Integrating digital skills and artificial intelligence into each course not only prepares students for their future careers but also creates a generation of technology-savvy citizens ready for the knowledge economy .
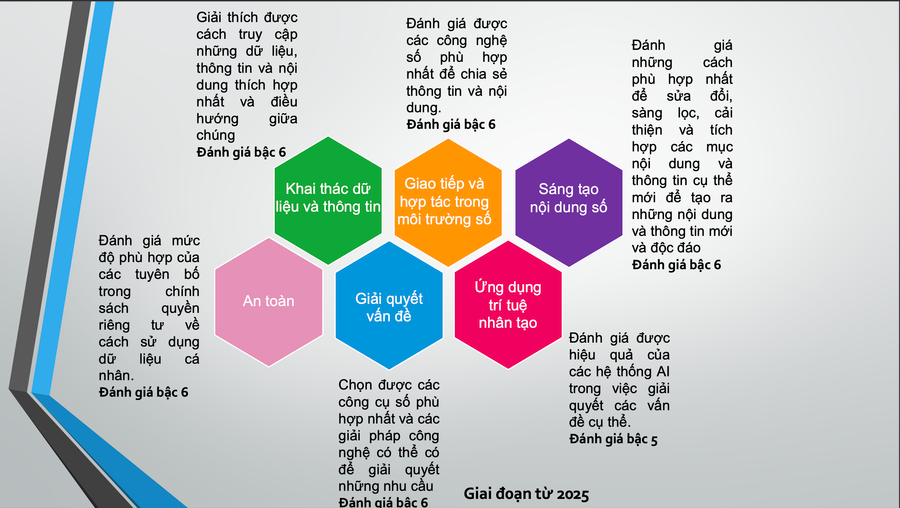
Six domains of competence
Not only domestic universities, but also international educational institutions consider digital competence a top priority. RMIT University Vietnam has a clear strategy in the context of the increasingly widespread presence of AI. Students are equipped with both digital and human skills, mastering technological tools for learning, creating, and collaborating. RMIT emphasizes the role of "empowering" learners, encouraging them to confidently use and critically analyze AI. The university is committed to applying AI in an ethical, transparent, and prudent manner.
In early 2025, the Ministry of Education and Training issued Circular No. 02/2025/TT-BGDĐT (Circular 02/2025) stipulating the Digital Competency Framework for Learners, marking a significant turning point in standardizing and developing digital competencies in the national education system.
This circular applies broadly to educational institutions, training programs, and learners throughout the entire national education system, and is also directed towards relevant organizations and individuals.
The digital competency framework is not only a tool for building curriculum standards and developing learning materials, but also a basis for evaluating learning outcomes, testing, and recognizing learners' digital competencies. The issuance of this framework helps ensure consistency in training requirements and facilitates comparison between educational programs domestically and internationally.
According to Circular 02/2025, the digital competency framework is designed with 6 competency domains and 24 component competencies, divided into 4 levels from basic to advanced in 8 tiers. The competency domains include: Data and information exploitation; Communication and collaboration in the digital environment; Digital content creation; Security in the digital environment; Problem solving; and Artificial intelligence (AI) application.
Each competency domain is described in detail, from data search and management skills; effective communication through digital channels; content creation; personal data protection; to critical thinking and the ethical and responsible application of AI. In this context, higher education plays a pioneering role in building digital competencies for students – the future workforce of the country.
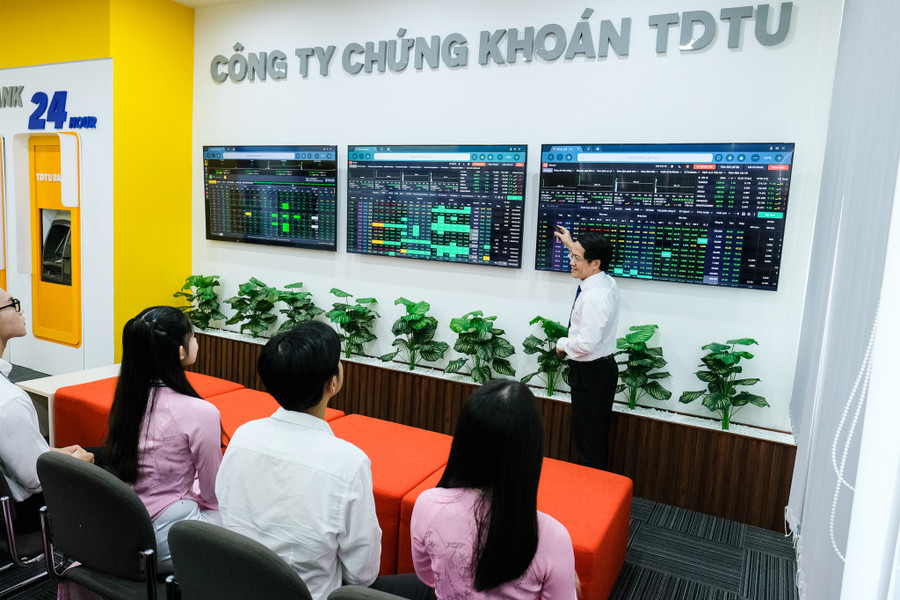

