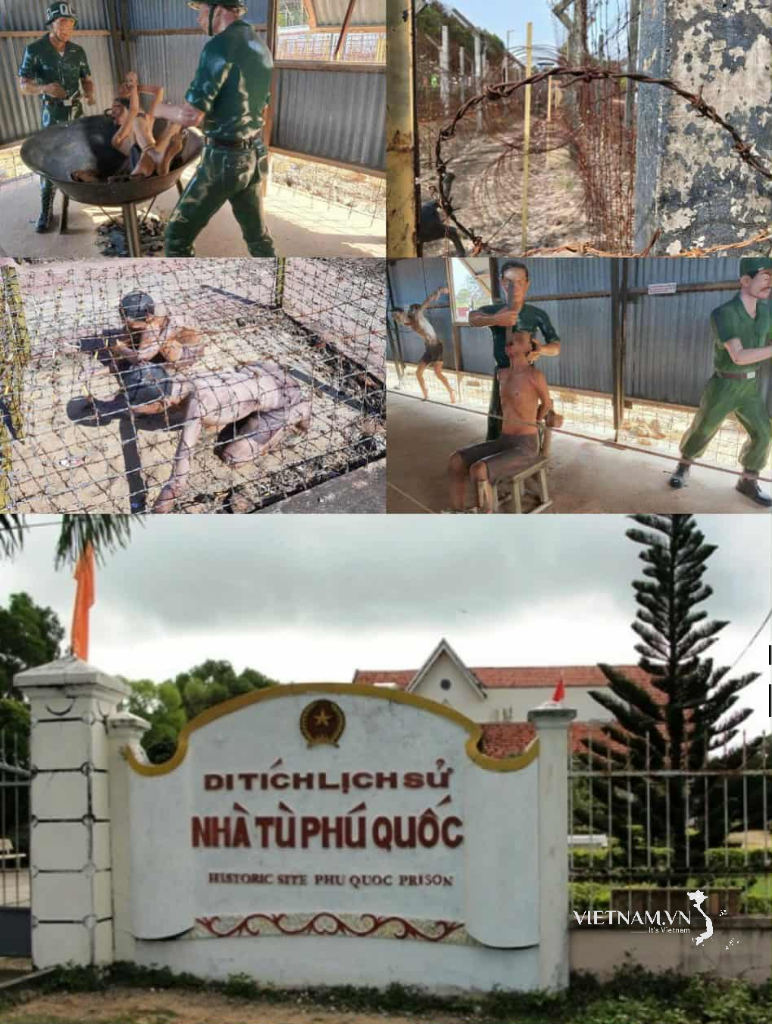
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) was adopted by the UN General Assembly on December 10, 1948 with the main contents including: affirming that all people are born free, equal, without discrimination, affirming human rights such as the right to life, the right to a fair trial, not being tortured, not being enslaved and other rights in the civil, political , economic, social and cultural fields.
Although not an international legal document, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights is the foundation for building international human rights law, including the Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the Covenant on Economic , Social and Cultural Rights; as well as being included in human rights documents of regional mechanisms and in the laws of countries. December 10 later became International Human Rights Day.
This is one of the most important documents of the 20th century, adopted by all countries and has become the foundation for countries, including Vietnam, to use in the process of building documents related to the protection of human rights.
The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action (VDPA) was adopted by the UN member states in 1993, at the international conference on human rights held in Vienna. The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action reaffirmed the values of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and clarified that the protection and promotion of human rights must be the highest priority of each country and the international community; emphasizing that while taking into account the particularities of each country and society, human rights must be recognized as universal values, and must be assessed in each balanced and interdependent relationship.
The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action also affirmed the role of the United Nations in promoting human rights worldwide and initiated the establishment of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights.
Source







![[Photo] Closing of the 13th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/08/1759893763535_ndo_br_a3-bnd-2504-jpg.webp)























































































Comment (0)