Precise drug delivery in medicine is nothing new because there has been a lot of research with nano robots for a long time.
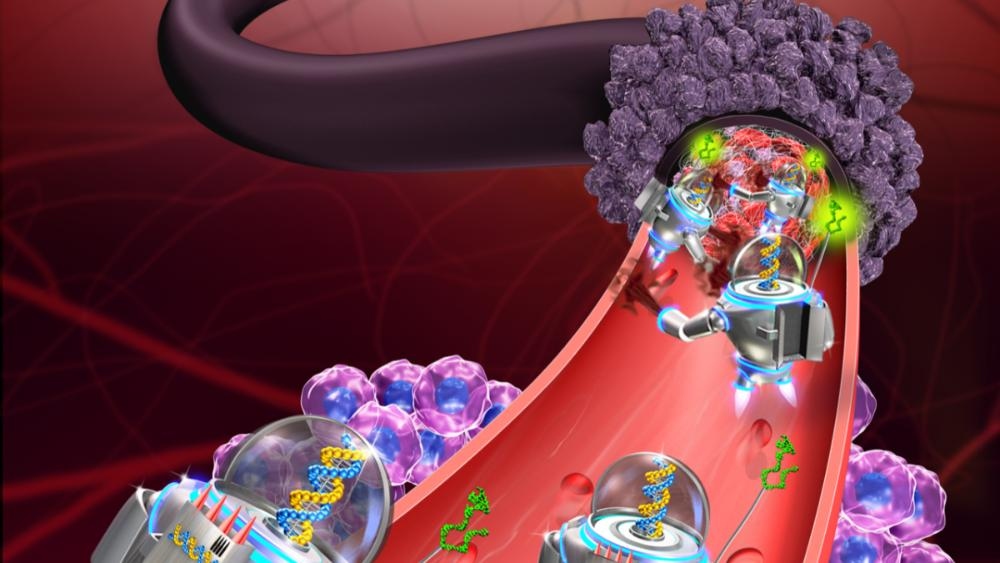
Researchers are always looking for ways to create robots or biological robots with extremely small sizes to transport special chemicals to reach diseased areas in the human body for manipulation and treatment.

However, there are many problems to solve, such as the robot's water size being too large, or being too difficult to control to achieve the desired access. In addition, the human body always reacts internally to "foreign components" entering.
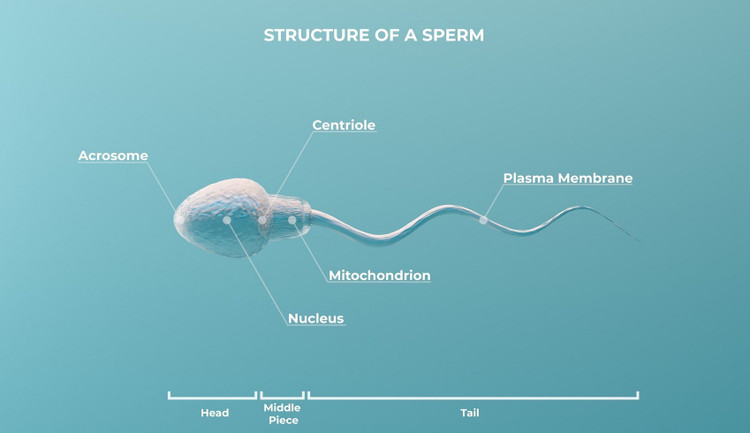
In a stunning scientific breakthrough, researchers have transformed sperm into tiny biorobots that can be remotely controlled to perform complex medical tasks. The study was published in the journal npj Robotics.
Seemingly only found in science fiction movies, these "sperm robots" have opened a new era for precision medicine, promising a future where disease treatment becomes more effective and safer than ever.
While traditional treatments such as chemotherapy, while effective in killing cancer cells, can cause serious side effects due to their effects on the entire body, the goal of modern medicine is to create “smart” delivery systems, tiny “postmen” that can move through the human body, recognize specific destinations, and deliver treatment drugs only where they are needed.
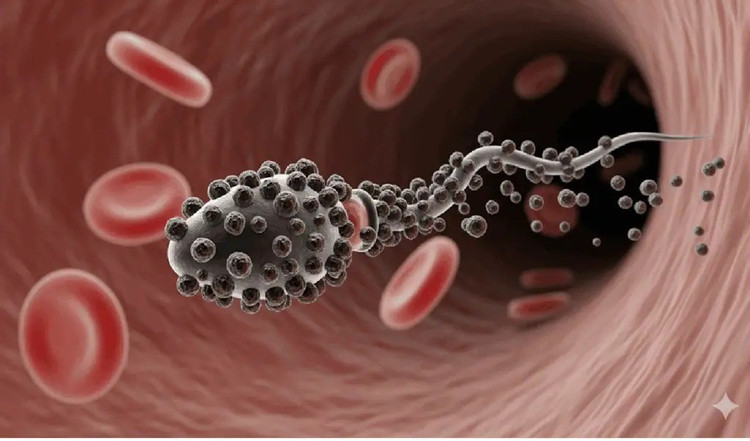
And surprisingly, sperm are the perfect candidates for this role. Sperm are natural swimmers, able to move quickly and flexibly through complex environments because they are the smallest cells in the body. This makes them ideal tiny “robots” for navigating the body’s canals and tissues.
Furthermore, because they are endogenous cells, they are whole and biocompatible. Sperm are easily found, can be degraded into nutrients for the body and, most importantly, are well tolerated by the body, minimizing the risk of immune reactions. The swimming motion of sperm has been studied and understood, facilitating their control.

