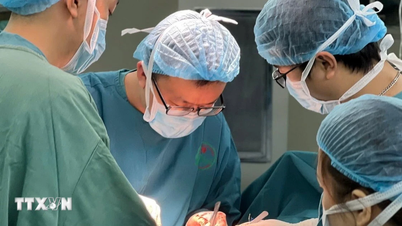
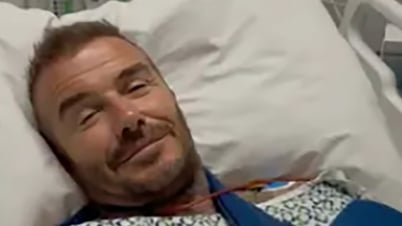
Recently, Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital (HCMUMPH) admitted and treated a patient named NVH (68 years old, residing in HCMC). Mr. H. was admitted to the hospital with severe pain in his left leg, and could only walk 10-20 meters before his calf ached badly, with ulcers on the tips of his toes that did not heal. At the Emergency Department, after performing tests and assessments, the doctor determined that Mr. H. had a narrowed artery in his limbs. The patient then underwent dilation and stent placement to re-open the blood vessels. After the intervention, the symptoms immediately subsided, and the patient could walk more than 100 meters easily. After that, the patient continued to be monitored and cared for his ulcers in the Thoracic - Vascular Department.
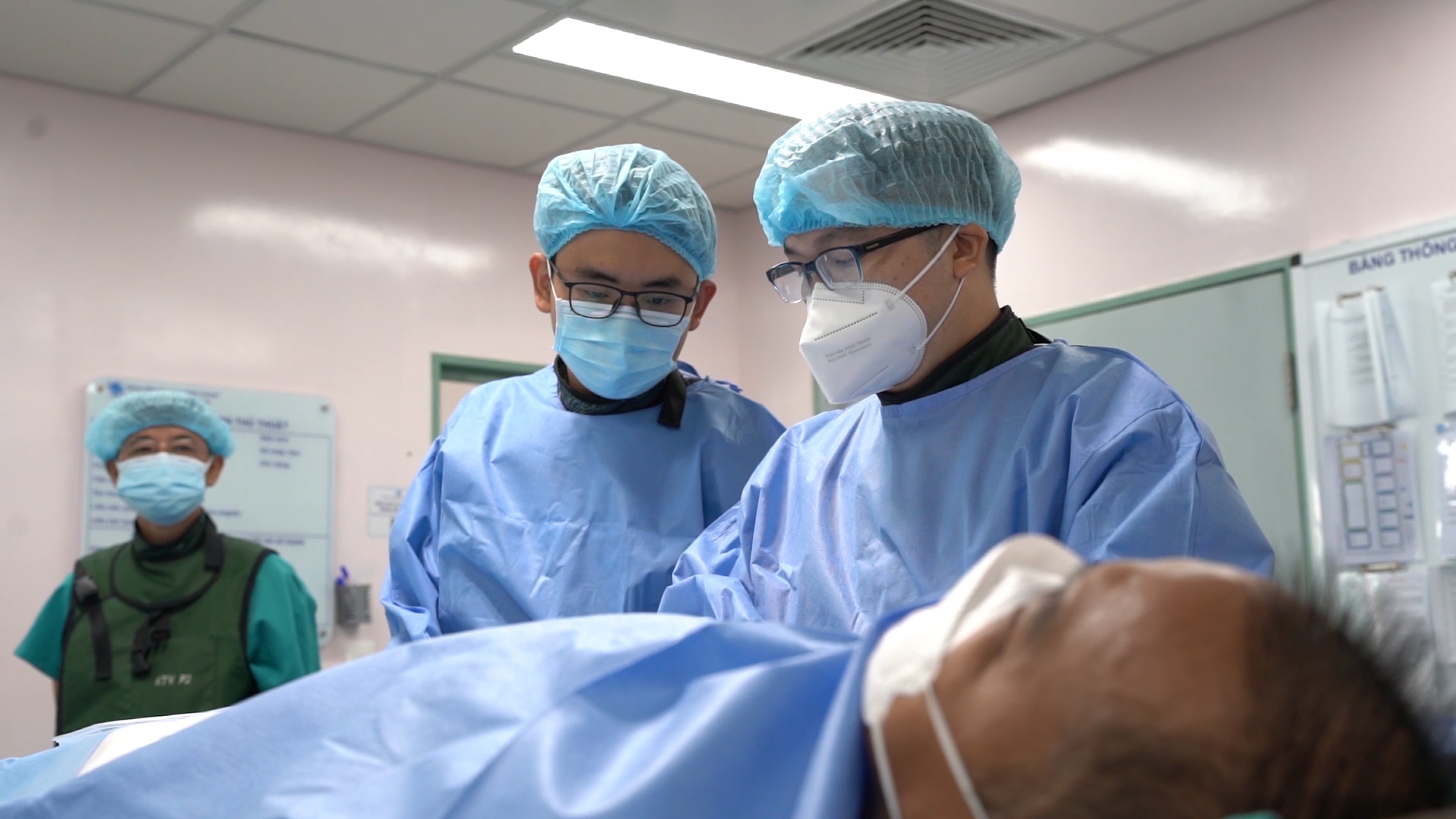
Doctor intervenes to treat the patient
Advances in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial stenosis
Dr. Tran Thanh Vy - Head of the Thoracic - Vascular Department, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that more than 75% of cases of limb artery stenosis have no symptoms at the onset of the disease. If not detected and treated early, the disease will have a very poor prognosis, specifically, about 25% of patients with limb artery stenosis will die and the remaining 30 - 40% will have to have their limbs amputated.
