, soybeans, and yeast.
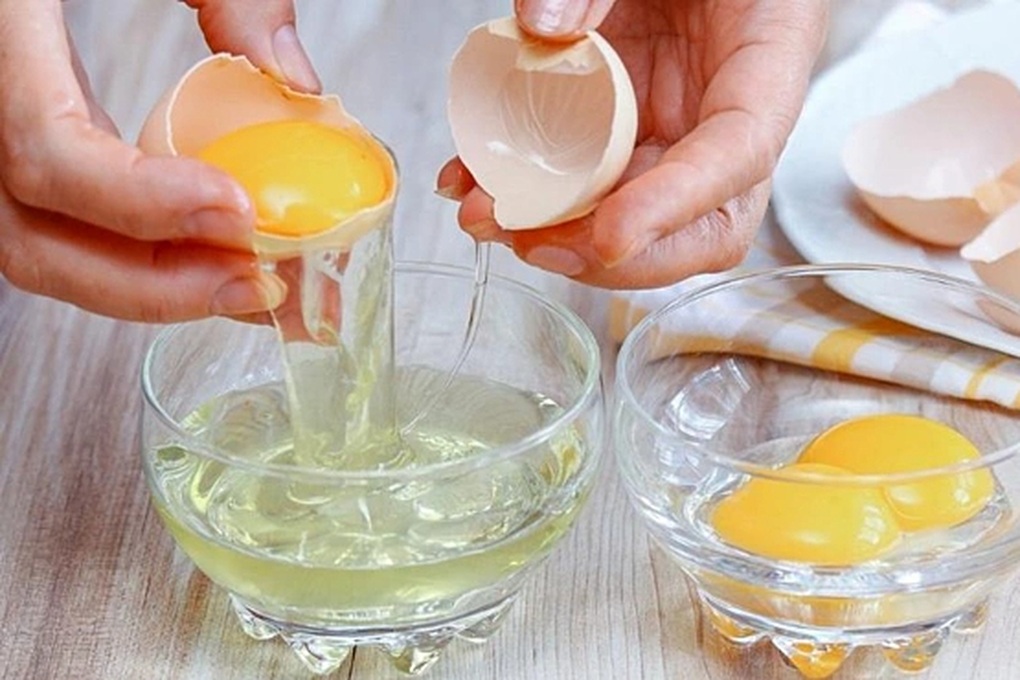

A diet containing only egg whites had negative effects on mice (Photo: Getty).
What surprised the team were the dramatic changes in the gut microbiota when the mice consumed egg white protein.
"Gut microbiome composition varied significantly with each protein source, but egg whites, brown rice, and yeast had the greatest impact," said study lead author Dr. Alfredo Blakeley-Ruiz.
Increased amino acid breakdown - good or bad?
One of the key findings of the study was the ability of egg whites to promote amino acid breakdown in the microbiota.
Rather than helping to synthesize or conserve essential amino acids, egg white consumption appears to accelerate the breakdown of amino acids in the gut.
This is a mechanism that can be risky.
“Some amino acids can break down into toxins, others can affect the gut-brain axis, which can have potentially serious consequences for overall health,” says Dr. Blakeley-Ruiz.
In other words, the substances created from this uncontrolled breakdown process can escape the digestive system, affecting other organs in the body, including the brain.
Enzyme action
Not only does it promote the breakdown of amino acids, a diet rich in egg whites also affects the enzymes that digest glycans - a form of carbohydrate important in many physiological activities.
In the group of mice fed egg whites, a type of bacteria "took over" the gut microbiota and activated a series of enzymes similar to those that break down mucin - the mucus lining the intestinal wall that protects the mucosa from acid and harmful bacteria, said Dr. Blakeley-Ruiz.
Overactivity of these enzymes can break down the mucin layer, leading to damage to the intestinal lining and allowing harmful bacteria to invade – impairing digestive health.
Associate Professor Manuel Kleiner, co-author of the study, affirmed: "Egg whites not only change the composition of the microbiota, but also change their function. This is really remarkable."
Cautionary advice on high protein diets
Egg whites have long been considered a "golden" food in a healthy diet - rich in protein, cholesterol-free, and low in calories.
However, this study shows that overconsumption of a single protein source, no matter how benign, may have the potential to have unwanted biological effects.
The new findings don't mean we should completely ban egg whites from our diets, but they are a reminder that dietary diversity is essential to maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbes – which are linked to digestive health, immunity, and even mood.
The next phase of the study will focus on analyzing the effects of mixed protein sources, rather than just single protein sources, the team said. This will help to better understand the interaction between food and the microbiome – which is increasingly considered the human “second brain”.
While waiting for results, consumers are advised to combine proteins from different sources - meat, eggs, beans, grains - instead of eating too much of one group, even if it is a "superfood".
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/phat-hien-moi-ve-mat-trai-cua-viec-chi-an-long-trang-trung-20250512070110716.htm





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761390212729_dsc-1484-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761390815792_ctqh-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres attend the Press Conference of the Hanoi Convention Signing Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761391413866_conguoctt-jpg.webp)



















![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam meets with General Secretary and President of Laos Thongloun Sisoulith](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761380913135_a1-bnd-4751-1374-7632-jpg.webp)












































































Comment (0)