Proactive implementation
In fact, even before Circular 02/2025 was issued, many universities had proactively implemented digital transformation programs, integrating technology into teaching and learning.
One of the leading institutions is the University of Social Sciences and Humanities (Vietnam National University, Hanoi). Since 2020, the university has collaborated with Meta Group to implement a project to enhance digital skills for students. The result is a digital competency framework specifically for students, announced in May 2024. Since 2023, the university has continued its collaboration with Meta in a project to train AI skills for faculty and students. More than 250 lecturers and staff members and 1,000 students have received comprehensive training in AI, contributing to the formation of a unique AI competency framework for students.
At the workshop on the Digital Competency Framework for Learners (Ho Chi Minh City, July 2025), Assoc. Prof. Dr. Do Van Hung, Head of the Faculty of Information and Library Science, emphasized a humanistic approach to digital competency, guided by the philosophy: "Technology for people - People mastering technology." The university has established new learning outcomes, reformed its training programs, and deeply integrated digital technology into each course. Liberal education and social responsibility are also incorporated to promote the holistic development of learners.
Specialized modules such as Digital Citizenship, Information Skills, Digital Ethics, and AI are systematically designed; along with workshops and intensive courses to enhance digital capabilities for faculty and students. The university's digital competency framework aims to develop long-term adaptive competencies: Flexibility, growth thinking, personal autonomy, creative problem-solving, communication and collaboration, and project management. These competencies develop along a four-level pathway: Proficiency, Expertise, Specialization, and Mastery.
Another example is Ho Chi Minh City Open University, which developed a roadmap for implementing digital capabilities quite early on, across four phases: Before 2013, 2013-2019, 2020-2025, and from 2025 onwards. According to Dr. Le Xuan Truong, Vice Rector, since 2020, the university has implemented a blended learning model for full-time students, creating a foundation for digitalization in education.
Ho Chi Minh City Open University utilizes a Learning Management System (LMS) to provide a rich resource library: video lectures, e-books, and in-depth materials. Students can access knowledge while actively checking their progress, participating in discussions on forums, and developing their communication and collaboration skills.
Interactive activities such as homework feedback and professional exchanges on the LMS are synchronized with in-person learning, creating a flexible and engaging learning environment. Since the end of 2022, when ChatGPT became popular, Ho Chi Minh City Open University quickly updated its program, guiding students to use AI to search for and develop ideas and solve problems. Lecturers also emphasized the skill of comparing and verifying information from AI with academic sources, fostering critical thinking and ensuring reliability.
Integrate digital skills into each course module.
The issuance of Circular 02/2025 not only requires the standardization of digital competencies but also creates an impetus for universities to proactively innovate their curricula. Many universities have quickly adapted, integrating digital competencies into individual subjects and modules, instead of confining them to basic information technology courses.
Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HUTECH) is building a modern educational ecosystem with three pillars: AI, digital transformation, and sustainable development. According to Professor Nguyen Trung Kien, Vice Rector, the integrated training program incorporates digital and AI competencies throughout each course, based on five core elements: Project Design Thinking, Sustainable Development, Applied AI, Technology, and Professional Experience.
Thu Dau Mot University (Ho Chi Minh City) has been working with senior experts since March 2025 to implement technological solutions to meet the requirements of Circular 02/2025. The university aims to apply AI and Blockchain in governance and training, focusing on student data management, document digitization, and developing AI tools to support teaching, academic advising, and admissions… in order to improve management efficiency and training quality in the digital age.
Dong Nai University also considers digital competency as a pillar of educational innovation. The university applies the digital competency framework in designing learning outcomes, developing curricula, and compiling materials. Digital competency content is directly integrated into many courses, especially in Informatics, Information Technology, research methods, and soft skills.
This also serves as an assessment tool – from defining requirements and measuring results to testing and certifying student competence. Simultaneously, the school is promoting the application of digital technology and AI in teaching, from LMS (Learning Management System) and classroom management software to automated assessment systems. AI will support many aspects: teaching, testing, assessment, and career counseling.
Notably, Ho Chi Minh City Open University continues to be a pioneer in updating its curriculum in accordance with Decision 1504/QD-BGDĐT on the popularization of digital knowledge and skills for students. The Informatics program for non-IT majors has been adjusted: Consolidating and enhancing IT knowledge blocks, helping students achieve digital competency levels 5-6 according to national standards.
Specifically, the program includes content on AI applications - competency domain 6. Students are equipped with fundamental knowledge of AI and Generative AI, learn how to use AI tools responsibly and ethically, and develop skills in selecting appropriate tools.
At Thu Dau Mot University, experts have outlined a framework for digital transformation in higher education with three pillars: governance, teaching and learning, and research and innovation. In this framework, digital transformation in governance is not just about digitizing processes, but about comprehensive restructuring.
The school integrates LMS, AI, and Big Data to optimize operations and manage students, faculty, and programs. Blended learning has become the dominant trend, helping faculty shift from traditional methods to a personalized approach, enabling students to learn anytime, anywhere, and develop self-learning skills and independent thinking.
Source: https://giaoducthoidai.vn/nang-luc-so-tro-thanh-xuong-song-cua-dao-tao-dai-hoc-post748238.html



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the Conference on the Implementation of Tasks for 2026 of the Industry and Trade Sector](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F19%2F1766159500458_ndo_br_shared31-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)














































































































Comment (0)