Heat stroke is caused by overheating of the body, usually due to prolonged exposure or exertion in a hot environment. During hot weather, you can prevent heat stroke by drinking enough water and avoiding going outdoors when the temperature is too high.
Heat stroke (or sunstroke) is a serious heat illness. Normally, the thermoregulatory center keeps the body's temperature at a balanced level, not changing much according to the impact of the environment. When exposed to prolonged heat, exertion causes the thermoregulatory center to be damaged or can no longer control that balance, the body's temperature will increase sharply, causing disorders in the body's functions, especially the nervous system, which can lead to coma and death.
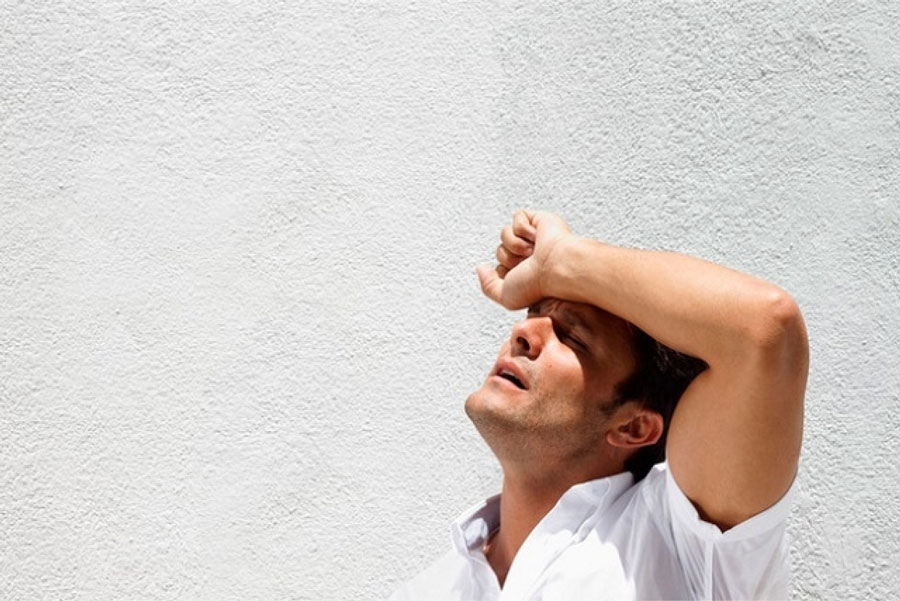

People at high risk of heat stroke include:
Elderly people, children, women: Are people with poor tolerance
People with chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, liver disease, cancer,...
Outdoor workers such as workers, farmers, athletes , soldiers training on the field, delivery staff,...
The patients all have in common the characteristic of working long hours in hot conditions, without rest and adequate water and electrolyte replenishment.
The most common complications in patients with late emergency heatstroke are seizures, rhabdomyolysis, renal failure, prolonged coma, irreversible damage to nerves and other organs, and even death.
Symptoms of heat stroke and how to treat it
Heat stroke can have a sudden or gradual onset. Some symptoms of heat stroke include:
Excessive sweating, muscle pain, muscle weakness, cramps, dizziness, headache, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness or fainting.
High fever above 39 - 40 degrees Celsius
Dry, hot skin.
Disorders of consciousness such as delirium, convulsions, coma. This is a dangerous condition that can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment on the spot and then emergency care.
How to treat a patient with signs of heat stroke by cooling the body quickly and providing supportive care through the following steps:
Quickly move the victim out of the hot area and into a cool place.
Lay the victim down and remove some of their clothing. Cover the entire body with cold water or a wet towel, and use a fan to cool the person down. You can spray water on the person, use a fan, or put the person in ice water.
Give water immediately if conscious and not vomiting heavily. At the same time, immediately call an ambulance and transfer the patient to the nearest medical facility.
On the way, turn on the air conditioning or the ambulance windows, continue to apply wet towels and cold water to the body to cool down. Administer intravenous fluids if possible and always monitor the patient's body temperature.
If the patient has kidney damage, he or she may need continuous dialysis. Intensive care depends on the patient's condition.
Prevention of heat stroke
If you have to go out in the sun, the strong sunlight on your skin will cause your body temperature to rise. In this case, the most effective preventive measures will include drinking enough fluids and avoiding excessive heat.
Wear sun protection clothing: Sun protection clothing is often designed with materials that can both block UV rays and reduce heat absorption, making it ideal for protecting your health from harsh sunlight, especially on summer days.
Wear a hat when going out in the sun: Not only does it protect your head, but your neck also needs to be protected from the heat of the sun because this is an extremely sensitive part of the skin.
Cover the nape of the neck (back of the neck): The body's thermoregulatory center is located in the nape of the neck. Direct sunlight on the nape of the neck can paralyze the center and cause loss of body temperature control. Therefore, it is very necessary to cover the nape of the neck by wearing a wide-brimmed hat, a shirt with a high collar, or using a large scarf that can be wrapped around the back to cover the nape of the neck when going out in hot weather.
For workers: To prevent heat stroke, workers need to wear sunscreen and protective glasses when working outdoors.
Maintain body moisture: Drink enough water, avoid dehydration and salt when working or going out in hot weather. The body often loses a lot of water and electrolytes due to heat in summer. Keep some salt, sugar and water nearby and replenish them whenever you feel tired and exhausted. This will help maintain water and electrolyte balance throughout the day.
Apply sunscreen: Sun exposure can lead to sunburn and pigmentation. Use sunscreen to protect your skin from sun damage. Be sure to choose a sunscreen with the appropriate SPF and PA.
Wear sunglasses: Exposure to bright sunlight, containing UV rays during the summer can damage the eyes, causing many eye diseases such as: conjunctivitis, keratitis, dry eyes,... Wearing sunglasses when going out will help protect the eyes.
Increase physical exercise: Physical exercise not only makes the body more flexible and energetic, but also helps increase the ability to adapt to harsh weather.
According to vov.vn
Source link


































































































Comment (0)