GĐXH - The patient was diagnosed with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction accompanied by multiple underlying conditions including: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
According to information from Hung Vuong General Hospital, doctors there recently successfully treated a 75-year-old female patient who was admitted with severe chest pain. The patient was diagnosed with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction accompanied by several underlying conditions including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
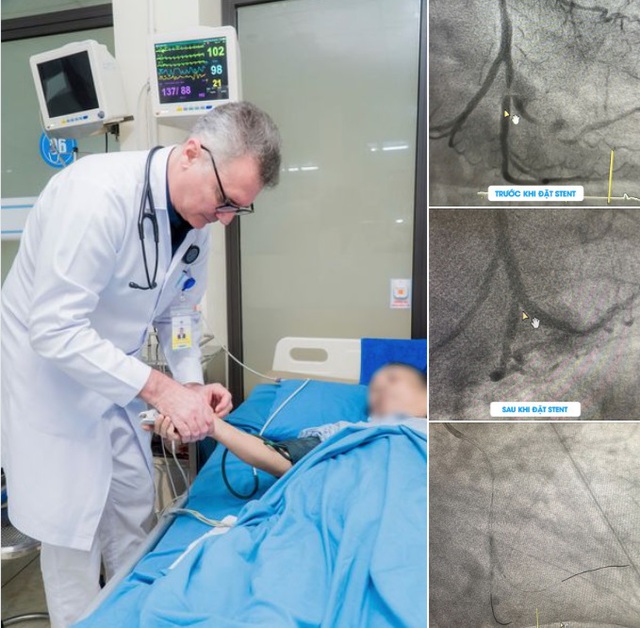
Following the intervention, the chest pain symptoms subsided, and vital signs stabilized. (Photo: Provided by the hospital)
After hospitalization, the patient underwent percutaneous coronary angiography to determine the extent of blockages and atherosclerosis. The results showed that the patient had damage to all three coronary arteries to varying degrees:
- Left main coronary artery (LM): Stenosis 30%.
- Interventricular artery (LAD): Narrowing of 40-50% in the proximal segment, 40% in the mid- and distal segments, with significant calcification.
- Circumflex artery (LCx): 60% stenosis in the proximal segment and severe stenosis up to 99% in the distal segment at the bifurcation point, with significant calcification.
- Posterior artery (PDA): 60% stenosis.
After careful consultation and consideration of the patient's underlying medical conditions, Dr. Peter and his colleagues decided to perform angioplasty and stenting in the proximal LCx artery (LCx(d)), where the stenosis was severe and dangerous. This procedure restored blood flow to the ischemic myocardial region, preventing the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction.
The stent placement procedure went smoothly with excellent recanalization results. The medical team worked diligently and carefully to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the intervention.
Following the intervention, the patient's condition improved significantly. Chest pain symptoms subsided, and vital signs stabilized. The patient has now been transferred back to the Cardiology department for continued monitoring and treatment, as well as adjustment of cardiovascular risk factors such as blood pressure, blood glucose, and blood lipid levels.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/nguoi-phu-nu-o-phu-tho-bi-nhoi-mau-co-tim-cap-co-tien-su-mac-4-benh-ly-nay-172241104101923976.htm


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)




















































Comment (0)