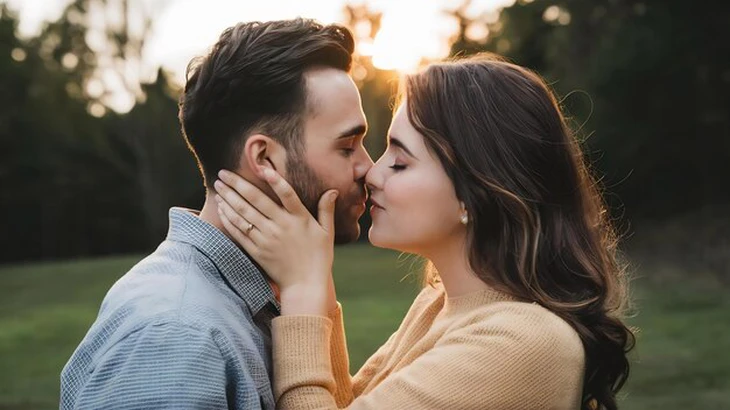

Depression and anxiety can be "contagious" between couples - not only through emotions, but also through kissing - Photo: FREEPIK
According to Earth , Iranian researcher Reza Rastmanesh has come up with a surprising hypothesis: depression and anxiety can be "contagious" between couples - not only through emotions, but also through kissing - by transmitting bacteria in the mouth.
Couples can "infect" depression through kissing
The researchers focused on couples who had been married for less than a year, recruited from two private sleep clinics in Tehran. They selected 268 couples, one of whom had moderate depression, anxiety, and severe sleep disturbances. They lived with a healthy partner who had no emotional or sleep problems.
After six months of marriage, healthy spouses living with partners who suffered from both depression and insomnia had marked changes in mood, sleep, and microbiome.
Their scores for depression, anxiety, and sleep all increased, and their oral microbiota began to resemble that of their sick partners. More notably, women appeared to be more susceptible to these changes than men.
The transfer of oral bacteria may seem strange, but it actually happens every day in close contact. Whether kissing, sharing a meal, or simply breathing the same air, couples "swap" millions of microorganisms.
In most cases, this poses no risk. But research in Iran suggests that these exchanges can affect mental health.
The oral microbiota of healthy partners began to show more bacterial groups that have been linked to mental disorders.
Cortisol increases with partner's depression level
The researchers measured levels of cortisol, a hormone that increases when the body is stressed. At the start of the study, healthy partners had low cortisol levels. But after living with a partner who was struggling with mental health, their cortisol levels increased dramatically.
Women saw particularly dramatic increases. In one analysis, cortisol levels in women nearly doubled. This suggests that the psychological synchrony in couples extends beyond behavior to microbiology and hormones.
Scientists have long known that couples can “sync up” in interesting ways. They can synchronize their heart rates, sleep cycles, or even have similar cortisol rhythms.
New research suggests that oral bacteria may be another connection that influences the risk of depression among couples. The closer the couple is, the more their emotional states influence each other.
This may be why couples tend to develop similar mental states over time. Depression and anxiety can run in families, not just through words and behavior, but also through silent “bacterial messengers.”
The study, published in the journal Exploratory Research and Hypothesis in Medicine, also found that treating both partners may be more effective if one partner develops psychological symptoms.
The study was conducted with caution. The team excluded people who were taking antibiotics, pregnant women, and couples who had separated during the study period. Microbial samples were taken from tonsils and throats.
DNA was extracted and sequenced according to industry standards. Samples were collected at baseline and six months later. All procedures followed the ethical guidelines of the National Science Foundation of Iran.
Despite its strengths, the team acknowledges some limitations. They collected saliva only in the morning, did not account for overall dietary changes, and used self-reported mental health. Still, the trends they found were consistent and compelling.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/tram-cam-lo-au-co-the-lay-qua-nu-hon-20250603153922264.htm

































































































Comment (0)