India is undertaking the construction and transformation of an archaeological site in Vadnagar, Gujarat, into an experiential museum for the public.
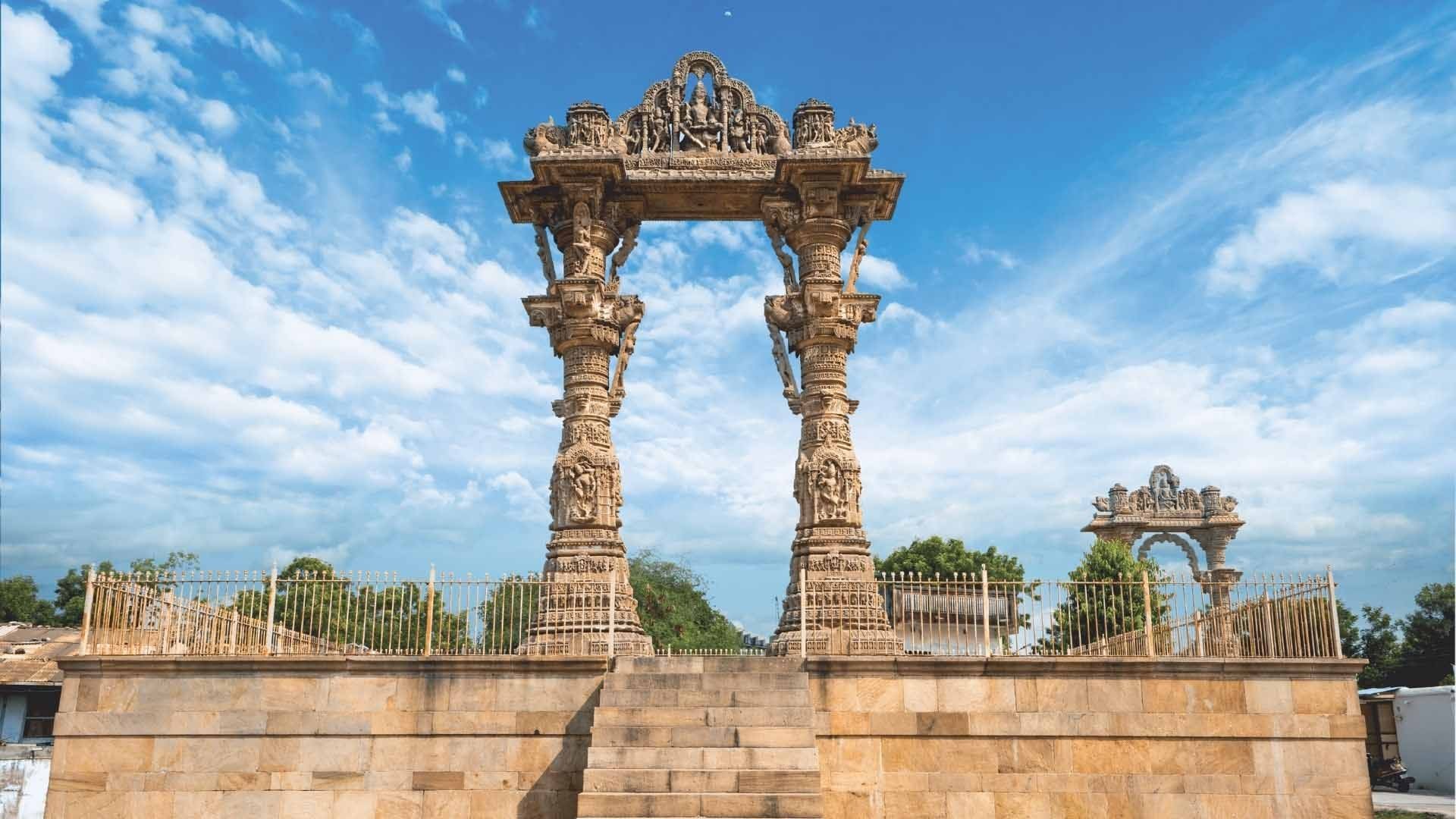 |
| A historical site in Vadnagar. (Source: Vadnagarnovarso.com) |
Located about 100 km from the capital Ahmedabad, Vadnagar in the Mehsana district of Gujarat state in western India is a historic town with a population of approximately 28,000 people.
