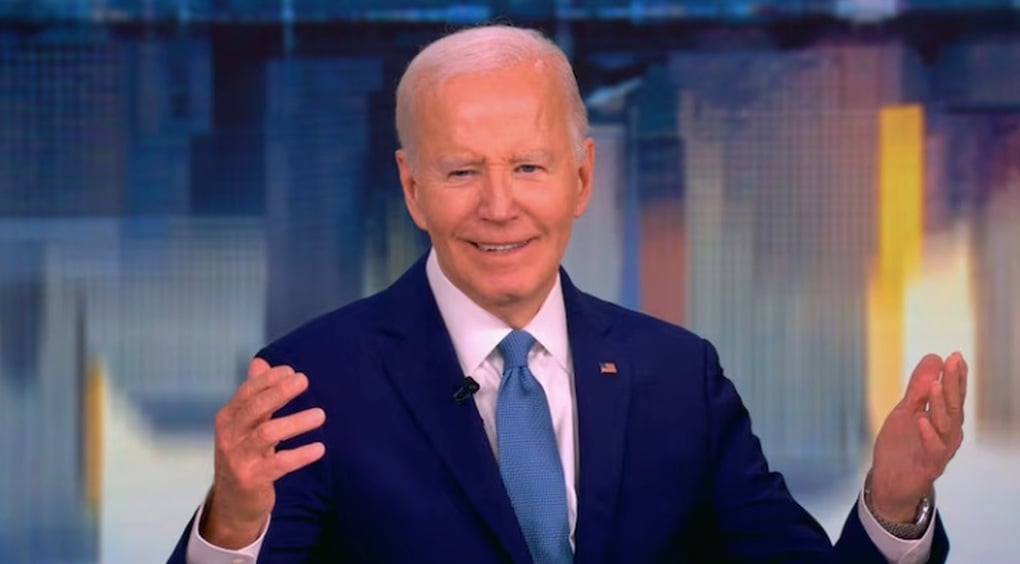
According to information from the office of former US President Joe Biden, last week, Mr. Biden was examined for a new prostate tumor after experiencing increasing urinary symptoms.
On May 16, he was diagnosed with prostate cancer, which had spread to his bones.
Former US President Joe Biden (Photo: ABCnews).
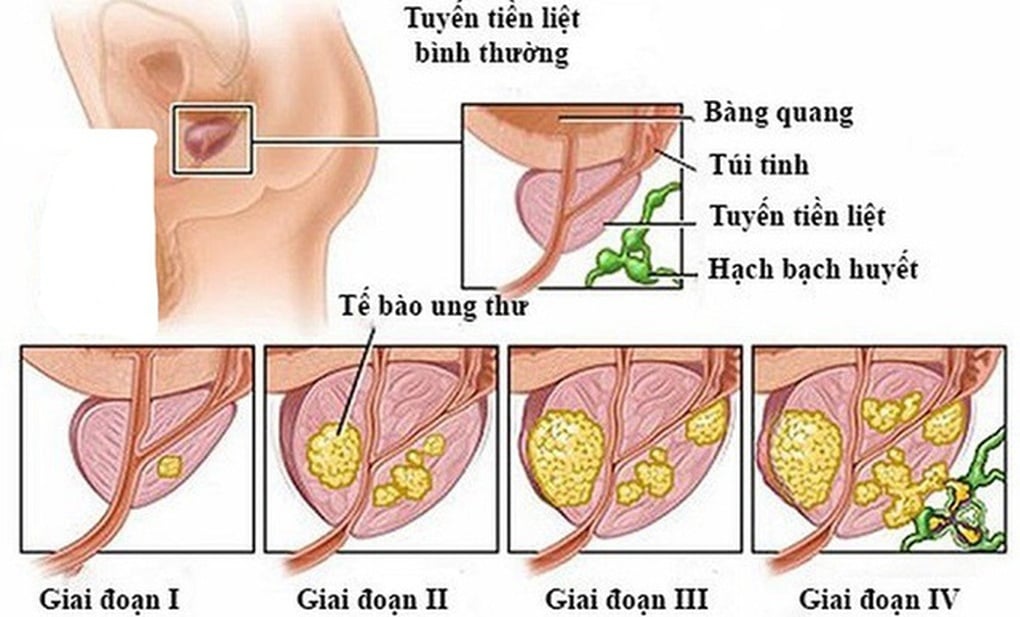
What is prostate cancer?
