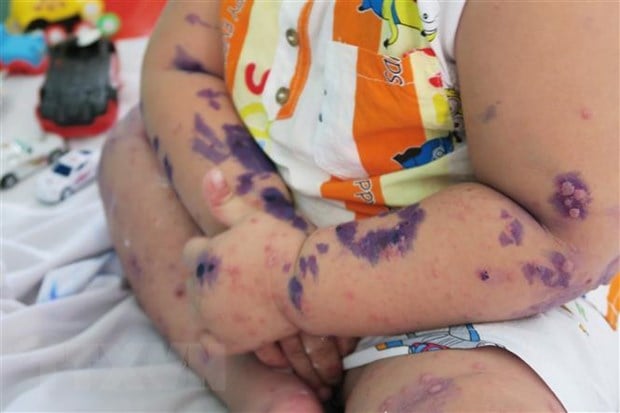
Hand, foot and mouth disease is characterized by blisters around the mouth, hands and feet.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an acute viral infection, the main route of transmission is through the digestive tract, transmitted directly through direct contact with saliva, nasal secretions or broken blisters of an infected person.
In both adults and children, the cause of the disease is intestinal viruses, including Coxsackie, Echo and other intestinal viruses, of which the most common are intestinal virus type 71 (EV71) and Coxsackie A16.
EV71 virus can cause severe complications and death.
The disease usually occurs in children, especially children under 5 years old. However, adults can also get it if their immune system is not strong enough to fight the virus that causes the disease.
Thus, adults who are directly caring for sick children without taking preventive measures, or adults with weak immune systems who are exposed to environments containing disease-causing viruses, will be easily penetrated by the viruses, causing them to become sick.
The signs of the disease in adults are similar to those in children; however, symptoms in adults are often difficult to recognize and easily overlooked, combined with the subjective mentality that "adults do not get hand, foot and mouth disease" will lead to the disease in adults not being detected and treated promptly, leaving serious consequences in some patients.
In addition, adults who care for or come into contact with sick people can carry the virus. If they do not take proper precautions, they can also carry the disease and become a source of infection for children and family members.
Recognizing hand, foot and mouth disease in adults
Hand, foot and mouth disease in adults has the same symptoms as in children. In the early days, the symptoms are often not too obvious and can be easily confused with other common diseases.
Incubation period in adults is 3-6 days; initially the patient may have a mild fever and sore throat, which can be easily confused with other diseases.
Vesicular rash:
+ On the body of the infected person, there will be small blisters, appearing in the mouth, hands, arms, feet, knees, thighs, buttocks, groin area...
+ Blisters in the mouth can easily be confused with canker sores, leading to delayed treatment and making the disease worse.
Mouth ulcers are red ulcers or blister-like lesions, about 2-3mm in diameter, on the oral mucosa, cheeks, gums, tongue, when broken, they will form ulcers in the mouth and cause pain.
However, in some cases, people with hand, foot and mouth disease do not have blisters, but instead only have a red rash, so it is easily confused with other diseases.
In adults, there may be additional signs: cough, fever, runny nose, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle aches, loss of appetite...
Complications of hand, foot and mouth disease in adults
Most adults with the disease will recover after more than 1 week and some adults with weak body resistance, the disease will progress more severely, such as lesions appearing on the skin and mucous membranes; blisters burst to form ulcers, easily infected with pus.
Hand, foot and mouth disease in adults, if not properly cared for and treated, can lead to dangerous complications such as neurological complications (encephalitis, meningitis, encephalomyelitis...), cardiovascular complications (myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema, heart failure, cardiovascular collapse...).
These complications can be life-threatening, so it is necessary to see a doctor early for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease in adults
There is no specific treatment for hand, foot and mouth disease. Signs and symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease usually clear up within 7-10 days.
When treating at home, note:
- Reduce fever, relieve mouth and throat pain: you can take Paracetamol when your fever is over 38 degrees Celsius.
- Reduce itching (if necessary): Unlike children, hand, foot and mouth disease in adults often causes more itching, so you can use topical creams or anti-allergy medications when the patient is very itchy.
- Care for blisters, rashes, ulcers: disinfect ulcers to limit ulceration and ulcer infection; use antiseptic solutions such as 1% Methylene blue, oral gel.