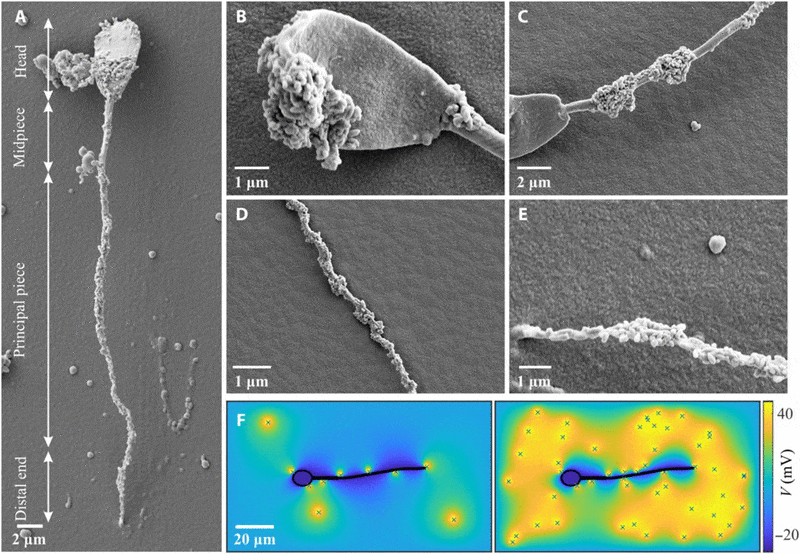
To turn sperm into controllable robots, an international research team led by Veronika Magdanz and Islam SM Khalil from the University of Twente (Netherlands) used an innovative method. They coated bull sperm cells (which have a similar structure to human sperm) with iron oxide nanoparticles.
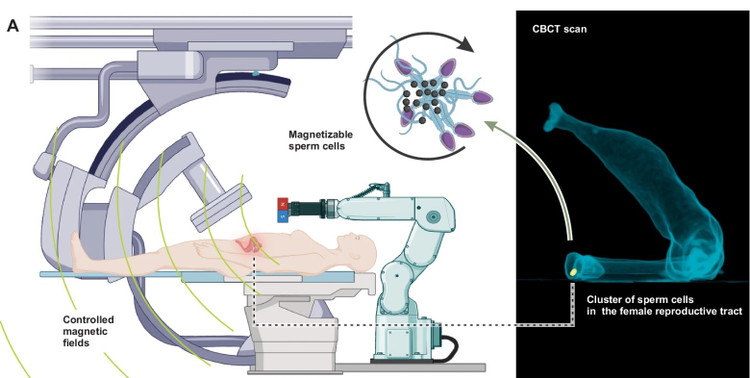
What's special is that these beads are not magnetic in themselves, but only become strongly magnetic when an external magnetic field is applied. It is this magnetic coating that allows the researchers to control the sperm with incredible precision. By applying a rotating magnetic field, they can make these "sperm robots" swim in any direction and even control their speed.
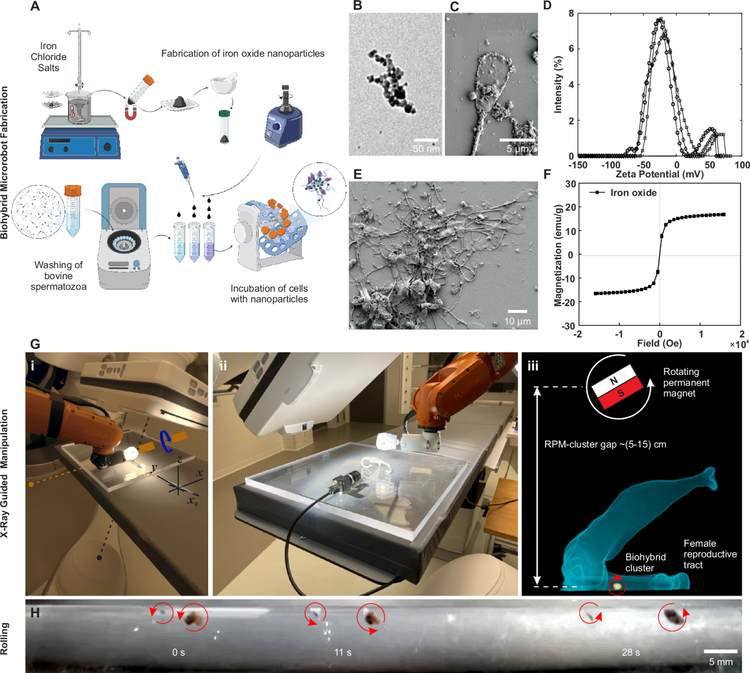
Furthermore, because the nanoparticles are visible on X-rays, scientists can track their movements in real time as they move through a 3D-printed model of the human body. Sperm robotics technology offers a wide range of potential applications. One of the most promising areas is reproductive health.
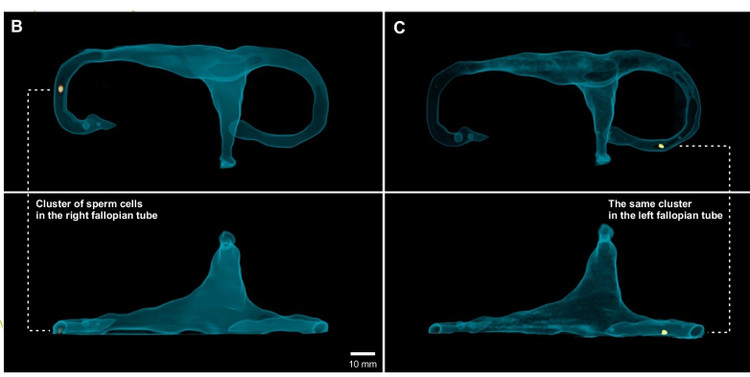
Unexplained infertility affects millions of people worldwide , and the ability to see and manipulate sperm in the female reproductive tract could revolutionize diagnosis and treatment. Doctors could use sperm robots to see what’s going on inside the fallopian tubes, identify blockages or other problems, deliver fertility-enhancing drugs directly to the egg, or even help weak sperm get there.

