 |
Qualcomm refreshes the computer chip race, but doesn't replace x86. |
Qualcomm has had nearly two years to deliver on its promise of a Windows PC future for Arm chips. But it’s still a new option on the market. In addition to providing new options for users, Snapdragon processors also spur x86 chip makers to innovate.
Recently, Asus introduced two Vivobook S models at the same time with similar prices and designs. The only difference is the chip. This model has become the most effective reference to compare the application level of Qualcomm processors compared to AMD.
Arm Chips Redefine the Game
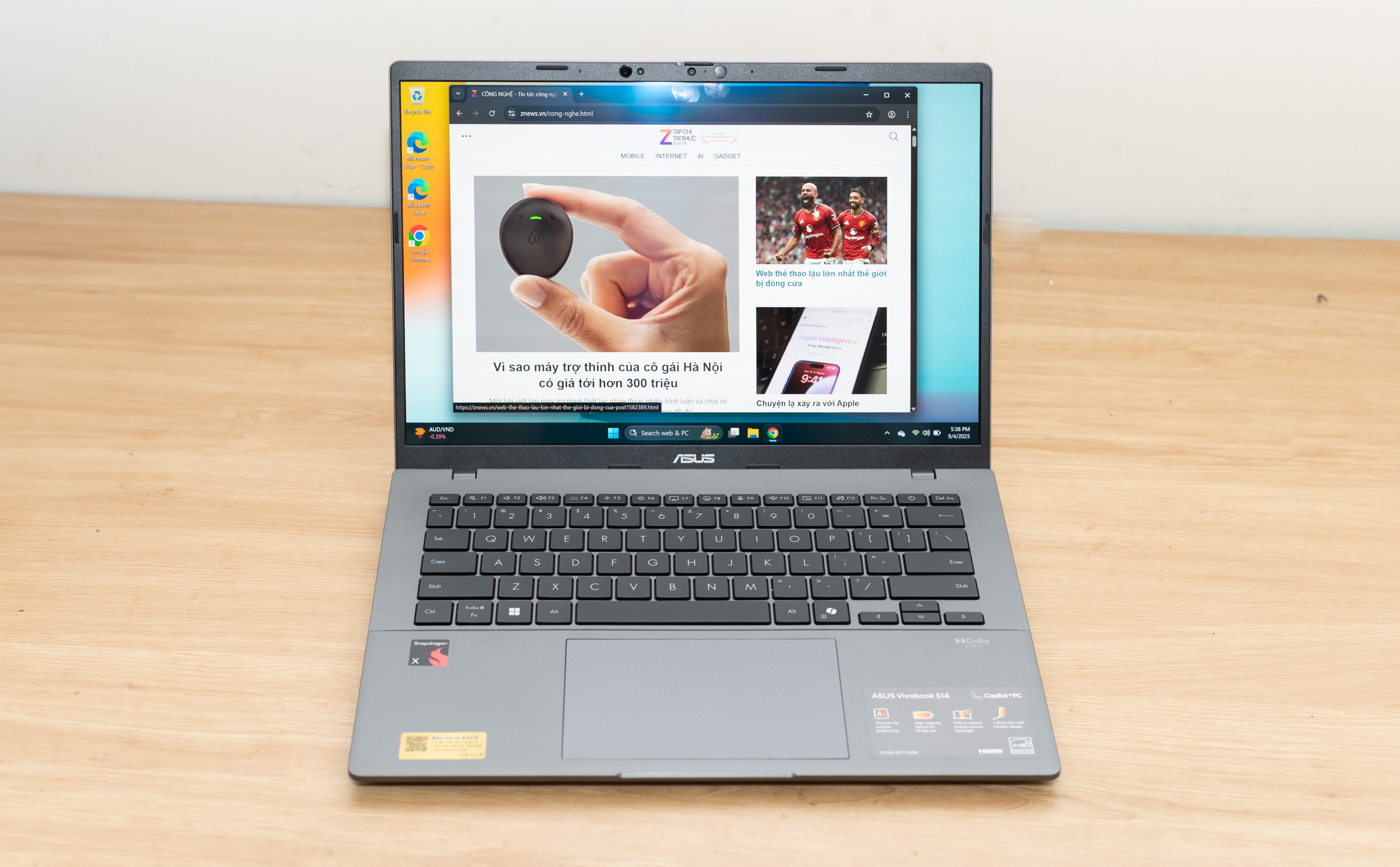
The Vivobook S14 (S3407QA) uses the Snapdragon X processor, the lowest version in Qualcomm's chip range. However, it still provides all the advantages of the Arm platform for Windows computers. The difference appears right from the first task, turning on the machine.
