The study was conducted by scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine at Cornell University (USA). The study was conducted on mice with the aim of finding a method that can help treat diabetes in humans, according to the Tribune India (India) newspaper.
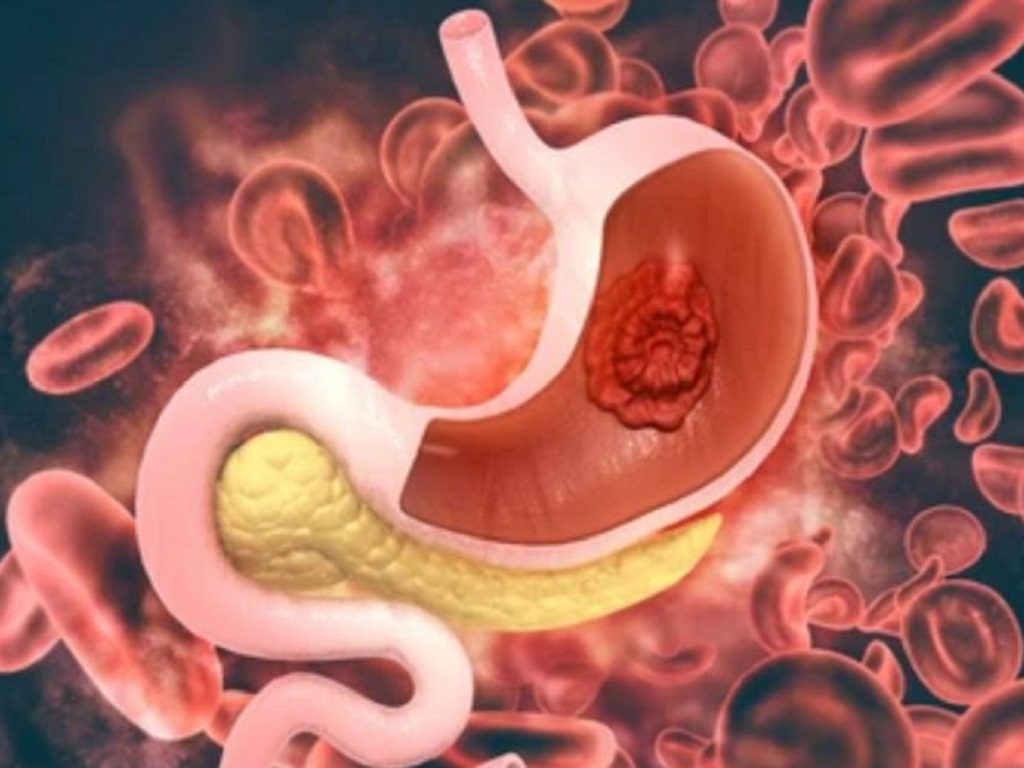
Stomach stem cells can be transformed into insulin-secreting cells, opening up new hope for diabetes treatment
The study was led by Dr. Joe Zhou. Previously, in another study on mice in 2016, Mr. Joe Zhou and his colleagues discovered that some stem cells in the stomach appeared to be sensitive to glucose and could be converted into cells that can secrete insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells in the pancreas to transport glucose from the blood to cells throughout the body.
In diabetic patients, the body lacks insulin or uses insulin ineffectively, leading to high blood sugar. Over time, this condition causes diabetes and can lead to many dangerous complications.
"The stomach produces cells that are capable of secreting its own hormones. During embryonic development, pancreatic cells and stomach cells are adjacent to each other. Therefore, it is not surprising that stem cells in the stomach can easily convert into insulin-secreting cells like beta cells," Dr. Zhou explained.
In a recently published study, he and his colleagues took stem cells from human stomach tissue and used cell reprogramming technology to transform these stem cells into cells that are similar to beta cells in the pancreas. Beta cells are the cells that secrete insulin for the body.
Next, the team grew the converted cells into small clusters and implanted them into diabetic mice. Over time, they found that the cell clusters responded sensitively to glucose and secreted insulin. As a result, the mice's diabetes symptoms improved. The results of the study were published in the journal Nature Cell Biology .
"This study provides new insights that will lay a solid foundation for us to develop a new treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, based on the patient's own cells," said Dr Zhou.
He and his team will conduct more experiments to perfect this method, then conduct clinical trials on humans. They hope that if this treatment is successful, diabetic patients will no longer have to take regular insulin injections, according to Tribune India .
Source link























![[Photo] Signing of cooperation between ministries, branches and localities of Vietnam and Senegal](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/24/6147c654b0ae4f2793188e982e272651)














































































Comment (0)