Fermented foods are rich in beneficial probiotics and have many health benefits, especially good for the gut.
Fermented foods are products that have undergone a natural fermentation process, which involves the use of microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast or mold to transform the food. During this process, the microorganisms break down sugars and other organic compounds in the food, resulting in changes in flavor, texture and possibly increased nutritional content.
1. What are fermented foods?
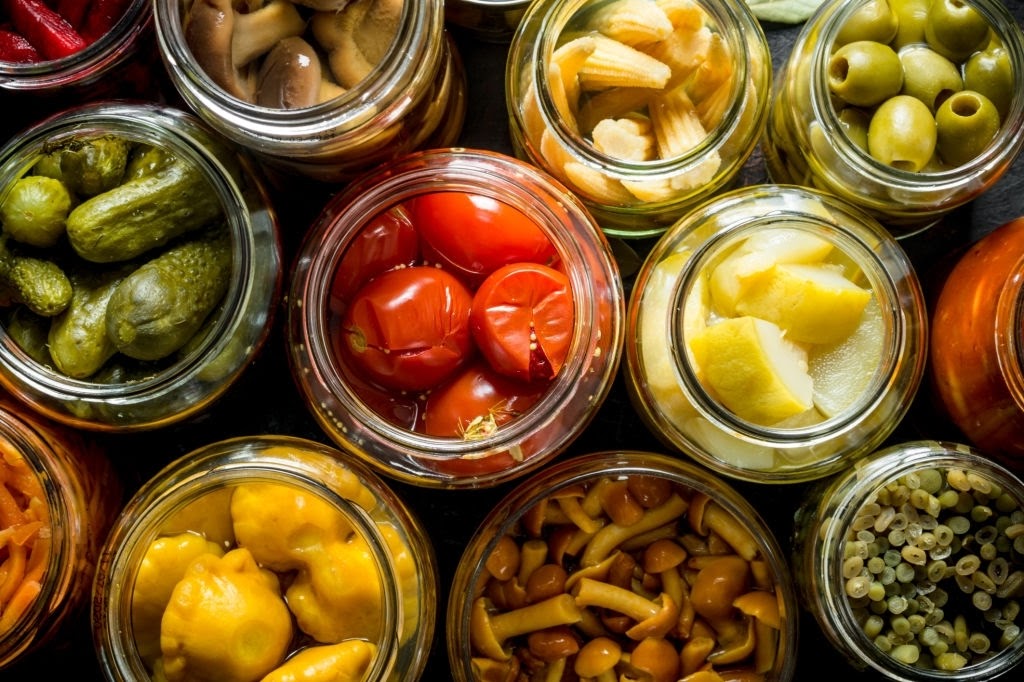

Fermented foods can promote better digestion and gut health.
Fermentation is a traditional method of food preservation and has been used by many different cultures for centuries. Fermented foods can promote better digestion and gut health by introducing beneficial bacteria into the body. When consumed, these probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut. This is important for proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Since different fermented foods contain different strains of probiotics, each with their own benefits, consuming a variety of fermented foods can be an effective way to reap the full range of digestive health benefits.
Fermented foods add delicious flavor to meals and are a great addition to a healthy diet, especially for the gut.
2. Some fermented foods help improve gut health
Tempeh
Tempeh is a high-protein meat substitute. It is made from fermented soybeans that are pressed into cakes. During fermentation, phytic acid (which reduces mineral absorption) is broken down. This improves digestion and absorption of food.
Tempeh is also high in prebiotics. Prebiotics are a type of fiber that promotes the growth of probiotics. Studies have shown that prebiotic supplementation can improve stool frequency and reduce inflammation in the gut.
Natto
In Japanese cuisine , natto is a staple probiotic food. It is known for its rich flavor, soft texture, and like tempeh, it is made from fermented soybeans.
Natto contains significantly more probiotics per serving than other probiotic-rich foods, ranging from one million to one billion colony-forming bacteria per gram.
In fact, research has shown that natto can act as the gut’s first line of defense against toxins and harmful bacteria. These benefits may help reduce bloating, constipation, and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Natto also contains a healthy amount of fiber (about 5.4 g per 100 g serving), which is known to support digestive health and prevent constipation.
Kefir
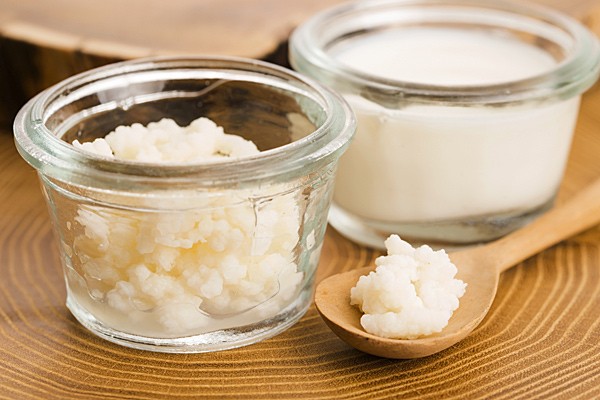

