Vitamin E is important for health, but taking too much vitamin E can cause unwanted side effects.
1. Lack or excess of vitamin E is harmful to the body.
Vitamin E deficiency is rare in healthy people because most people get the vitamin E they need from their diet. Vitamin E deficiency is associated with certain chronic diseases or rare genetic disorders that impair fat absorption, such as Crohn's disease or cystic fibrosis. Vitamin E deficiency can also occur if you follow a very low-fat diet.
In people with genetic disorders that cause severe vitamin E deficiency, it can lead to neurological problems, such as poor coordination and muscle control. If left untreated, vitamin E deficiency can lead to permanent nerve damage, blindness, heart disease, decreased ability to concentrate, and can indirectly cause infertility in men.
However, too much vitamin E can also cause dangerous health complications. In case of overdose of vitamin E, the body will have symptoms such as: headache, fatigue, nausea, mild rash. Some people also have stomachache, digestive disorders, and physical weakness.
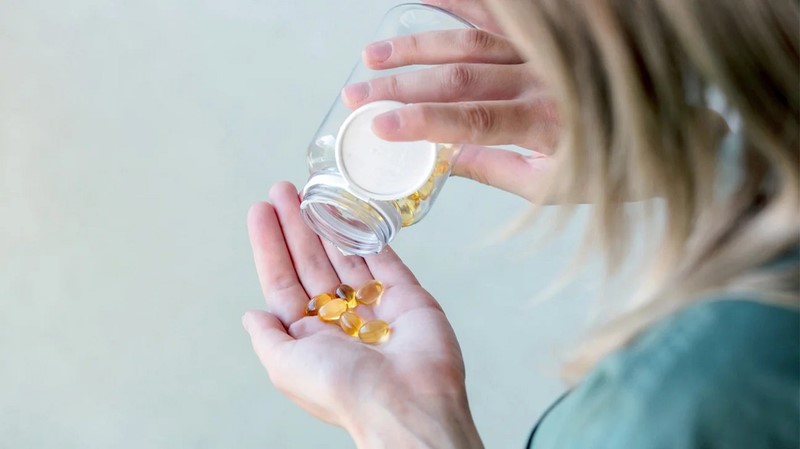

