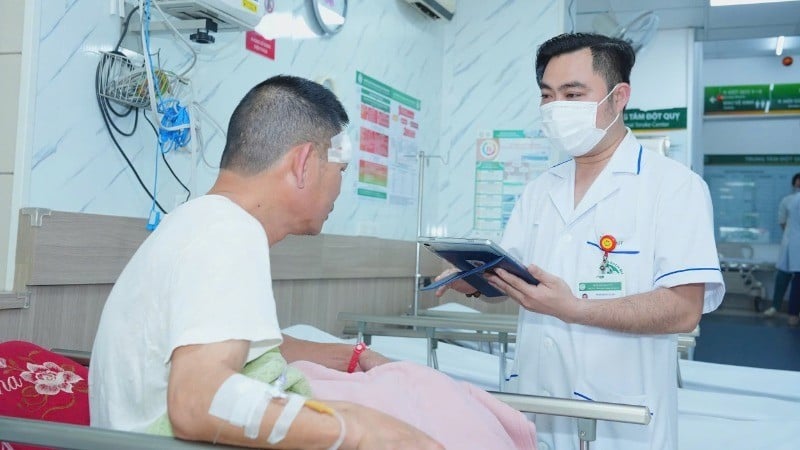
Electronic medical records are one of the important pillars in the digital transformation roadmap of the healthcare sector, contributing to improving the quality of medical examination and treatment; optimizing the management, storage and sharing of medical information; ensuring the accuracy, connectivity and confidentiality of people's health data.
According to records from a number of hospitals that have implemented electronic medical records, it has brought practical results for hospitals, patients and health insurance funds. In addition to shortening the time to handle administrative procedures, it also saves billions of dong, even up to hundreds of billions of dong (for each hospital) for purchasing films to print diagnostic imaging results, stationery, ink, etc.
In particular, electronic medical records help to ensure transparency in all compliance with professional regulations (diagnosis, prescription, test indications, throughout the admission and treatment process). Electronic medical records will become a large data warehouse for research and evaluation of disease models; a basis for units to serve the planning of procurement and bidding for drugs, medical supplies, etc.
However, according to statistics from the Ministry of Health , as of July 18, only 270 hospitals nationwide have announced the implementation of electronic medical records, a very small number compared to the total of about 1,400 hospitals nationwide.
Meanwhile, Directive No. 07 dated March 14, 2025 on promoting the implementation of the project to develop applications of population data, identification and electronic authentication to serve national digital transformation in the period of 2022-2025, with a vision to 2030 in ministries, branches and localities in 2025 and the following years, the Prime Minister assigned the Ministry of Health to direct hospitals to complete the implementation of electronic medical records before September 30, 2025. Thus, there are only more than two months left to complete the goal, so the implementation of electronic medical records cannot be delayed any longer.
The main reason for the delay is that many medical facilities still face difficulties in funding, technological infrastructure, human resources, and lack of coordination between sectors and levels.
At the recent workshop on solutions for implementing electronic medical records, there were still hundreds of questions and concerns for the organizers to answer and clarify, focusing on the following issues: Funding sources for units to develop electronic medical records; procedures for renting software; when will the Ministry of Health publish a list of popular software; electronic signatures, digital signatures for patients and their families; regulations on standards for shared and consumed equipment to purchase software; infrastructure and information security; digital signatures on VNeID...
Director of the National Center for Health Information (Ministry of Health) Do Truong Duy said that, in order to contribute to accelerating the implementation of electronic medical records nationwide, after working with enterprises providing solutions for implementing electronic medical records to remove obstacles for medical facilities and enterprises, the center agreed to report to the Ministry of Health with the following recommendations: The Ministry of Health reports and advises the Prime Minister to issue a decision directing localities to deploy electronic medical records so that localities have a basis to allocate funds to medical facilities for implementation.
In addition, the Ministry of Health also issued a document requesting the secretaries of provincial and municipal Party Committees to issue resolutions on the implementation of electronic medical records to mobilize the participation of the entire political system in implementation.
Notably, Circular No. 13/2025/TT-BYT guiding the implementation of electronic medical records, effective from July 21, 2025, has provided specific guidance on the principles of management and implementation of electronic medical records. Accordingly, electronic medical records are medical records specified in Clause 17, Article 2 of the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment 2023, which are established, updated, displayed, signed, stored, managed, used and exploited by electronic means. Medical records are a collection of data, including personal information, medical examination results, paraclinical results, functional examination results, diagnosis, treatment, care and other relevant information during the treatment process of patients at medical examination and treatment facilities. Connecting information of electronic medical records with personal identification numbers of Vietnamese citizens and foreigners who have been granted electronic identification accounts in accordance with the law on identification.
Regarding the regulations on electronic signature and confirmation in electronic medical records, the Ministry of Health also provides forms to require medical staff, patients or patient representatives to electronically sign or confirm related content. Hopefully, these newly regulated contents will remove obstacles to accelerate the implementation of electronic medical records.
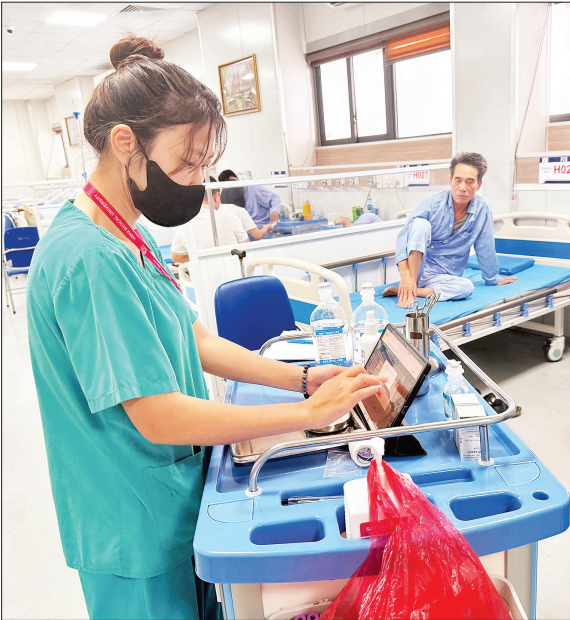

