
Physicists have been able to predict when the universe will end (Illustration: Getty).
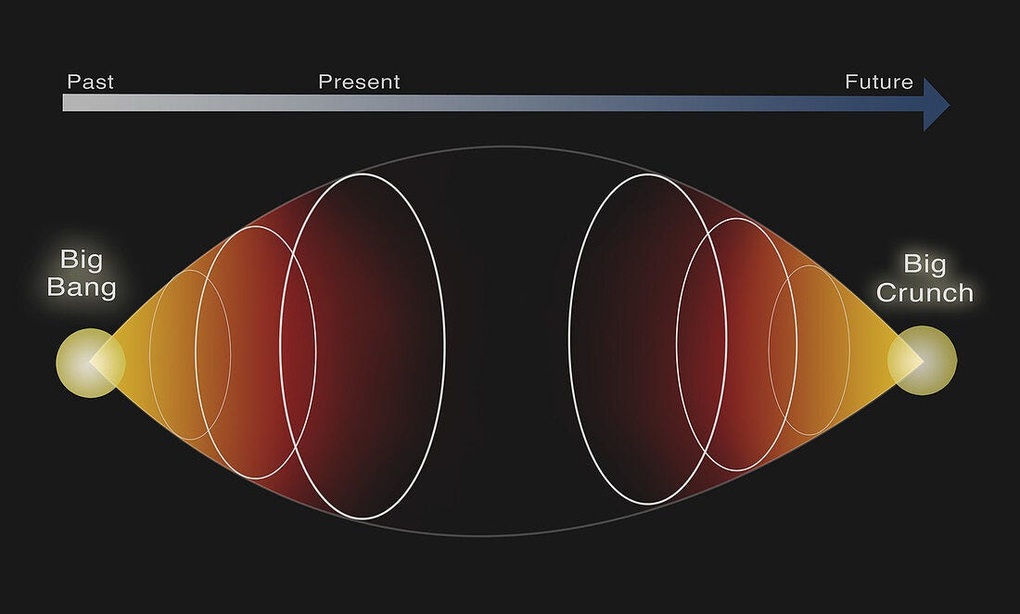
A new study suggests that the universe may not be expanding forever, as we have long thought. Instead, in less than 20 billion years, all of space may stop expanding and begin contracting, ending in a “reverse Big Bang” where everything collapses to a single point.
The universe will not expand forever.
For decades, scientists believed that the universe would expand indefinitely due to the influence of dark energy, a mysterious energy that is thought to make up 70% of the total energy in the universe.
However, an international research team including Spanish, Chinese and American scientists has just come up with a new model showing that the opposite may happen.
According to the team’s calculations, the universe is only about 33.3 billion years old. However, since we’ve been around for 13.8 billion years since the Big Bang, that means there are less than 20 billion years left before everything collapses back in a “Big Crunch.”
The Big Crunch is considered the most likely ending for our universe (Photo: Medium).
To determine this number, physicists relied on the cosmological constant λ (lambda), which is also the quantity that Albert Einstein once proposed to describe the expansion of the universe.
Accordingly, if λ is positive, the universe will expand forever; but if λ is negative, gravity will prevail, pulling the universe back. Recent observational data suggest that λ may be small negative, which means that the universe may be approaching its end.
Axion: The mysterious particle that could decide the fate of the universe
The team's new model goes beyond the constant λ and also considers a hypothetical particle called an axion.
In theory, axions are extremely light particles that permeate space, acting as a weak repulsive force that helped the universe expand for billions of years. But over time, the axion's energy would weaken, allowing gravity to take over again.
The universe will then stop expanding at its maximum size (about 1.7 times its current size) and then start contracting. This process is similar to a car climbing a hill slowing down as it loses momentum, stopping at the top and then speeding down.
During the “downhill” phase, matter becomes more and more dense, gravity becomes stronger, and eventually everything is collapsed into an extremely small, hot, and dense point, marking the “reverse Big Bang.”

Can humans rely on natural elements to change the fate of the universe? The answer is still ahead (Photo: Prime).
Scientists stress that this is not a firm prediction, but a possible scenario if observations of dark energy changing over time are confirmed.
In the future, space telescopes such as Euclid (ESA) and Nancy Grace Roman (NASA) will help collect more data to verify this hypothesis.
“The universe had a beginning: the Big Bang,” said Professor Henry Tye, a member of the research team. “Now the question is: does it also have an end? If the model is correct, then the reverse Big Bang is the inevitable end of the universe.”
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/khi-nao-vu-tru-tan-bien-khoa-hoc-da-co-cau-tra-loi-20251009082541420.htm


![[Photo] General Secretary attends the parade to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the founding of the Korean Workers' Party](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/11/1760150039564_vna-potal-tong-bi-thu-du-le-duyet-binh-ky-niem-80-nam-thanh-lap-dang-lao-dong-trieu-tien-8331994-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Opening of the World Cultural Festival in Hanoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/10/1760113426728_ndo_br_lehoi-khaimac-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Discover unique experiences at the first World Cultural Festival](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/11/1760198064937_le-hoi-van-hoa-4199-3623-jpg.webp)






























![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City is brilliant with flags and flowers on the eve of the 1st Party Congress, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/10/1760102923219_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-43-png.webp)































































Comment (0)