The gallbladder stores and releases bile, which helps digest fats. Bile contains cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts.
When these components are out of balance, they can crystallize and form stones in the gallbladder. Currently, gallbladder stones are divided into three main types: cholesterol stones (at least 80% cholesterol, usually single, about 2-3 cm in size), bile pigment stones or bilirubin stones (less than 20% cholesterol, often numerous) and mixed stones (consisting of 20-80% cholesterol with calcium and bile pigment, often occurring after biliary tract infections and can be detected by X-ray). In Vietnam, the most common type of stone today is cholesterol stones.
 |
| Illustration photo. |
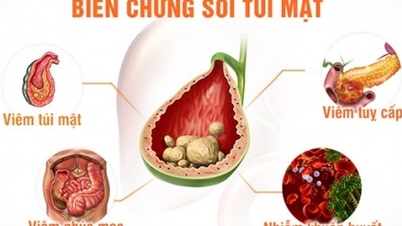
According to Dr. Vu Truong Khanh, Head of the Department of Gastroenterology - Hepatobiliary - Pancreas, Tam Anh General Hospital Hanoi , if not detected and treated promptly, gallstones can cause many serious complications such as cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, gallbladder perforation, biliary tract infection, and even lead to gallbladder cancer. In particular, large stones can easily cause obstruction of the bile duct, making the disease progress more quickly and dangerously.
Previously, gallstones were mainly found in middle-aged and elderly people. However, nowadays, the rate of young people with the disease is increasing rapidly due to the influence of unscientific modern lifestyles: irregular eating, excess fat, lack of green vegetables, lack of exercise and frequent stress.
According to statistics from the US National Library of Medicine (Pubmed), about 6% of the world's population has gallstones, with women suffering more than men.
In Vietnam, according to the Ministry of Health, gallstones account for about 60-70% of all cases of gallstones. Notably, only 10-20% of patients have no symptoms immediately after detection and may develop symptoms 5-20 years later. The majority of the rest only go to the doctor when the disease has progressed and caused complications, making the treatment process more complicated.
A typical case is Ms. Ha (29 years old, Hanoi), due to her busy work, she often eats irregularly, skips breakfast or replaces it with coffee or tea; while the remaining meals she consumes a lot of fried foods, fast food and sweets.
The rapid weight gain made her overweight (BMI 26). Recently, she often had dull pain in the right hypochondrium after eating. When she went to the doctor, an ultrasound revealed gallstones. The doctor recommended that she change her diet, increase exercise to control her weight, and have regular check-ups. If the stones cause pain or complications, laparoscopic cholecystectomy will be considered.
Another case is Mr. Long (42 years old, Hanoi), who was admitted to the emergency room due to severe pain in the right hypochondrium, mild fever and nausea. Ultrasound and MRI results showed a 1.2 cm stone causing obstruction of the gallbladder neck, leading to acute cholecystitis.
Before that, he had a dull pain but was subjective, only taking painkillers. Irregular living habits, frequent drinking of beer and alcohol and eating a lot of meat and few vegetables caused the stones to progress silently and become more severe over time.
Dr. Khanh said that alcohol does not directly cause gallstones, but drinking alcohol often goes hand in hand with overeating, especially fat and animal protein, which increases the risk of developing the disease or causing potential stones to turn into acute biliary colic. Many patients only discover the disease after parties or large meals when severe symptoms appear.
Mr. Long was treated with antibiotics and intravenous fluids to stabilize the inflammation, then underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy to remove the gallstones and prevent complications from recurring. After surgery, his health recovered well and he was advised to limit alcohol, reduce fat in his diet, and maintain a moderate lifestyle to protect his digestive system in the long term.
According to Dr. Khanh, a diet high in fat, animal meat, processed foods but lacking in green vegetables and fiber, plus the habit of skipping meals, fasting or sudden weight loss are factors that increase the risk of crystallization of stones in the bile. In addition, sitting for long periods, lack of exercise, being overweight, dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome all contribute to increased total cholesterol, leading to bile metabolism disorders and the formation of gallstones.
To prevent gallstones, doctors recommend maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, and maintaining a reasonable weight. The diet should be rich in fiber and green vegetables, limiting fatty foods, fast food, alcoholic beverages, and stimulants. At the same time, it is necessary to drink enough water and maintain physical activity to support the digestive system and reduce the risk of stone formation.
When symptoms such as pain in the right hypochondrium, bloating after eating, nausea appear, people should not be subjective but should go to the doctor early for timely diagnosis and treatment. Even when the stones have not caused symptoms, regular monitoring is still necessary to detect dangerous complications early and have appropriate treatment plans.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/soi-tui-mat-tang-nhanh-o-nguoi-tre-vi-loi-song-thieu-khoa-hoc-d388262.html


![[Photo] Highways passing through Dong Nai](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/12/1762940149627_ndo_br_1-resize-5756-jpg.webp)





























































































![Dong Nai OCOP transition: [Article 3] Linking tourism with OCOP product consumption](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/10/1762739199309_1324-2740-7_n-162543_981.jpeg)








Comment (0)