Current status of the process of improving Vietnam's export production capacity
In recent times, the improvement of Vietnam's export production capacity has achieved remarkable results, including:
Firstly , according to the General Statistics Office, the number of exported goods has changed positively, increasing from 773 items according to the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS4) in 1995 to 1,173 items in 2023. Also in the period 1995 - 2024, the export value of goods increased nearly 75 times from 5.45 billion USD to 405.53 billion USD.
Second , the structure of exported goods has changed positively towards becoming more diverse and modern. Before 2010, the structure of goods sharply reduced the proportion of agricultural and mineral products, such as vegetables, crude oil and gradually increased labor-intensive goods, such as textiles, footwear, and hats. From 2010 onwards, goods with high scientific and technological content, such as broadcasting equipment, computers, telephones and electronic microchips accounted for the largest proportion and continued to show an increasing trend.
Third , forming groups of industries producing high-value export goods in industrial parks of similar scale and production capacity thanks to the concentration of large amounts of capital, labor and technology.
Besides the above positive characteristics, Vietnam's export production also faces the following limitations and challenges:
Firstly , the export commodity space reflects a structural change from a low-level, undiversified economy from the previous century to an economy with a medium-level, more diversified production level but still quite far from the export commodity space of advanced, high-income economies.
Second , export growth still relies heavily on quantity rather than quality. The proportion of domestic value added in exported goods is low and has been slow to improve due to its dependence on cheap labor costs and imported materials and machinery. This relatively low proportion of value added is not enough to create a high, sustainable economic growth rate and help increase workers' incomes to reach the level of high-income economies.
Third , export production activities depend heavily on foreign-invested enterprises, especially those in which foreign investors hold more than 50% of capital contributions in branches and subsidiaries (contributing to nearly 80% of the export value of goods). These enterprises mainly process according to orders from the parent company with accompanying supply and distribution channels, making the value spread to the domestic sector relatively low. Domestic production activities increasingly depend on these enterprises to maintain the growth rate of export turnover, employment and economic growth.
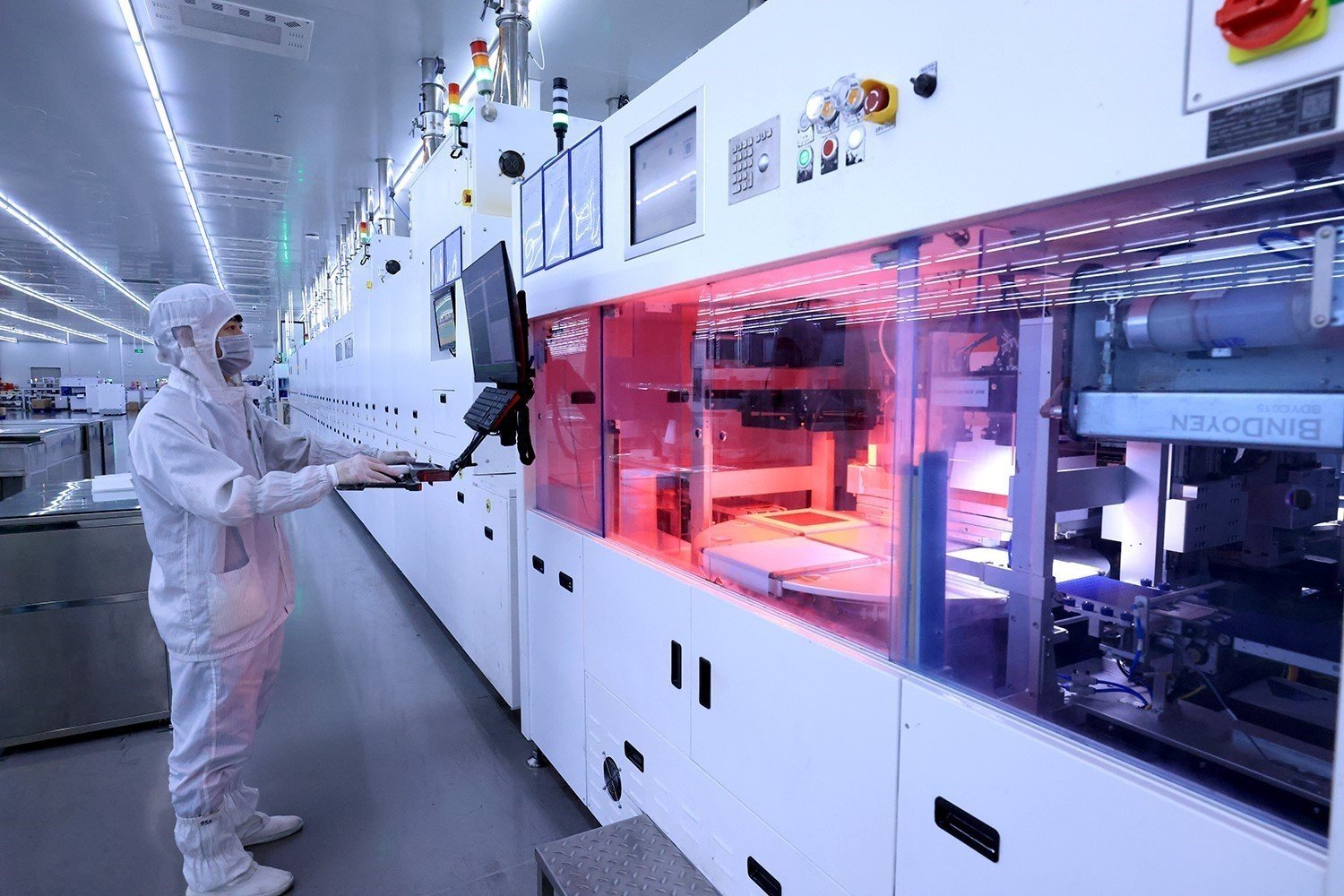

Fourth , labor costs continue to increase and the rate of increase is faster than the rate of increase in labor productivity. The supply of high-quality domestic labor has not met the demand for economic restructuring, creating barriers to the process of upgrading production capacity to produce export goods with high scientific and technological content and bringing greater added value.