- Do not use antibiotics or any other medication without a doctor's prescription because antibiotics are not effective for this viral infection.
-Bathe daily with warm water, avoid scrubbing or rubbing the blisters to prevent them from breaking; you can dilute antiseptic solutions in the water for bathing.
Use methylene blue or betadine solution to dab on blisters after bathing. Choose clothes made of soft, loose-fitting, sweat-absorbent fabric.
- Nutrition: have a nutritious diet, avoid eating sour, salty or spicy foods, avoid foods that require a lot of chewing to help prevent mouth ulcers from being damaged.
Eat soft foods for a few days and drink plenty of fluids. Drink cool drinks and rinse your mouth with water after each meal.
Measures to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease
There is no vaccine for hand, foot and mouth disease, so measures still focus on detecting, treating properly and preventing infection.
Adults need to take the initiative to prevent infection when caring for sick children. They need to strictly follow infection prevention measures for themselves and not become a source of infection for others.
Wash your hands often with soap and water or hand sanitizer, especially after touching blisters or sores after caring for a sick person.
Regularly clean surfaces and tools that come into daily contact with disinfectant solutions containing chlorine such as: school supplies, doorknobs, stair handrails, table tops, chairs, floors, etc.
Eat cooked food and drink boiled water, do not share eating utensils with sick people; avoid close contact (hugging, kissing) with family members to limit the spread of disease.
Last week, 20 southern provinces and cities recorded more than 2,000 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, an increase of 23% compared to the previous week.
Currently, statistics are based on the number of severe cases hospitalized, while the number of mild cases that have not been counted could be much higher.
According to reports from the provinces of Binh Duong , Dong Nai, Long An..., the rate of cases per 100,000 people is currently higher than last year and compared to the average of the past 5 years. These are also the provinces with a high rate of severe cases.
Dong Thap has recorded more than 900 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, of which 68% are cases under 3 years old, and there has just been 1 death.
Dong Nai also had 1,694 cases, down 56.37% compared to the same period in 2022 (3,883 cases), with no deaths recorded. However, the number of cases has tended to increase since the beginning of March, especially since May, with 200-300 hospitalizations per week.
In particular, the classification of hand, foot and mouth disease has not been clearly reported, 81% of cases in Ho Chi Minh City have not been clinically classified, affecting clinical assessment and determining disease trends.
Seven patients have died, mostly 5-year-old children, and the cause of death in 5/7 cases was determined to be the Entero 71 (EV17) virus. This is a virus that often causes hand, foot and mouth disease in children and has many risks of dangerous complications, so schools and playgrounds with a large concentration of children are identified as places with a high risk of spreading the disease.
Medical experts also say that 50% of adults have the disease but have no symptoms, this is an important source of infection, but because there are no symptoms, it is very easy to spread to children.
Many other cases also have the disease but the symptoms are not clear. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to early diagnosis and early hospitalization to prevent complications and death.
Noting that the hand, foot and mouth disease situation has increased rapidly since the beginning of May and there have been many cases of severe complications, the Ministry of Health has actively implemented epidemic prevention measures and recommended that provinces urgently issue plans to prevent infectious diseases in 2023, ensuring 4 on-site and proactive implementation.
Along with that, we need to strengthen monitoring and supervision of the epidemic situation, early detection and timely handling of outbreaks.
Medical facilities must organize treatment and medical examination and treatment teams; higher levels must strengthen training, closely monitor, and implement cross-infection prevention in medical facilities.
Early detection of epidemics, communication in the community and at schools to prevent epidemics.
Vietnam currently has no vaccine to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease, so the Ministry of Health recommends that provinces ensure equipment, chemical supplies and treatment drugs to be ready to respond to the epidemic./.
According to VNA
Source link





























































![[Infographic] Circular guiding the functions, tasks and powers of the provincial Department of Culture, Sports and Tourism and the commune-level Department of Culture and Social Affairs](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/29/877f24989bb946358f33a80e4a4f4ef5)






























Comment (0)