Intel and AMD always have problems when waking up from sleep mode. The Vivobook S14 with Qualcomm chip has a smartphone-like experience, always ready when the user needs it. With just a press of a button, the product immediately enters work mode. The product has a fan, but is almost completely silent in most cases. This is the standard for modern offices, where quiet is a priority, avoiding affecting colleagues.
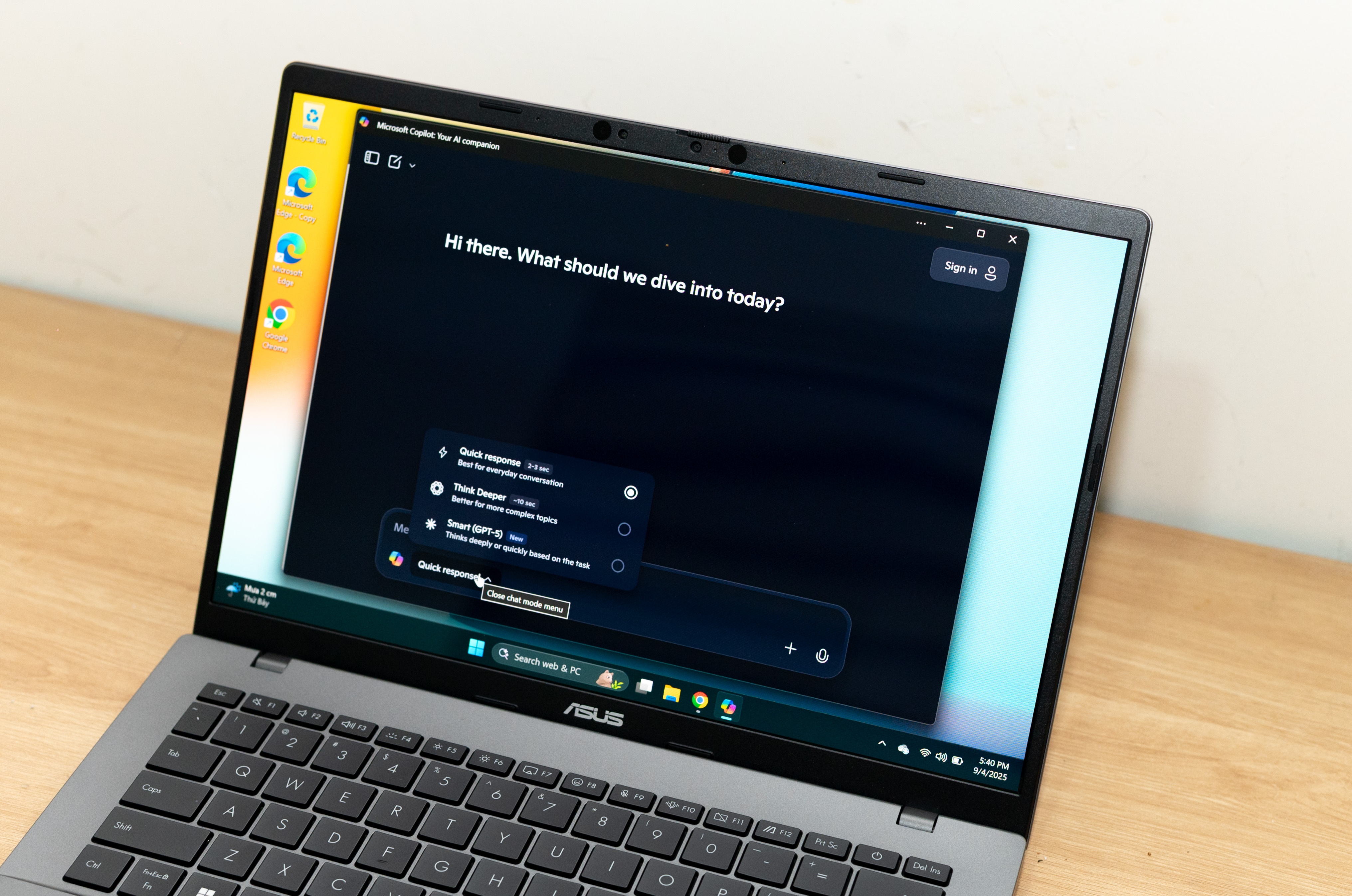    |
Manufacturers have the opportunity to make high-performance computers in thin and light designs thanks to the Arm architecture. |
Dissipating less heat and not using a fan also helps the Vivobook S14 save more battery. With mixed usage, it reaches 10-12 hours of continuous use. This is a very good level, rarely seen on previous Windows computers. Users are also guaranteed almost constant performance when plugged in and unplugged. The product also does not lose battery when in standby mode.
