To move smoothly and safely, drivers need to pay attention to the instructions of the traffic sign system. So how effective are traffic signs on the road?
What is a traffic sign?
Clause 1, Article 10 of the 2008 Road Traffic Law only stipulates that the road signaling system includes traffic controllers' commands; traffic lights, signs, road markings, markers or protective walls, and barriers.
Thus, traffic signs are part of the road signaling system, these are signs that contain information related to vehicles participating in traffic. Complying with the instructions of traffic signs installed on the road will help drivers move safely and avoid being fined for traffic violations.
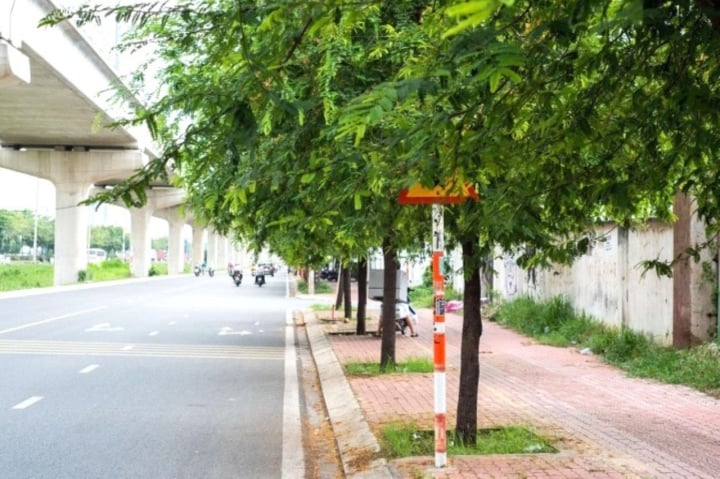

The sign is obscured as a "puzzle" for traffic participants.
According to QCVN 41:2019/BGTVT, current traffic signs are divided into the following 5 basic groups:
1. Prohibition signs: A group of signs indicating prohibitions that traffic participants must not violate.
2. Command signs: A group of signs used to indicate commands that must be obeyed. Road users must obey the commands on the signs (except for some special signs) or they will be fined.
3. Danger and warning signs: A group of signs that inform road users of dangers on the road in advance so they can proactively prevent them in time.
4. Signage: A group of signs used to provide information and necessary instructions to traffic participants.
5. Supplementary signs, signs written in words: Group of signs intended to supplement the content of prohibition signs, command signs, danger and warning signs, guidance signs or used independently.
Regulations on the validity of traffic signs
According to Clause 1, Article 11 of the 2008 Road Traffic Law, traffic participants are obliged to comply with the commands and instructions of the road signal system.
In which, the order of effectiveness of traffic signs in the signaling system is determined according to Article 4 of QCVN 41:2019/BGTVT: "If a road section simultaneously arranges different types of signaling forms with different meanings, traffic participants must comply with the following order: Commands of traffic controllers. Commands of traffic lights. Commands of traffic signs. Commands of road markings and other signs on the road surface".
In case there are both permanent signs and temporary signs with different meanings, obey the command of the temporary sign.
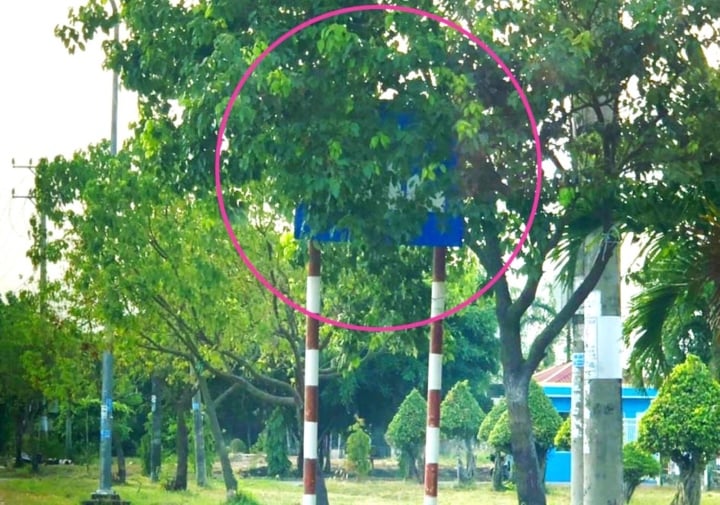

The sign "hiding" behind the tree canopy causes difficulties for traffic participants.
Is an obstructed sign valid?
The Road Traffic Law in Article 37.2 only stipulates in general that "The People's Committees of provinces and cities are responsible for posting signs" but lacks regulations on supervision, coordination and sanctions for violations by units assigned to post signs.
In addition, according to Clause 1, Article 59 of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations 2012, the person with the authority to impose penalties must verify other circumstances that affect the decision to impose penalties. The fact that the sign has unclear parameters, is obscured, or is installed in an unreasonable location is an “other circumstance” that is important for the consideration and decision to impose penalties.
However, Article 59 only stipulates that "in necessary cases, the competent person to impose penalties is responsible for verifying the details...", so it is not a mandatory provision that the competent person to impose administrative penalties is obliged to prove the violation of the violator because if it is deemed "unnecessary", the competent person to impose penalties will not be required to verify even if the person whose record is made disagrees with the error recorded in the record.
Thus, when encountering a case of being ticketed for traffic violations due to improper or obscured traffic signs, traffic participants should request to take photos, describe the current state of the sign, and write their disagreement in the ticket.
Traffic participants who are ticketed and fined have the right to file a complaint with the competent authority or sue the traffic police for administrative acts (wrong ticketing) or wrong administrative decisions (unfounded decisions) to a competent court for resolution.
CHAU THU
Source




































































































Comment (0)