Below are common misconceptions about stroke that can cause patients to lose their chance of survival:
Stroke only occurs in the elderly
This is one of the most common and dangerous misconceptions. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says 10% of strokes occur in people under 50. The risk of stroke in young people is increasing due to a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in salt and fat, obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes, according to the US health website Healthline .
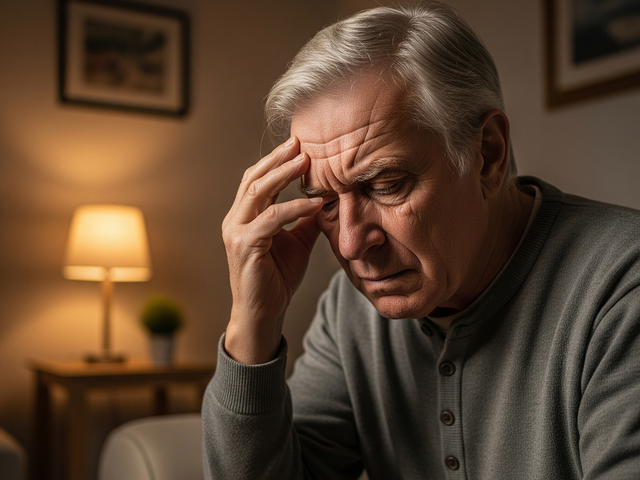
Stroke causes symptoms such as headache, numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking
PHOTO: AI
Research published in the Stroke Journal shows that the rate of stroke in people aged 18-45 has increased steadily over the past two decades. Stroke does not discriminate by age. Because they think they are young and healthy, many young people are subjective when experiencing stroke symptoms such as numbness, weakness on one side of the body, stuttering, severe headache, causing them to miss the golden time for treatment.
Subjective when seeing abnormalities
Some early symptoms of stroke can be vague or mistaken for minor problems such as low blood pressure or fatigue. As a result, people who are unwell may delay going to the hospital, waiting to see if the symptoms improve.
Therefore, when experiencing symptoms such as facial distortion on one side, difficulty speaking or stuttering, weak or unable to lift limbs, the patient needs to go to the hospital immediately. Waiting or self-treatment at home such as cupping, taking cold medicine, applying oil only causes brain damage to spread more widely. For every minute of delay in stroke treatment, nearly 2 million brain cells will die.
Do not go to the hospital if symptoms go away.
Many people experience mouth distortion, slurred speech, or numbness in their limbs for a few minutes and then it goes away on its own. This makes the patient and their family members think that everything is fine and do not go to the doctor.
In fact, it could be a sign of a transient ischemic attack, a type of mini-stroke. Statistics show that without preventative treatment, about 1/3 of people who have had a TIA will have a full-blown stroke within a few days to a few weeks. However, early intervention can reduce the risk of stroke by up to 80%, according to Healthline .
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/3-hieu-lam-ve-dot-quy-khien-nguoi-benh-mat-co-hoi-song-185250724190709264.htm



































































































Comment (0)