Kefir has many health benefits, including improving digestion and fighting inflammation for good gut health.
Kefir is a cultured dairy product made by mixing kefir grains (a combination of yeast and bacteria) and milk together. This results in a thick, tangy drink that many people say tastes similar to yogurt.
Research has shown that kefir has many health benefits, including digestive and anti-inflammatory benefits. Kefir grains contain up to 61 different strains of bacteria and yeast, making them a rich and diverse source of probiotics.
Kombucha
Kombucha is a fizzy, slightly acidic beverage made by fermenting symbiotic cultures of bacteria and yeast, sometimes referred to as “mushroom tea”. The large amount of healthy bacteria that grows in the mixture makes kombucha a good source of probiotics. It contains probiotics and organic acids that can improve digestion and overall gut health.
Kombucha comes in a variety of flavors and is a healthier alternative to soft drinks. Regular consumption can help reduce bloating, promote regular bowel movements, and improve the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Miso
Miso is a popular seasoning used in Japanese cuisine. It is made by fermenting soybeans with salt and koji (a type of fungus). Miso is most commonly used to make miso soup.
Miso is packed with probiotics, which research shows can improve digestion and reduce bloating, constipation, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea or gas. Oryzae is the main probiotic strain found in miso and has been shown to reduce symptoms associated with digestive issues like inflammatory bowel disease.
Kimchi
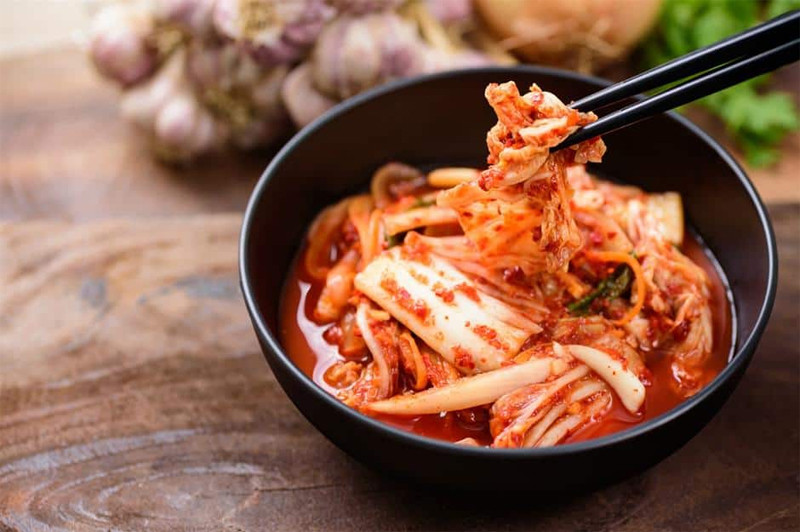

Kimchi has been linked to improved digestive health.
Kimchi is a Korean dish consisting of fermented vegetables such as cabbage, radish, Chinese cabbage... often combined with salt, sugar, onions, garlic and chili for flavor.
Kimchi is made through a process called lacto-fermentation, which uses lactobacillus bacteria to break down sugars into lactic acid, aiding digestion and improving nutrient absorption. Lactobacillus has been shown to help treat certain types of diarrhea, and eating kimchi has been linked to improved digestive health.
Cabbage
Sauerkraut is fermented cabbage. During fermentation, the beneficial bacteria in it produce probiotics that aid in digestion. This process also increases the amount of vitamins and minerals in the cabbage. Sauerkraut can be used as a condiment or side dish.
Yogurt
Yogurt is made from milk that has been fermented, most commonly with lactic acid bacteria. It contains many important nutrients such as potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin B12.
The probiotic bacteria in yogurt help improve digestion. Some Greek yogurts also contain probiotics like lactobacillus, which are known to increase healthy bacteria in the gut.
Regular consumption of yogurt can enhance nutrient absorption and help maintain a balanced gut microbiome. However, not all yogurts contain probiotics, as these healthy bacteria are often killed during processing. Therefore, it is best to look for yogurts that contain live cultures. For added health benefits, you can also choose products with minimal added sugar.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/8-thuc-pham-len-men-giup-lam-sach-va-thai-doc-duong-ruot-172241227221601574.htm




















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)












































Comment (0)