SGGP
Ethnic minority communities in the mountainous regions of Northern Vietnam and the Central Highlands often have the custom of harvesting and using wild mushrooms as food. Many people have mistakenly confused edible wild mushrooms with those containing dangerous toxins, leading to numerous serious cases of poisoning.
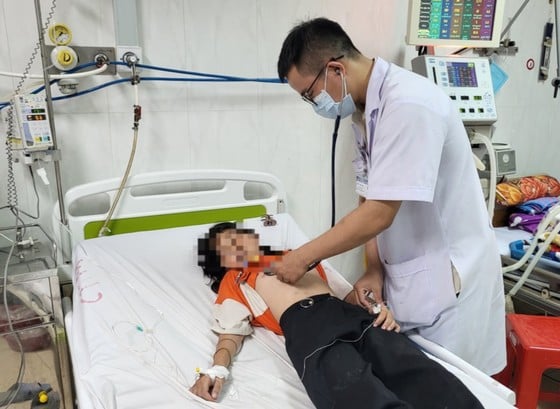 |
| Patients suffering from food poisoning after eating cicada mushrooms are being treated at the Central Highlands Regional General Hospital. Photo: MAI CUONG |
Mistaking poisonous mushrooms for cordyceps.
On June 5-6, Dr. Trinh Hong Nhut, Deputy Director of the Central Highlands Regional General Hospital (Dak Lak province), said that the hospital is treating six patients in the emergency room due to poisoning from eating mushrooms that grew on cicada nymphs, mistakenly believing them to be cordyceps. Previously, on the afternoon of June 3, the six patients were transferred from the Ea Sup District Medical Center (Dak Lak province) with symptoms of vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Three of them were lethargic, experiencing muscle tremors, nystagmus, and weakness in their limbs. After two days of intensive treatment at the hospital, the patients' health has stabilized. Those with severe symptoms have also regained consciousness.
Similarly, recently a 34-year-old resident of Duc Linh district, Binh Thuan province, went to his garden and found horn-shaped mushrooms resembling cordyceps, so he picked about 15 plants to cook. After eating, he felt normal, but the next day at noon, he experienced severe vomiting, abdominal cramps, and altered consciousness, so his family took him to Cho Ray Hospital (Ho Chi Minh City) for emergency treatment. According to Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy Ngan, Deputy Head of the Department of Tropical Diseases, Cho Ray Hospital, the patient was admitted in a conscious state, with urinary retention, muscle weakness, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Currently, the patient is able to communicate and breathe on his own; muscle strength in all four limbs has improved; heart rate is slightly slow and is being closely monitored for pulse and blood pressure.
At the Poison Control Center of Bach Mai Hospital ( Hanoi ), doctors frequently receive many severe cases of mushroom poisoning transferred from lower-level hospitals. Specifically, the center recently received two patients with wild mushroom poisoning from the Mai Chau District Health Center (Hoa Binh province). Previously, these patients, from the same family in Mai Hich commune, exhibited symptoms of poisoning, including abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea after eating a meal at home containing wild mushrooms cooked in soup with betel leaves. Despite intensive treatment, including detoxification, shock treatment, mechanical ventilation, continuous hemodialysis, adsorption hemodialysis, and plasma exchange, one patient subsequently died due to worsening condition and multiple organ failure.
Do not use mushrooms of unknown origin.
According to Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy Ngan, cicadas lay their eggs in the soil, which then develop into larvae (also known as cicada pupae). The pupae reside in the soil, possibly alongside fungal spores. These fungi attack and parasitize the host (the cicada pupae), replacing the host's tissues and growing long stems that absorb nutrients from the host, causing its death, and then growing outside the host's body. "Depending on the type of fungus parasitizing the host, they can be classified as either beneficial or toxic to humans. Currently, it's impossible to pinpoint the exact type of fungus causing the poisoning; diagnosis is primarily based on the patient's medical history and symptoms," Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy Ngan explained.
According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, hundreds of mushroom poisoning cases occur nationwide each year, with dozens resulting in death. These cases frequently occur in mountainous provinces such as Cao Bang, Ha Giang, Thai Nguyen, Hoa Binh, Lai Chau, and the Central Highlands. The consequences of these poisonings are almost always severe. Dr. Nguyen Trung Nguyen, Director of the Poison Control Center at Bach Mai Hospital, stated that there are currently over 5,000 types of mushrooms worldwide; in Vietnam, there are approximately 100 poisonous species, and it is very difficult to distinguish between edible and deadly poisonous mushrooms based on their appearance. Emergency treatment for mushroom poisoning is very expensive, but the mortality rate is very high (over 50%), with some families experiencing the deaths of entire members after consuming poisonous mushrooms. “For safety, people should only eat cultivated mushrooms. It is absolutely not advisable or possible to distinguish between edible and poisonous mushrooms based on their shape or color. Even more importantly, one should not try them to see for themselves. Poisonous mushrooms, even after cooking, retain their toxins and are not destroyed. It's important to note that many poisonous mushrooms can cause poisoning in animals without causing illness, but can still cause poisoning in humans,” advised Dr. Nguyen Trung Nguyen.
The Food Safety Department (Ministry of Health) recently requested that directors of provincial and city health departments intensify information and communication efforts regarding measures to prevent poisoning from poisonous mushrooms to households through various means, in both Vietnamese and ethnic minority languages. Accordingly, people should absolutely not pick or consume unfamiliar or unidentified mushrooms; if symptoms of poisoning related to mushroom consumption appear, they should immediately go to the nearest medical facility for emergency treatment.
Identifying signs of poisonous mushrooms
Mushrooms with a complete cap, gills, stem, ring, and volva are usually poisonous. Mushrooms with a pale pink interior, a red cap with white scales, and hyphae that glow in the dark are also poisonous. The toxins are found throughout the entire fruiting body (cap, gills, ring, stem, volva), and the toxicity varies depending on the season, the mushroom's growth process, and the soil and climate conditions.
Source








































































































Comment (0)