The plan was announced on June 26. The funding is part of the Broadband Equitable Access and Deployment Program, allocated based on the coverage map recently released by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
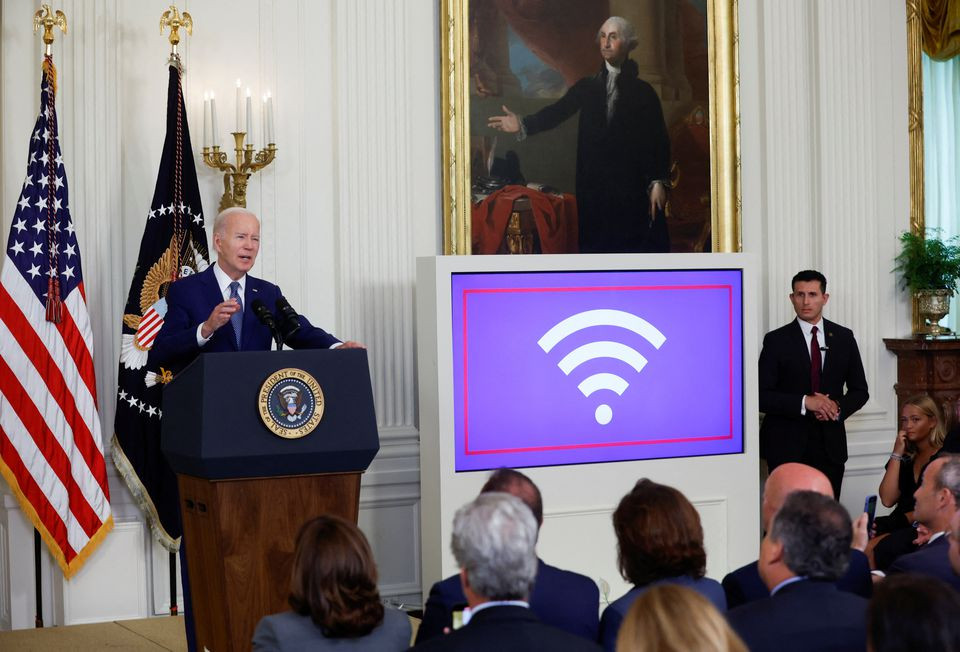

Texas and California, the two most populous states, topped the list of recipients, receiving $3.1 billion and $1.9 billion, respectively. Other states with smaller populations, such as Virginia, Alabama, and Louisiana, also made the top 10 for funding due to their lack of broadband access. These states all have large areas of remote areas with less internet access than major cities.
US President Joe Biden declared that this is the largest investment in high-speed internet in history. He assessed that internet access is as important as electricity, water and other basic services. The minimum amount that a state can be granted is 107 million USD.
The Biden administration estimates that 8.5 million locations in the United States lack broadband access. Vice President Kamala Harris said 24 million Americans lack high-speed internet because they cannot afford the monthly fee or live in areas that are not fully connected to fiber.
Broadband companies like Verizon, Comcast, Charter Communications, and AT&T are reluctant to provide service to remote, low-population areas because of the high cost of investment and low subscriber base. This situation has attracted attention since the Covid-19 pandemic when students had to stay home from school and study online.
States will submit preliminary plans by the end of the year to receive 20% of the funding. Once the plans are finalized, the government will provide the remaining money.
(According to Reuters, Tomshardware)

Source

































![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the VinFuture 2025 Award Ceremony](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764951162416_2628509768338816493-6995-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)






































































Comment (0)