These strengths make the machine a more comfortable choice for customers who understand their needs, do not use specialized software systems or gaming, which the Arm platform is not compatible with. The Asus Vivobook S14 Qualcomm version is a competitor to the MacBook Air M4, with similar advantages to Apple's computer model but cheaper.
The product targets a group of customers who work mainly on web browsers, Microsoft tools and Adobe graphics software. These people rarely play games, do not draw CAD or do complex programming.
x86 architecture strikes back
Qualcomm’s strengths aren’t necessarily AMD’s weaknesses. Since its rival’s launch, x86 chips have continued to improve to deliver better performance per watt. AMD’s Ryzen AI 5 series processors are also built on TSMC’s 4nm process, just like Qualcomm.
The machine achieved about 8-10 hours of continuous work, the same task as the test on the Qualcomm version. There are differences, but the factors in return are worth it. One of them is absolute application compatibility. Almost all Windows software runs well on this Vivobook S14.
Especially Autodesk's dedicated software group, serving technical drawings or complex working tools. ESports or AAA games are also fully compatible with the product, something that the Qualcomm model does not have.
 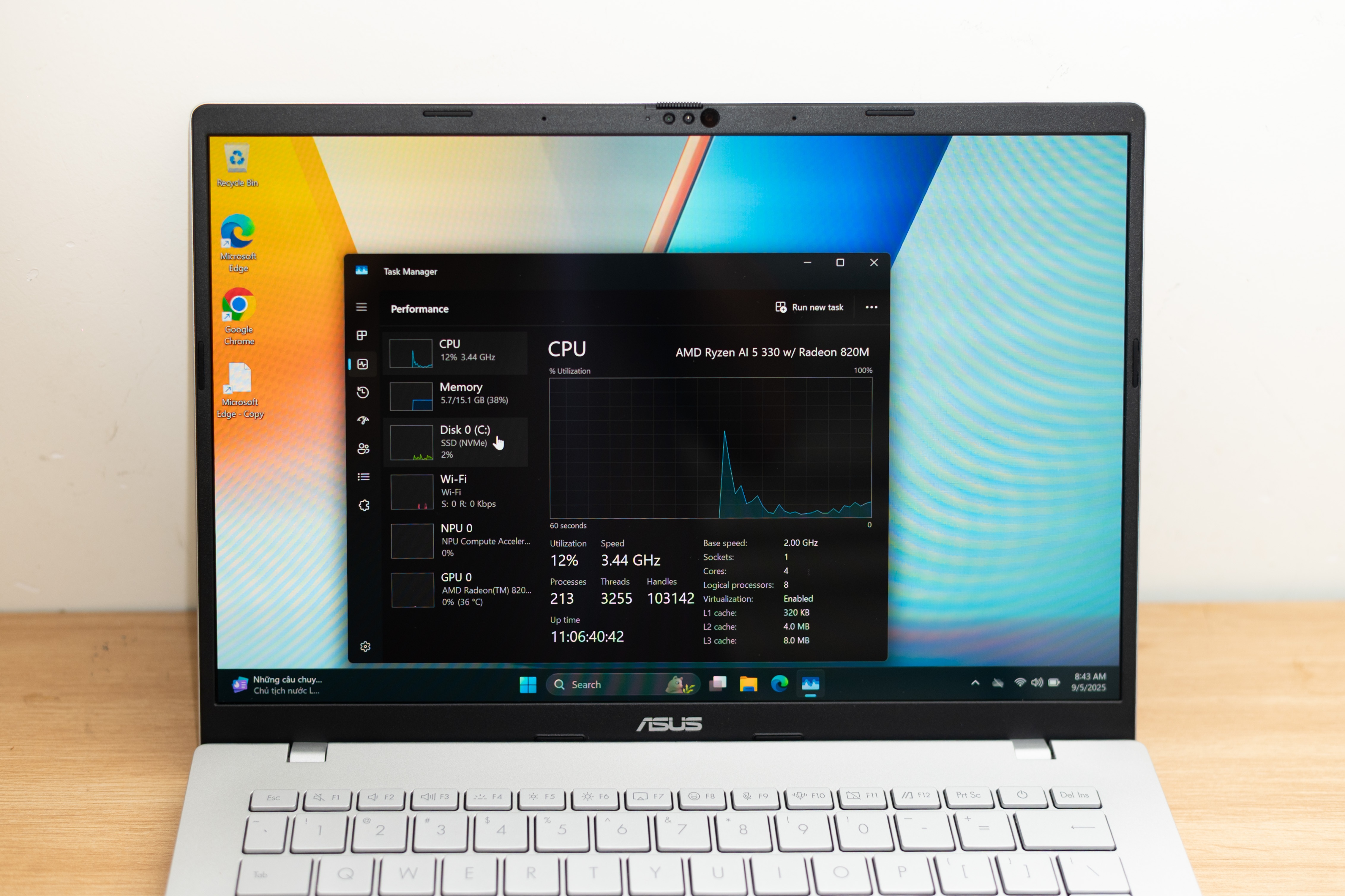 |
AMD with x86 ensures pure performance and superior compatibility. |
Of course, an office computer with an integrated GPU like the Radeon 820M isn't powerful enough for modern games. Playing League of Legends, Valorant , or racing in Dirt5 is still possible with the right settings.
AMD platforms have a slight problem with the Adobe suite. When using functions on Photoshop or Lightroom, the machine does not respond as well as it should. Some laptops with weaker Intel chips still handle RAW images smoothly in these software.