But that’s just the beginning. Researchers also envision a future where these tiny biorobots could be used to deliver drugs to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer. Sperm could be “loaded” with chemotherapy drugs and delivered directly to tumors, killing cancer cells without harming other healthy cells.
They could also be equipped with sensors to detect chemical markers of disease, allowing for earlier and more accurate diagnoses. While the potential is limitless, there are still many hurdles to overcome before this technology can be widely applied. First and foremost is the issue of safety. While iron oxide nanoparticles are thought to be non-toxic to human cells, their long-term effects still need to be studied.

The study is a powerful demonstration of how human ingenuity can transform something that took millions of years of evolution into a high-tech tool for the benefit of medicine. Who would have thought that a tiny sperm cell would hold the key to a new era of precision medicine? The answer seems to have been right in front of us all along.
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/robot-tinh-trung-cuoc-cach-mang-trong-y-hoc-hien-dai-post2149051661.html



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the Digital Popular Education Symposium - Digital National Assembly](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/13/43ebd93f0f5e4d98a2749dab86def7cd)


![[Photo] Hundreds of meters of Hoi An coastline seriously eroded](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/13/57c85b745a004d169dfe1ee36b6777e5)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 80th Anniversary of the People's Court's Traditional Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/13/ff42d08a51cc4673bba7c56f6a576384)
![[Photo] Vinh Hao-Phan Thiet Expressway has a frog's jaw](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/13/a89ffa426f7a46ffb810cb1d7bdfb1b8)























































































Comment (0)