In December 2022, officials from the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) announced that Vadnagar and the Temple of the Sun in Gujarat, along with the rock relief sculptures at Unakoti, Tripura, had been added to the UNESCO World Heritage nomination list.
Heritage City
Vadnagar is situated within the walls of an ancient fortress with six gates named Arjun Bari, Nadiol, Amarthol, Ghaskol, Pithori, and Amarthol. Of these, the area with the Amarthol gate is the oldest part of Vadnagar.
India's long history has left behind a vast number of relics that help historians understand the influence of the ancient land of the Ganges. Archaeological excavations have helped unveil the mysteries of the homeland of current Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
According to the Indian news agency PTI , the first archaeological excavation was carried out in Vadnagar in 1953-54. The Gujarat Archaeological Service conducted excavations at various sites from 2005-2006 to 2012-2013, “establishing a cultural chain spanning 2,500 years.”
In 2008, excavations uncovered “important findings about an ancient Buddhist monastery and stupas, founded around the 1st century AD and continuing until the 7th century AD.”
Ydubirsingh Rawat, head of the Gujarat State Archaeology Department, told Deshgujarat.com: “We discovered a grey stone slab. It depicts a monkey offering honey to the Buddha while he was meditating in the forest.” The slab is estimated to be around 1,900 years old.
Gujarat is home to numerous Buddhist statues and ancient artifacts. Rawat stated, “In three different excavation sites in Vadnagar, we have discovered approximately 2,000 important artifacts of diverse types and traditional art styles, with the most numerous being ancient Buddhist art.”
Having taken over excavations since 2014, ASI has discovered early defensive structures, sustainable water management solutions (connecting artificial lakes), a shell bracelet manufacturing industry, and external maritime trade links.
Members of ASI's Gujarat regional archaeological project reported the discovery of five sites dating back to the 13th or 19th centuries. In addition, the archaeological team found a metallurgical artifact, an ancient wall, several other artifacts including vases, coins, beads, seals, and a human skeleton dating back to the 16th century.