The development of science and technology in the medical field has provided patients with many methods to diagnose limb arterial stenosis such as: Measuring arterial pressure in the extremities and calculating the ankle and arm systolic blood pressure index (ABI), ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Among them, diagnosis through the brachial-ankle index with a sensitivity of 79 - 95% and a specificity of 96 - 100% is considered the most commonly performed method. People without vascular stenosis often have equal blood pressure at all locations or insignificant differences. Therefore, if the brachial-ankle blood pressure index is less than or greater than 1, it is considered an abnormal result, with a risk of limb arterial disease.
However, patients should note that there is no common diagnostic method for everyone. Depending on each patient, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate diagnostic method. For example, with the CT scan method, the patient must use intravenous contrast agents during the scan. Therefore, not everyone has a compatible physical condition to perform this diagnostic method.
Advances in the treatment of peripheral arterial stenosis
With the development of science and technology in the medical field, treatment methods for limb artery stenosis are constantly being improved to provide patients with minimally invasive solutions but still achieving the highest efficiency.
Dr. Nguyen Duc Chinh - Department of Interventional Cardiology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City shared that there are 4 basic methods of treating limb artery stenosis that can be performed separately or combined depending on the patient's health condition, including: physical therapy, drug treatment, arterial bypass surgery and endovascular intervention. In which, using antiplatelet drugs is one of the main methods of treating limb artery stenosis.
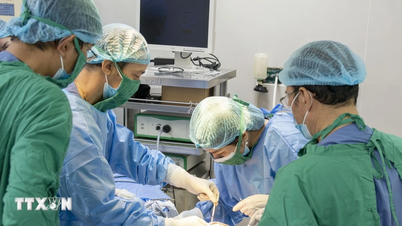
Classical methods such as arterial bypass surgery have also made great advances in technology and implementation. To improve the phenomenon of arterial stenosis, the doctor will take a graft of another healthy blood vessel in the body to create an oxygen-rich bridge across the narrowed artery. In addition to autologous blood vessels, artificial blood vessels are also being studied today to be grafted with similar features. Some blood vessels are also placed with drugs on top to make an effective bridge.
Advances in endovascular intervention surgery over the past 20 years have been made possible by tools that make the procedure easier, including stents, balloon angioplasty, and small guidewires. These tools can help doctors treat narrowed or blocked areas. For severe calcifications, the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City has also applied the technique of removing atherosclerotic plaques inside the blood vessels, combined with stent or balloon placement to help clear the blood vessels. This allows the limbs to receive adequate blood supply, maintaining the patient's limbs intact.
In order to help patients understand and feel more secure in the diagnosis and treatment of limb artery stenosis, the Communication Center of University Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, in collaboration with Bayer Vietnam Company Limited, implemented the "Cardiovascular Bridge" consultation program with the topic: "Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of limb artery stenosis", follow at: https://bit.ly/tienbodieutritachepdongmachchi

Source link































































































Comment (0)