Fifth , energy and transportation infrastructure for export production activities still have many bottlenecks and increasingly larger impacts on the environment. Industrial production infrastructure in general and for export production activities are at risk from climate change. Urban infrastructure, especially social housing, has not met the needs of developing economic zones, industrial parks, and export processing zones and is creating overload in urban areas.
Analysis of Vietnam's export activities over the past four decades shows both quantitative and qualitative progress from a country that mainly exported resources and raw products to a more diversified production and export structure with products from the processing and manufacturing industry. From a backward economy with limited production capacity, Vietnam has accumulated significantly new and more modern production capacity, thereby producing more sophisticated goods with greater export value. Export production activities not only help the economy grow, attract foreign investment and accumulate foreign currency, but also help create more jobs, solve income problems for a large part of the workforce, and promote the urbanization process. However, due to the high dependence on foreign-invested enterprises while the ability to absorb knowledge and the level of participation in the production value chain are still low, the domestic economy has not yet accumulated new and modern production capacity. The risk of two economic sectors in one country and the low position in the global value chain is present, making the economy increasingly dependent on foreign-invested enterprises to maintain export growth, employment in particular and economic growth in general.
Main trends affecting economic activities of countries
The world context in general and the world economy in particular show that a number of major trends are taking place at a rapid and strong pace, contributing significantly to the process of shaping economic activities of most countries, including Vietnam:
Firstly, globalization and economic integration continue to be major trends, but the economic and trade landscape has undergone many continuous, complex, rapid and profound changes. The content of economic integration continues to expand and penetrate into new issues and fields, such as infrastructure connectivity, science, technology, production capacity, high-quality human resources, disease prevention and control, cyber security, environmental protection and climate change response.
Second, there are more forms of economic competition, trade defense measures from technical standards, environmental protection, human rights are continuously applied and recently the application of industrial policies by many countries' governments to intervene more deeply in strategic competitive areas.
Third , the world economic balance is shifting toward Asia and emerging economies in parallel with the shift of political, economic, diplomatic, scientific and technological power from the West to the East.