The prostate gland is only found in men. It is located just below the bladder, connecting to the urethra. Glands in the prostate tissue produce a white fluid that is pushed down the urethra during sexual intercourse, forming semen.
Prostate cancer or prostate cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the prostate gland of men. This is a common malignant disease in elderly men, progressing slowly and continuously with different levels, so the disease has an impact on a wider age range.
According to Times of India , often, the symptoms of prostate cancer are easily overlooked or confused, leading to late detection of the disease.
Because the prostate is located near the bladder and urethra, a person is likely to experience a range of urinary symptoms. These usually occur in the early stages of cancer and depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Symptoms of prostate cancer
According to doctors at Viet Duc Friendship Hospital, common functional symptoms of prostate cancer include:
In the early stages of prostate cancer, symptoms are often unclear or similar to benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Irritation symptoms: Frequent urination, urgent urination, urinary incontinence.
- Symptoms of pressure: Difficulty urinating, straining, dropping urine last, incomplete urination.
- More severe cases may include complete or incomplete urinary retention, urinary tract infections, and hematuria.
In late stages, the disease has symptoms of cancer metastasis:
- Urinary disorders due to tumor invasion of the bladder neck and ureteral opening.
- Bone metastasis causes bone pain. If metastasis to the spine can cause spinal cord compression, paralysis of limbs, and sphincter disorders.
- Pelvic lymph node metastasis, causing leg edema.
- Bloody ejaculation if seminal vesicle metastasis.
Prostate Cancer Treatments
Optimal treatment: Radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection.
This method is optimally applied in patients:
- Localized stage cancer.
- Expected life expectancy ≥ 10 years.
- No associated diseases such as: cardiovascular disease, diabetes, sequelae of stroke...
- No lymph node metastasis (in fact, about 2-4% of patients with pelvic lymph node metastasis can still undergo radical prostatectomy).
- Gleason score ≤ 8.
- PSA below 20 ng/ml.
Temporary treatment: Endoscopic resection of the tumor through the urethra or bladder drainage, with orchiectomy when optimal treatment is no longer indicated.
Combination treatment:
- Endocrine therapy: Use drugs that counteract androgen activity and prostate proliferation, including hormones and non-hormonal substances. This method is mainly applied to late-stage prostate cancer when there is recurrence and distant metastasis that is no longer amenable to radical treatment.
- Radiation therapy: External radiation therapy to the pelvis or local radiation therapy to the prostate.
Who needs prostate cancer screening?
According to Verywell Health , because prostate cancer diagnosed early has a 100% five-year survival rate, proper screening is important, especially for those with risk factors.
Risk factors for prostate cancer include:
- Age, most cases occur in men over 40 years old.
- African American men tend to be at higher risk.
- Geography, because people in North America, northwestern Europe, Australia, and the Caribbean islands are at higher risk.
- Family history of prostate cancer.
Doctors have not yet found the exact cause of prostate cancer, but some risk factors are associated with this disease. For example, family history, some genes such as BRCA2, can put you at higher risk.
So if you have a relative with prostate cancer, such as a brother or father, you are at high risk for the disease.
Additionally, men who eat a lot of fatty foods are also more likely to develop prostate cancer. Age is also a risk factor if you are over 50.
You can reduce your risk of prostate cancer by:
- Maintain a healthy diet with lots of fruits and vegetables and little red meat.
- Prioritize natural foods over functional foods.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain weight.
- Talk to your doctor if you are at high risk for prostate cancer.
- Regular health check-ups.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/suc-khoe/can-benh-ung-thu-cuu-tong-thong-my-joe-biden-mac-phai-nguy-hiem-the-nao-20250519081700997.htm



































































































Comment (0)