In 2016, the ASI agency began surveying and excavating structures in the area to search for traces of ancient monasteries – places mentioned in the diary of the Chinese wandering monk Xuanzang. Xuanzang visited the area in 632 AD and recorded that the city had a rich and prosperous history with many Buddhist temples.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated in June 2017 that he wished to build a large Buddha statue in the Aravalli district of Gujarat state, where Buddhist relics were discovered during excavations.
The Indian Prime Minister 's "dream" is "to build a large Buddha statue in the area, so that people from all over the world can come here and worship."
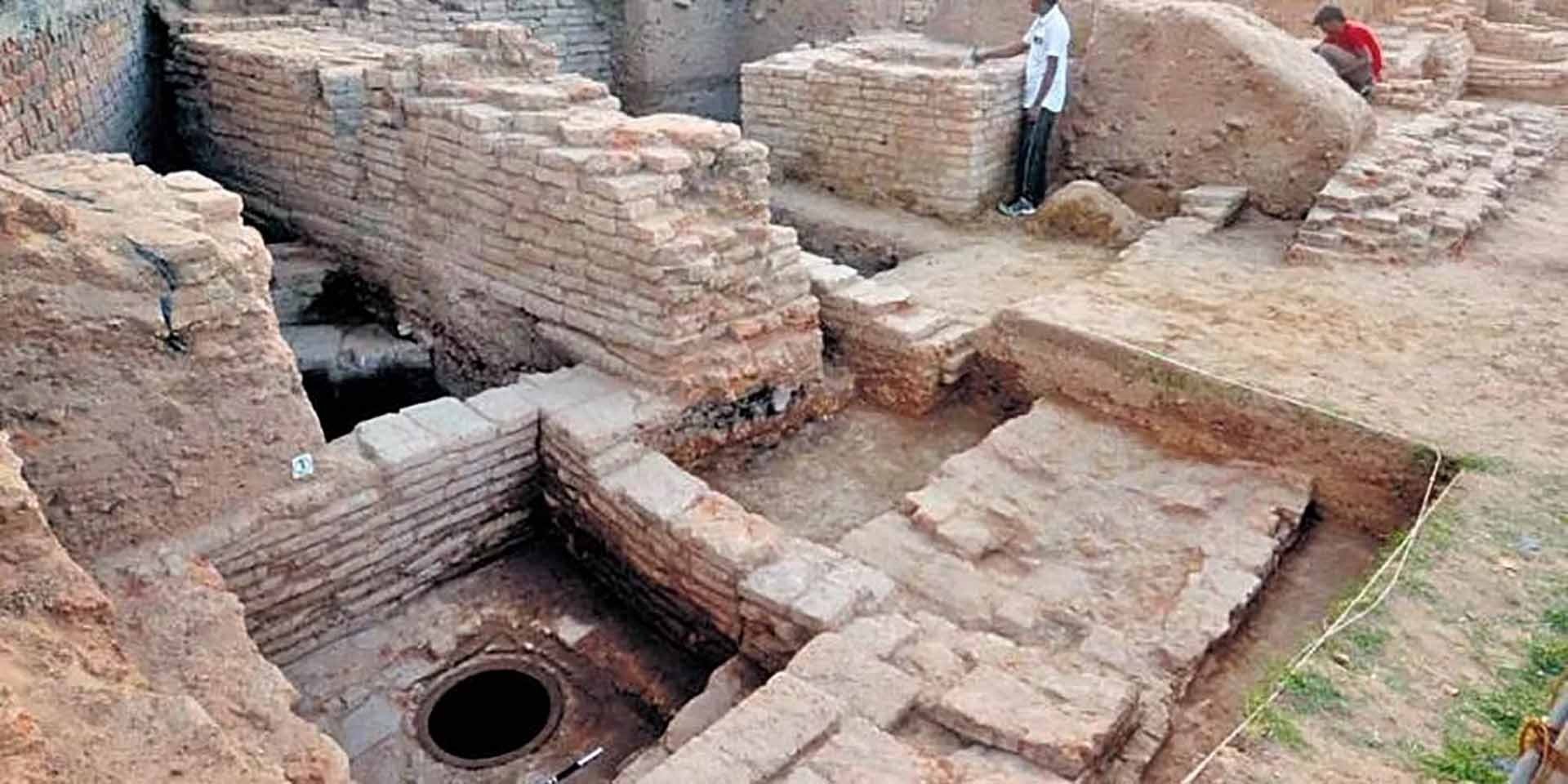 |
| Vadnagar: From historical site to museum |
Experience through time
Since November 2022, the Indian Ministry of Culture, through the Gujarat state government, decided to build a modern archaeological experience museum in Vadnagar to showcase the development of the ancient city through the lens of seven cultural periods, spanning 2,500 years. In a written response to a question in the Rajya Sabha (Indian Upper House) in December 2022, Minister G Kishan Reddy stated that the project cost for the museum is currently being established at approximately 2.121 billion Rupees (equivalent to about 25.54 million USD).
According to PTI , citing sources, based on excavations at a site near Ambaji Kotha Lake and Vihar village, the site is being transformed into India's first experiential archaeological museum, modeled after the famous Acropolis Museum in Athens (Greece).
The main museum building, constructed on an area of 13,525 m2, tells the story of the continuous human settlement history of Vadnagar, while recreating history and displaying important artifacts from antiquity with over 40,000 artifacts recovered during excavations.
According to the design plan, the future museum will feature diverse settings. The history of this land is divided into seven periods: Pre-Rampart, Rampart, Kshatrapa, Post-Kshatrapa, Solanki, Mughal Sultanate, and Gaekwad (names of ancient Indian dynasties). Each period will have its own exhibition hall.
According to the Indian Express , India's first experiential archaeological museum will be ready to welcome visitors by February 2024. Besides viewing artifacts that bear witness to Vadnagar's rich history, museum visitors will have the opportunity to experience life in the ancient city through immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), 3D displays, installations, models, and more.
Source















































































































Comment (0)