Glucosamine products are widely used in the community, especially among people with bone and joint problems. So who should not use glucosamine?
Glucosamine is a natural amino sugar produced by the body. The highest natural concentrations of glucosamine are found in joints and cartilage, which are essential for joint health. It is also a very popular dietary supplement on the market today.
Does taking glucosamine have side effects?
Glucosamine supplements are likely safe for most people. However, there are some risks to be aware of when using them.
Possible side effects include:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Stomach-ache...
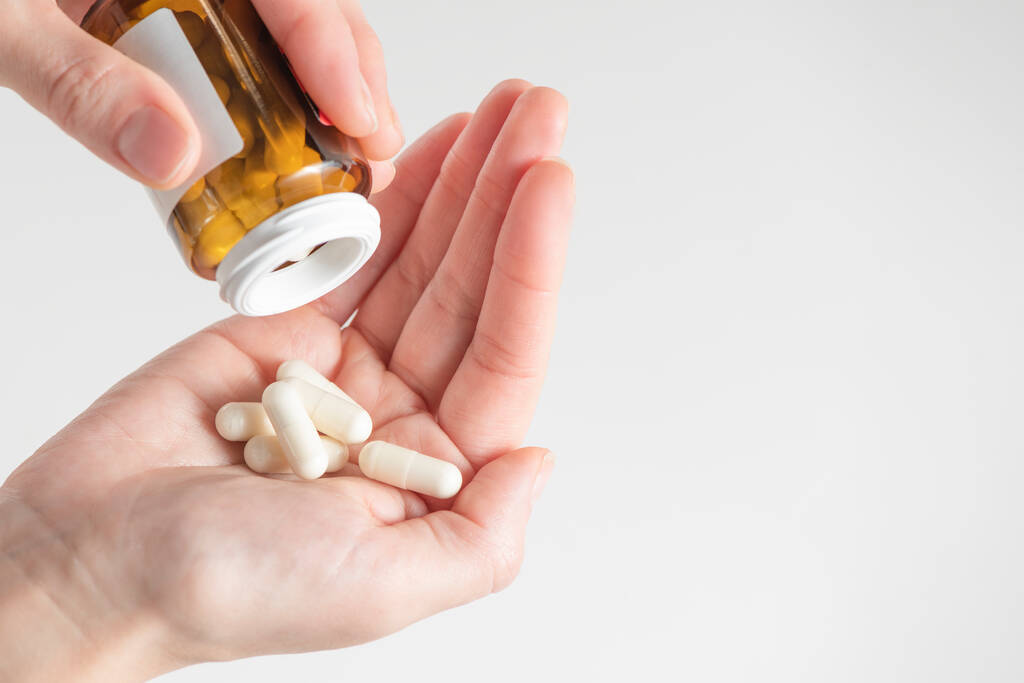

People with chronic diseases should consult their doctor before taking glucosamine.
Most glucosamine products contain potassium or sodium salts. Therefore, people with specific medical conditions that require potassium or sodium restriction should pay attention to the label when taking them and carefully calculate the sodium content when taking them. In general, the recommended daily sodium intake for normal people is less than 2400 mg.
Additionally, research has shown that glucosamine supplements may interact with other medications. For example, when used in combination with warfarin, an anticoagulant (blood thinner), the PT-INR value (a test used to check blood clotting) will increase, increasing the risk of bleeding.
How much glucosamine is best to consume?
The recommended dosage of glucosamine is usually 1,500 mg per day. This amount is considered sufficient to support joint health and many supplements are based on this recommended amount. However, the amount you need will vary depending on your weight, health status... so before supplementing, users should consult a doctor to determine the appropriate dosage for themselves.
Note that glucosamine is not the only treatment for improving joint pain. Lifestyle changes such as exercise and weight control to strengthen joint cartilage are important to reduce pain and discomfort. It is best for patients to see a doctor for appropriate treatment.
Who should not take glucosamine?
Some people need to be very cautious or should not take glucosamine:
- People with seafood allergies: Most glucosamine supplements are extracted from crustacean shells, so people with seafood allergies should avoid taking them.
- People with chronic diseases and special physical conditions: Glucosamine can affect metabolism, so people with chronic diseases or special physical conditions should consult a doctor before use.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid glucosamine supplements due to the lack of safety studies related to this group of subjects.
Dr. Vu Thuy Duong
Source: https://giadinh.suckhoedoisong.vn/ai-khong-nen-dung-glucosamine-172241118163616476.htm



















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)













































Comment (0)