Immediately after Circular No. 13/2025/TT-BYT was issued, the National Center for Health Information also issued a document providing technical guidance on the implementation of electronic medical records. In addition, in the coming time, the center will continue to issue technical guidance on the implementation of the PACS System.
Proposing financial solutions for hospitals when implementing electronic medical records, Mr. Pham Ngoc Duc, Director of Project 06 implementation of Mobifone global (Ministry of Public Security) said that units can rent data storage or rent infrastructure. When implementing, hospitals can completely "give questions" about their needs so that software providers can choose the appropriate solution. Currently, the cost of implementing electronic medical records has many different levels, some up to billions of VND, but if you do not research carefully, you can buy expensive ones without using all the features, causing waste; but if you buy cheap ones, they may not meet the hospital's requirements.
According to Mr. Hoang Van Tien, Deputy Head of the Department of Solutions and Quality Management, National Center for Health Information, one of the major barriers is investment in information technology infrastructure, software and security solutions. Currently, the bidding process for purchasing information technology equipment at medical units is still complicated, time-consuming, directly affecting the implementation progress. Another reason comes from the people, especially the elderly in remote areas, who are not familiar with using digital utilities such as chip-embedded citizen identification cards for lookup and cashless payment, making the implementation difficult...
Although there are still many problems, the timeline is clear. We expect that, with close direction from the Government and synchronous participation from localities, the implementation of electronic medical records will be completed by September 30.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/can-quyet-liet-de-hoan-thanh-benh-an-dien-tu-dung-tien-do-post895617.html



































































![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of Morocco-Vietnam Friendship Association](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/26/b5fb486562044db9a5e95efb6dc6a263)

































Comment (0)