Fourth, the Fourth Industrial Revolution creates both opportunities and challenges for the economic transformation of countries. The application of achievements in automation and smart processing and manufacturing can create a turning point for the common production method and shift the production chains of goods.
Faced with the shortcomings in Vietnam's export production activities and these profound changes in the world economy, Vietnam's export production activities are facing both opportunities and challenges. Vietnam is and will continue to lose its advantages as a latecomer in the production and export of goods, including cheap labor, resources and energy as well as abundant foreign investment capital thanks to large financial incentives. If the export production activities are considered an important growth driver of Vietnam's economy in the coming time, there must be a fundamental change in the production capacity of goods in general and the production capacity of export goods in particular. On the contrary, failure to improve production capacity not only hinders the economy from achieving high growth rates, but also hinders the process of enhancing internal capacity, reduces the independence and autonomy of the economy in the context of geopolitical and political fluctuations, increases the risk of the economy falling into the middle-income trap and slows down the process of achieving the goal of becoming a high-income developed country by 2045.
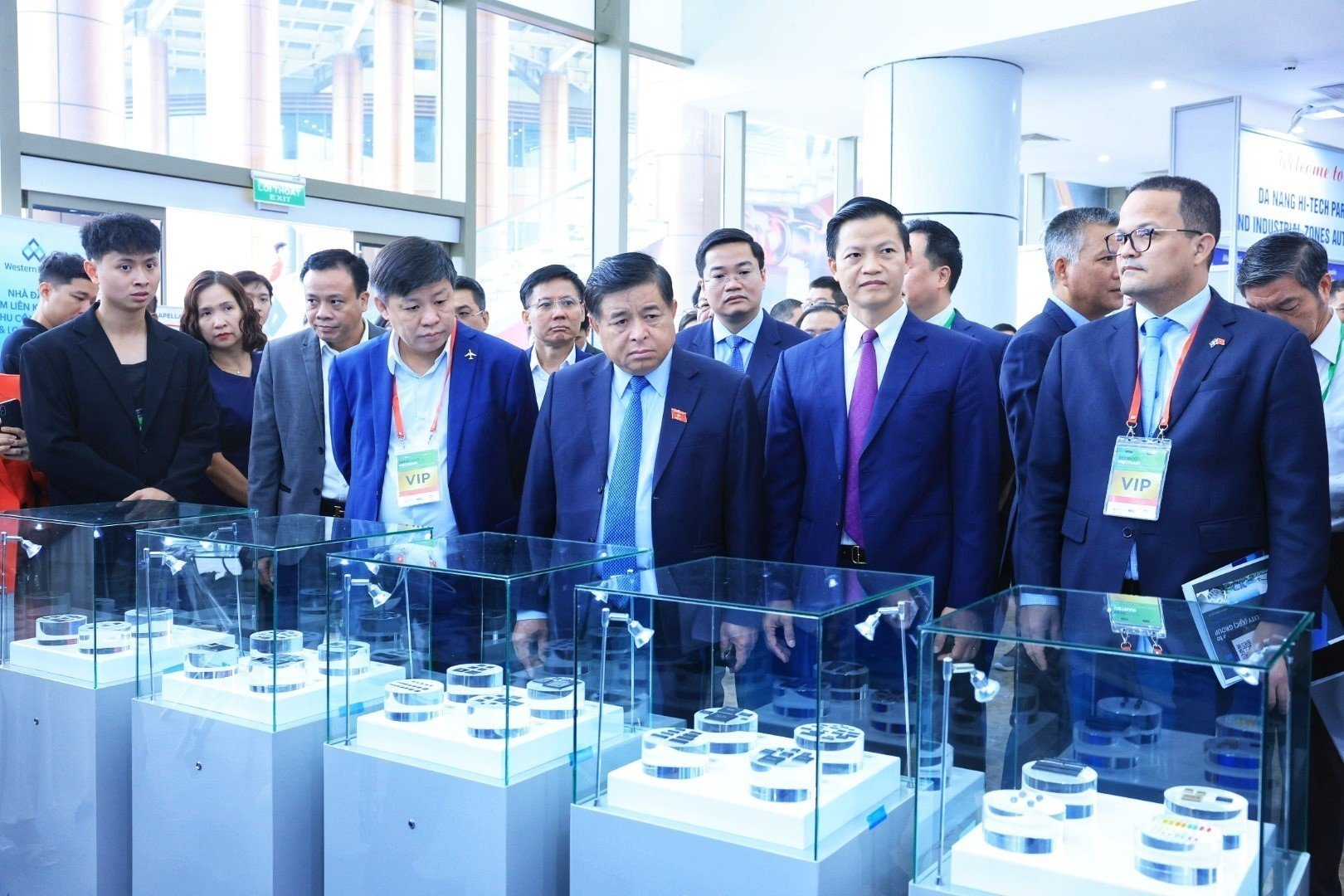

Some key solutions to restructure export production activities in the coming time
Firstly , improve the internal capacity and autonomy of the economy in the production of export goods through: 1- Renewing thinking and viewpoints, unifying awareness and action through resolutions, programs, and action plans of the Party and the State for the production and export of goods; 2- Researching, promulgating and effectively implementing industrial development programs in general and strategic industries in particular, in order to be large-scale industrial research and development projects of the State, developing strategic industries through applying the results of research projects into practice and enhancing commerciality and applying the results of the two previous stages to the entire industrial sector nationwide to amplify influence and achieve maximum efficiency; 3- Establishing and consolidating Vietnam's position in the network of commodity production linkages towards becoming a key country in the trade of a number of key commodities; Actively and proactively gather economic forces and promote links with potential trade partners, avoiding over-dependence on a few specific trade partners; 4- Change the mindset of international economic integration from export orientation to combining export orientation with domestic market development by improving the quality of domestically produced goods and services and ensuring consumer interests, forming commodity supply chains in the process of restructuring the economy, reorganizing the government apparatus, developing regional linkages; 5- Continue to reform economic institutions by clarifying how the State intervenes in the economy (including direct and indirect tools, ways of establishing and applying market principles, presence and level of participation in commodity production sectors and fields, etc.) and creating an institution flexible enough to conduct economic experiments in regions, localities and fields.