The manufacturer also optimized the chip to deliver high performance on a thin and light body. The Vivobook S14 AMD and Qualcomm models have the same weight and thinness at 1.3 kg and 1.7 cm, respectively. Users do not have to trade portability for performance or compatibility.
 |
Windows users have more options according to their needs. |
With the advent of the Snapdragon X platform on Windows, manufacturers have begun to expand their product lines. Asus introduced three Vivobook S14s with similar designs and components, including OLED screens, two metal sides, and AI engines inside. The only difference lies in the chips from Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm.
Each of these versions has its strengths and weaknesses that offset each other. The wide product range helps manufacturers provide more choice for users and compete with Apple, which is expanding with its M-series chips.
Source: https://znews.vn/may-tinh-snapdragon-da-thay-duoc-kien-truc-x86-post1582573.html





![[Photo] Hanoi students excitedly and joyfully open the new school year 2025-2026](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/5/ecc91eddd50a467aa7670463f7b142f5)
![[Photo] Opening ceremony of "Digital Citizenship - Digital School" and commitment to civilized behavior in cyberspace](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/5/222ec3b8892f443c9b26637ef2dd2b09)

![[Photo] The drum beats to open the new school year in a special way](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/5/b34123487ad34079a9688f344dc19148)






















































































Comment (0)