A breakthrough in solar cell technology has just been announced in Japan when a prototype device can control the generated current by the influence of an external magnetic field. Instead of using a traditional p–n junction, the new cell takes advantage of the bulk photovoltaic effect in a “stacked” structure between two materials: a two-dimensional semiconductor layer of MoS₂ and a magnetic material layer of CrPS₄.
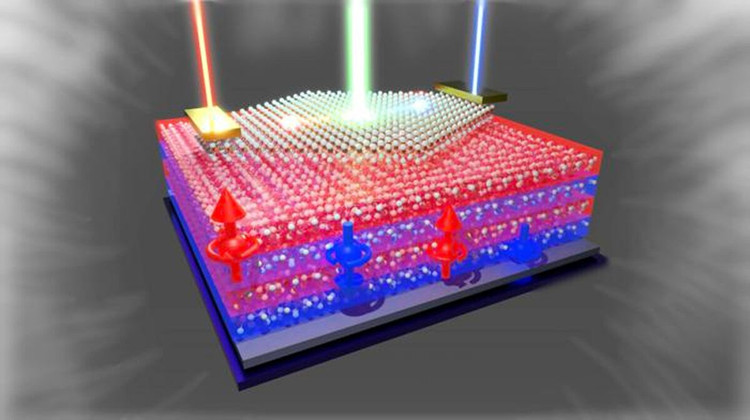
Under normal light conditions, the battery operates like a bulk photovoltaic cell, converting light into electricity. When a magnetic field is applied to the surface of the battery—for example, by placing a magnet or a field-generating coil near the device—the current instantly changes in intensity, increasing, decreasing, or turning off completely.
This feature allows real-time adjustment of power output without the need for additional control components such as diodes or transistors.
The fabrication process involves mechanically exfoliating MoS₂ and CrPS₄ sheets from the bulk crystal, followed by a dry transfer technique to precisely assemble the two layers in a van der Waals structure. The finished device is illuminated and its electrical properties are measured under various magnetic field strengths.
The results show not only that the light conversion efficiency is higher than the equilibrium limit of traditional silicon cells, but also that the current can be flexibly controlled by simply changing the magnetic field.
The outstanding advantage of this technology is its simplicity and flexibility in design. Without the need for complex control circuits, the panels can be thin, light, and easily bent to be glued to glass surfaces, roofs, or even mobile device cases.
Potential applications include self-powered sensors, energy-efficient wood, smart glass that self-regulates power, and many Internet of Things devices that require ultra-thin batteries.
Magnetic field current control technology also promises improved performance in low-light or fragmented conditions. Combining the bulk photovoltaic effect with the ability to tailor magnetic fields opens up opportunities to overcome the performance limitations of current photovoltaic cells.
The prototype is still in the laboratory stage, but its potential applications have attracted interest from many international research institutes and businesses. Further experiments will focus on optimizing the materials, expanding the operating temperature and magnetic field range, aiming for large-scale production in the next 5–10 years.
In Vietnam, where solar capacity is expanding rapidly, the technology could bring practical benefits. Magnetically controlled panels can be easily integrated into roofs, windows or mobile charging stations. When the distributed grid (smart grid) needs to balance power, batteries can automatically disconnect when there is surplus power or increase capacity to compensate for load when needed. This helps reduce transmission losses and improve system stability.
Not only limited to civil applications, magnetically controlled batteries are also suitable for energy projects serving research, environmental sensors or autonomous drones that require flexible power sources. The ability to instantly turn on/off the current using magnetic fields promises to create a generation of smart "super batteries", in line with the global greening and digitalization trends.
When commercialized, magnetically controlled solar cell technology will mark a turning point in the renewable energy industry: from passive solar panels to “active” energy devices that interact with the environment. This is the premise for smart cities, self-regulating energy buildings and a series of future applications, contributing to the construction of a sustainable energy ecosystem.
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/nhat-ban-phat-trien-pin-nang-luong-mat-troi-nhan-dien-tu-truong-post1551512.html


























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman attends the seminar "Building and operating an international financial center and recommendations for Vietnam"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/28/76393436936e457db31ec84433289f72)










































































Comment (0)