Second, strongly innovate industrial policies, especially the processing and manufacturing industry for export goods in the direction of: 1- Shifting from a "catch-up" policy to a "leapfrog" policy through selecting a number of capital-intensive and high-tech industries; gradually shifting from applying and mastering technology to building innovative capacity with breakthrough characteristics to be able to take shortcuts and anticipate key industries in the future. 2- Assessing the current production capacities of the economy, forecasting the growth of global demand for goods, assessing the competitiveness of competitors to identify the country's strategic export sectors and goods. 3- Promoting the import of modern production equipment associated with technology transfer from abroad and promoting domestic technological innovation, especially key technology industries in the process of implementing major national projects. 4- Continue to maintain full employment through selecting and expanding labor-intensive industries at both ends of the value chain to avoid the situation of not having innovative solutions of their own but having to import them from abroad, overcoming the current reality where innovation activities take place in products and do not extend to the production process; continue to diversify and improve the knowledge and skills of workers crystallized in products. 5- Create a mechanism for state-owned enterprises, especially corporations and general companies to participate in large, strategic industrial projects of the country, including under the State's ordering mechanism, to create momentum and enhance the international competitiveness of these enterprises. 6- Implement industrial policies associated with state management of socio-economy and apply achievements of the Fourth Industrial Revolution to create a large enough market for products and services for people and businesses nationwide.
Third , promote science, technology, innovation and digital transformation activities in the whole economy in general and production and export of goods in particular in the direction of: 1- Taking manufacturing enterprises as the center through strengthening links with research institutes, universities, innovation centers and supporting innovation, focusing on improving the capacity to absorb, master and participate in creating new technologies to meet the needs of enterprises in producing export goods. 2- Promote the transfer, mastery and development of production technology associated with knowledge transfer, training of high-quality scientific and technological human resources from abroad into the country's strategic industrial sectors and fields, which are decisive for the quality and quantity of exported goods. 3- Issue mechanisms and policies to support the formation and development of a number of manufacturing enterprises to develop and enhance their capacity for self-reliance in science and technology in the fields of digital technology, information technology, electronics - telecommunications and security, network safety, sufficient to lead the country's digital transformation process, create favorable conditions for the production of export goods and enhance competitiveness in the international arena; 4- Issue mechanisms to attract scientific and technological talents and form a network of domestic and international experts in strategic fields. 5- Increase investment in basic scientific research, invest in the development of a number of foundational industries for production activities.