Vitamin E is important for health, but taking too much can cause serious side effects.
2. Why is excess vitamin E dangerous?
Excess vitamin E can lead to dangerous side effects to health:
- Blood thinning: One of the most serious side effects of excess vitamin E is blood thinning, increasing the risk of bleeding. This can lead to dangerous complications such as internal bleeding.
- Inhibits blood clotting: Vitamin E can reduce the body's ability to clot blood, making it difficult for wounds to heal and increasing the risk of infection.
- Effects on the nervous system: Some studies show that long-term supplementation of high doses of vitamin E can cause neurological problems such as headaches, dizziness, and fatigue.
- Drug interactions: Vitamin E can interact with some drugs, reducing the effectiveness of the drug or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs simvastatin, niacin, substances used in chemotherapy and radiotherapy,...
Vitamin E is inherently antagonistic to vitamin K and interacts with aspirin. If used in excess, it will increase blood clotting time and prevent platelet aggregation. At the same time, when used with estrogen for a long time, it can cause blood clots.
3. Signs of excess vitamin E
Normally, using vitamin E supplements in limited doses will not cause any side effects. Dietary supplements usually contain vitamin E from 400-1,000 IU per day. People at risk of excess vitamin E are: people who use functional foods containing vitamin E in high doses for a long time; people with liver disease; people who use many different types of drugs at the same time,...
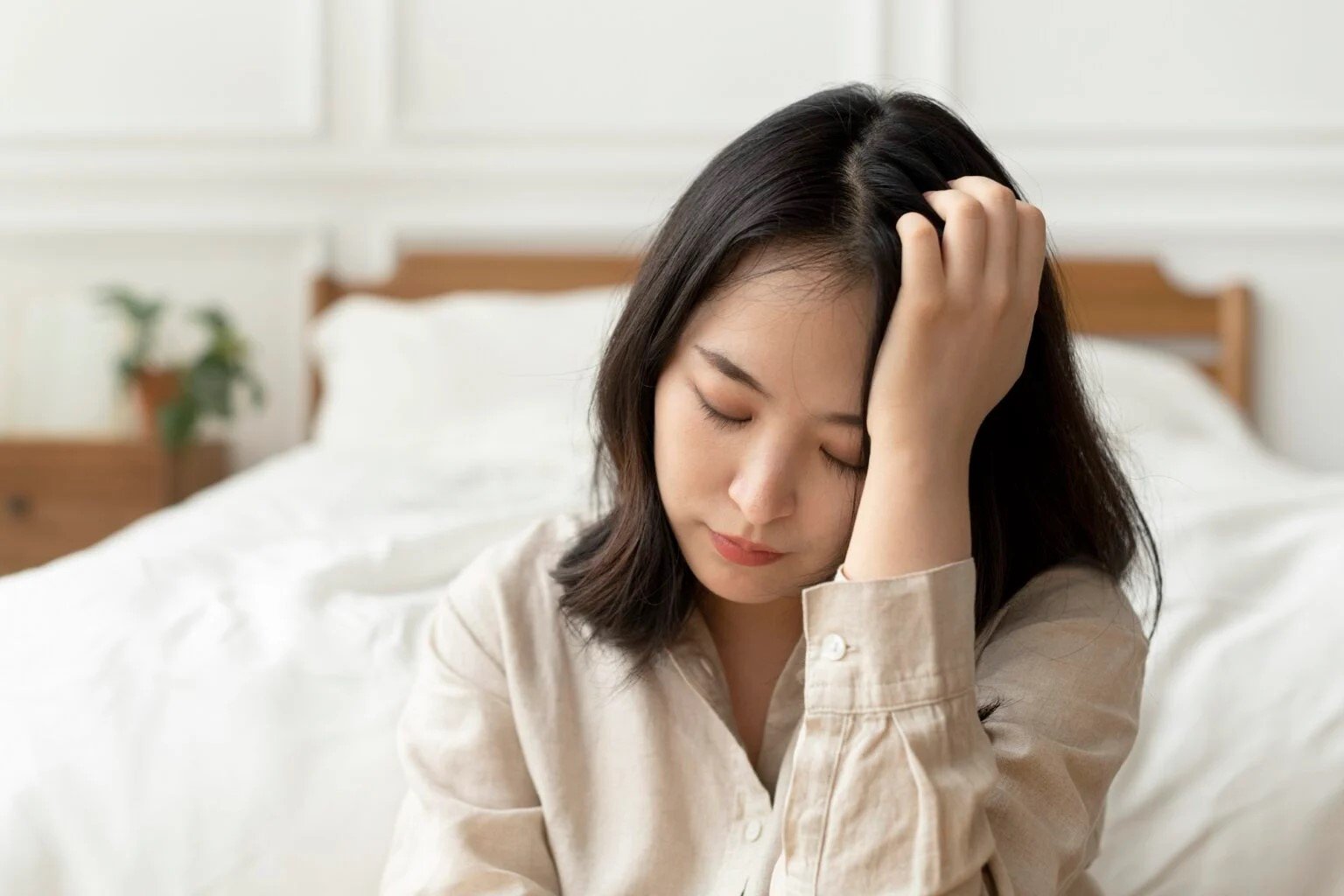

Too much vitamin E can cause side effects such as headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and even increase the risk of bleeding.
Although vitamin E supplements are safe, taking too much can put you at risk of bleeding—especially if you’re taking blood thinners—so the recommended upper limit for adults is 1,000 mg (1,465 IU) per day. When your body stores too much of this vitamin and can’t get rid of it, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue, muscle weakness;
- Headache, dizziness;
- Nausea, diarrhea;
- Easy bruising, bleeding;
- Visual disturbances...
When these signs appear, you should immediately stop using vitamin E and monitor your body. These symptoms will disappear in 1-2 days. However, if this condition does not improve, you should see a doctor immediately for a remedy.
4. How to avoid excess vitamin E?
Vitamin E supplementation should be done scientifically and under the guidance of a medical professional. Arbitrary vitamin E supplementation can cause many health risks. Before using any functional food, everyone should consult a doctor and must use it consistently within the allowed dosage.
Too much vitamin E can be dangerous, so limit your intake to less than 1,000 mg or a maximum of 1,500 international units per day. When taking supplements, read the label carefully and do not exceed the recommended dosage. Healthy adults, including those who are pregnant or breastfeeding, are advised not to take more than 300 mg of vitamin E per day, which is about 27 times the recommended daily allowance for this vitamin.
It is best to supplement the vitamins your body needs from daily food sources. Instead of supplementing vitamin E with pills, prioritize natural food sources rich in vitamin E such as seeds, avocados, and vegetable oils.
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/thua-vitamin-e-co-gay-hai-cho-suc-khoe-khong-172250111171343398.htm


































































































Comment (0)