According to Dr. Bui Thi Kim Oanh - Department of Hepatobiliary Medicine, National Children's Hospital, jaundice is a common condition in children, especially in the newborn stage.
Jaundice in infants is caused by high levels of bilirubin in the blood. There are two types of bilirubin: free (indirect) bilirubin and direct bilirubin.
Accordingly, physiological jaundice often occurs 7-10 days after birth, accounting for about 60% of full-term babies and 80% of premature babies.
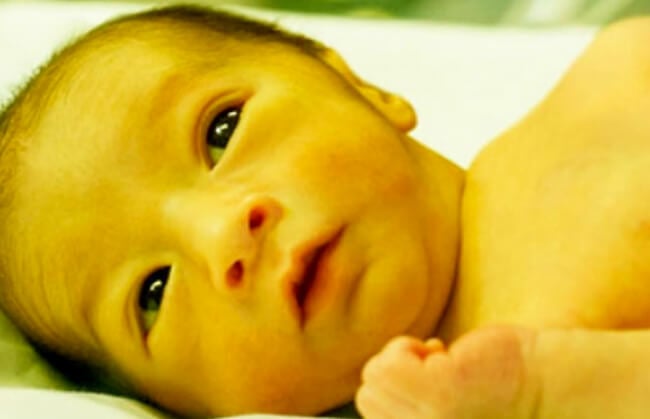

Parents need to take their newborns to medical facilities for examination at an early stage if they have jaundice (photo TL).
Usually occurs in the first few days after birth, due to the destruction of red blood cells leading to increased free (indirect) bilirubin. Free bilirubin easily dissolves in fatty tissue, penetrates the brain, causing kernicterus in the first week after birth.
Cases of jaundice with increased free bilirubin lasting more than 15 days are considered abnormal and need to be monitored and evaluated by specialists.
“Jaundice due to increased direct bilirubin is also known as cholestatic jaundice. Cholestatic jaundice does not cause jaundice but is a symptom found in many hepatobiliary diseases such as congenital biliary atresia, hepatitis, and genetic metabolic disorders,” emphasized Dr. Bui Thi Kim Oanh.
Symptoms and ways to detect jaundice, jaundice is most easily seen in natural light, the sclera of the baby is often the place where symptoms can be detected most easily.
Physiological jaundice in infants usually has bright yellow skin that only appears within 1 week to 10 days after birth, is mild and gradually decreases over time.
Cholestatic jaundice can appear early in the first 1-2 weeks after birth or a few months after birth with symptoms of dull yellow skin, accompanied by a number of symptoms such as pale stools, dark urine, poor appetite, refusal to breastfeed, slow weight gain, etc.
To detect jaundice in a baby, parents can use their fingers to gently press on the baby's forehead, nose, or breastbone. If the skin appears yellow where the pressure was applied, the baby likely has mild jaundice. If the baby does not have jaundice, the skin color at the pressure point may only be lighter than the normal skin color at that time.
According to Dr. Bui Thi Kim Oanh, newborns have jaundice early in the first 1-2 days after birth or signs of jaundice, yellow eyes increase rapidly, jaundice spreads to the abdomen, hands and feet, the child is lethargic and difficult to wake up or has increased muscle tone, the child does not gain weight or suckles poorly, the child cries for no reason and any signs that make parents feel insecure or worried, they need to take the child to see a doctor.
In addition to the newborn stage, if the baby has jaundice accompanied by pale yellow or pale stools, dark yellow urine, abdominal distension, bruising or the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash on the skin, itchy skin, slow weight gain, and malnutrition, these are symptoms suggesting jaundice that may be related to liver and biliary disease.
Doctor Bui Thi Kim Oanh said that the cause of jaundice is due to blood type incompatibility, hemolysis diseases due to abnormal red blood cell shape, abnormal hemoglobin, deficiency of enzymes on the red blood cell membrane, and some genetic diseases...
Children with congenital biliary atresia, choledochal cysts, and other systemic diseases. Congenital biliary atresia is a disease that needs to be detected early for timely surgery. If left too late, the patient will no longer be able to undergo surgery, and the disease will progress to cirrhosis, which can be life-threatening.
Causes in the liver due to hepatitis caused by viruses A, B, C, D, E, Cytomegalovirus, Epstein Barr virus, toxoplasma, rubella, ...; caused by bacteria: syphilis, ricketsia, sepsis, urinary tract infection. Causes of metabolic disorders, genetic and hereditary causes, chromosomal abnormalities, autoimmune, long-term intravenous nutrition, poisoning, ...
When a child shows signs of prolonged jaundice, blood will be drawn for testing according to each diagnostic step, determining the total bilirubin level, quantifying direct and indirect bilirubin and checking basic liver functions, thereby orienting to find the cause of the disease.
In addition, the child will have blood drawn for liver function tests and other tests to find the cause of the disease and predict the severity of the disease.
Children may also have ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to look for biliary tract abnormalities and liver parenchyma damage, if any.
When children have symptoms of prolonged jaundice, they should be taken to a medical facility immediately.
Source




![[Photo] Closing of the 13th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/08/1759893763535_ndo_br_a3-bnd-2504-jpg.webp)























































































Comment (0)