Fourth , promote the development of high-quality human resources, gradually making human resources the most important factor to improve the internal capacity and autonomy of the economy: 1- Develop human resources at all levels with qualifications to meet the development requirements of industries, localities and the country through the development of criteria and standards to assess the quality of human resources, in the direction of starting from the demand side (the level of meeting the demand for jobs) instead of relying on criteria related to degrees and certificates as at present. 2- Combine with mechanisms and policies on human resource recruitment to create a change in awareness in the whole society about training, self-training in human resource development and apply the "career-based talent" regime by innovating methods of recruitment, evaluation, salary payment, reward, promotion and appointment. 3- Build a learning society, constantly innovate and create learning and training models right in enterprises. 4- Create favorable conditions for skilled workers to change jobs, fields and locations to maximize job opportunities in the context of economic transformation.
Fifth , continue to implement synchronous, consistent, timely and flexible macroeconomic policies with the goal of stabilizing the macro economy, creating a foundation for export production activities to take place smoothly and effectively: 1- Upgrade national governance capacity and macroeconomic management in the context of the economy continuing to deeply integrate into the world economy. 2- Strengthen the capacity to research and forecast world economic trends and developments affecting domestic production and business activities and enhance the ability to adapt, transform forecasts into specific policies and solutions for export enterprises and other related subjects. 3- Closely coordinate fiscal, monetary, investment, trade, diplomatic policies and other major policies, ensuring consistency between policies, between policy formulation and implementation, between the Central and local levels to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of policies, creating a stable foundation for export activities. 4- Encourage the development of clean energy sources, renewable energy, and environmentally friendly production technologies to minimize damage to the ecosystem and adapt to climate change. 5- Develop advanced construction and transportation capacity to meet the needs of people and businesses for technical infrastructure, social infrastructure of urban areas and industrial parks in an environmentally friendly direction and enhance social security.
Sixth, improve the effectiveness and efficiency of state management in attracting and using foreign direct investment for production and export activities: 1- Innovate the mechanism of decentralization of state management of foreign investment, establish an effective coordination mechanism between ministries, branches and localities in planning and implementing laws and policies on foreign investment. 2- Shift the focus of policies on attracting and using foreign investment from quantity to quality, with added value, taking efficiency as the main measure. 3- Promote cooperation in the direction of multilateralization, diversification of partners, investment forms and increase intertwining of interests in cooperation, connecting global supply chains, having a widespread impact on the domestic economic sector. 4- Innovate investment incentive mechanisms and policies based on output results such as the level of participation in the value chain, domestic added value, and technology use components, in parallel with supporting domestic enterprises to connect with foreign-invested enterprises. 5- Implement policies to attract and select foreign investment in a way that harmonizes benefits and risks between parties, encourages foreign-invested enterprises to link up and create conditions for domestic enterprises to participate in the global production network and value chain, and enhances the transfer of technology and modern management skills./.
Source: https://tapchicongsan.org.vn/web/guest/kinh-te/-/2018/1097202/tao-dong-luc-moi-cho-tang-truong-kinh-te-viet-nam-thong-qua--cau-truc-lai-hoat-dong-san-xuat-hang-hoa-xuat-khau.aspx























![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Australian Foreign Minister Penny Wong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/20/f5d413a946444bd2be288d6b700afc33)




![[Photo] Politburo works with Standing Committees of Lang Son and Bac Ninh Provincial Party Committees](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/20/0666629afb39421d8e1bd8922a0537e6)








































































Comment (0)