The Mori JP Tower building is over 325 m high and is equipped with many systems to help reduce strong vibrations and can withstand earthquakes up to 9 degrees.
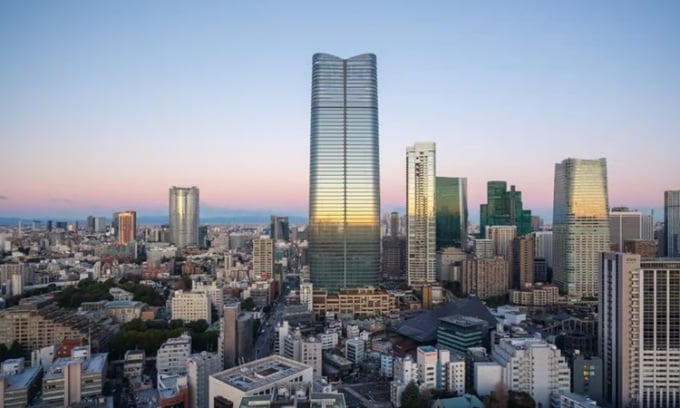

Mori JP Tower has 64 floors. Photo: Jason O'Rear
Mori JP Tower becomes Japan's new tallest building. Standing 325.2 meters tall in Tokyo, the building is designed to reduce its use of energy from the grid with sustainable features and seismic resistance. Designed by Pelli Clarke & Partners, Mori JP Tower is located in Azabudai Hills, a new green district that includes Heatherwick Studio's buildings and two other skyscrapers, New Atlas reported on March 19.
The new skyscraper features a glass facade that evokes the symmetry of a lotus flower and four curved glass panels that resemble petals. The exterior is also illuminated by integrated light strips designed by the American company L'Observatoire International, which help the structure glow harmoniously at night. Inside, the building has 64 floors, combining residential and office space.
Mori JP Tower is the tallest skyscraper in Japan, but it is not the tallest structure. That title belongs to Tokyo Skytree (634 m). Tokyo Tower (332.9 m) is also taller than Mori JP Tower. Both are broadcasting and observation towers, and are not included in the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat's height classification because they do not meet the criteria of having at least 50% of their area occupied by people.
In fact, the height of the Mori JP Tower may not seem impressive on its own. It is only the 134th tallest building in the world , but it is a remarkable structure considering the challenges of construction in a seismically active area like Tokyo. According to the contractor, Mori, the building would continue to function normally even during a magnitude 9 earthquake like the Great East Japan Earthquake of 2011.
To ensure the skyscraper's stability, steel pipe piles filled with high-strength concrete and several damping systems were installed to reduce swaying. In addition, the building also has an emergency shelter with a capacity of 3,600 people and a place to store essential supplies in case of natural disasters.
"High-strength steel and concrete are used to balance the structure. We also installed vibration control devices in key areas, which effectively reduce vibrations during earthquakes, resulting in strong sway resistance. In addition, a large-scale device called an active mass damper also helps to limit swaying at the top of the building during strong winds," Mori said.
All electricity for the building comes from renewable sources, with heat harvested from the sewer system. The building also stores and processes rainwater for irrigation, while wastewater from residential homes is collected and used in the bathrooms of the office floors.
An Khang (According to New Atlas )
Source link



















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)












































Comment (0)