1. Causes that prevent the body from absorbing vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that has antioxidant and immune-boosting properties, meaning it helps reduce free radical damage. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, vitamin A and other fat-soluble vitamins are able to travel through fat and are stored in the body's fat or organs, including the liver.
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Thi Lam, former Deputy Director of the National Institute of Nutrition, in addition to protecting the eyes, preventing night blindness and dry eyes, vitamin A also ensures the normal development of bones and teeth, protects the mucous membranes and skin, enhances the body's resistance, and helps fight infectious diseases.
Vitamin A deficiency causes dry eyes, dry cornea, keratomalacia; degeneration, keratinization of epithelial cells, reduced body's protective function; reduced immunity...
According to nutritionists, because vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, if the daily diet lacks fat, it will reduce the absorption of vitamin A. Lack of protein or zinc is also the cause of vitamin A deficiency because they play a role in the metabolism and transport of vitamin A.
In the body, active vitamin A exists as retinol, bound to fatty acids. Beta-carotene, which is found mainly in plants, must first be converted into active vitamin A for the body to use. This occurs in the lining of the intestine and the liver.
Often the vitamin A found in plant foods is not converted into active vitamin A, especially in people with poor gut health that makes the conversion difficult. This is why it is important to treat gut problems such as inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome, as these digestive problems can interfere with the ability to properly absorb vitamin A-rich foods.
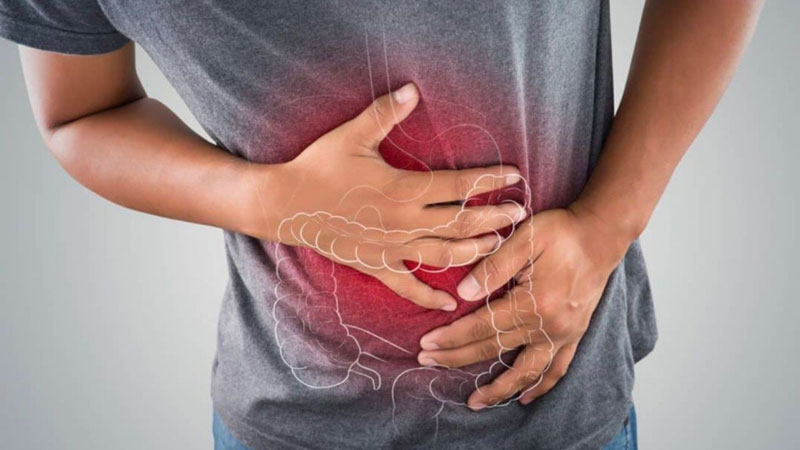
Poor gut health hinders vitamin A absorption.
2. How to supplement vitamin A through diet
How can we effectively get vitamin A through our diet? The best way is to eat healthy whole foods from plants and animals to provide two different forms of vitamin A.
The two main forms of vitamin A obtained from foods are beta-carotene (found in some plant foods, especially those that are orange, red, and yellow) and active vitamin A, also known as retinol (found in some animal foods such as eggs and liver).
The best plant sources of vitamin A are mainly orange, yellow, or red fruits and vegetables.
Regarding animal foods rich in vitamin A, foods with high fat content (such as eggs, butter, liver or whole milk) are more likely to provide vitamin A because it is a fat-soluble vitamin. Of these, liver is the food that contains the most vitamin A.
3. List of foods richest in vitamin A
Beef liver
85g of boiled beef liver contains 17,800 mcg of vitamin A (1977% DV - daily value) and 128 calories.
Sweet potato
1 boiled sweet potato without skin, (about 151g) contains 1,190 mcg vitamin A (132% DV) and 115 calories.
Pumpkin
1 cup (205g) of cooked, unsalted pumpkin contains 1,140 mcg of vitamin A (126% DV) and 82 calories.
Spinach
1 cup (180g) of cooked spinach without salt contains 943 mcg of vitamin A (105% DV) and 41 calories.
Tuna
About 85g of cooked bluefin tuna contains 643 mcg (71% DV) and 156 calories.
Carrot
1 raw carrot (61g) contains 509 mcg vitamin A (56% DV) and 25 calories.
Watermelon
1 cup (160g) of fresh cantaloupe contains 270 mcg (30% DV) and 54 calories.
Mackerel
About 190g of canned mackerel contains 247 mcg of vitamin A (27% DV) and 296 calories.
Kale
1 cup (118g) of cooked kale without salt contains 172 mcg of vitamin A (19% DV) and 42 calories.
Lettuce
1 cup (36g) of chopped green leaf lettuce contains 133 mcg (15% DV) and 5 calories.
Broccoli
About 180g of boiled, drained, unsalted broccoli contains 139 mcg of vitamin A (15% DV) and 63 calories.
Papaya
1 cup (230g) of pureed raw papaya contains 108 mcg (12% DV) and 99 calories.
Egg
Two whole eggs (122g) contain 98 mcg (11% DV) and 182 calories.
Whole milk
1 cup (244g) of whole milk (3.25% milkfat) contains 112 mcg (12% DV) and 149 calories.
Goat cheese
About 28g of soft goat cheese contains 82 mcg of vitamin A (9% DV) and 75 calories.
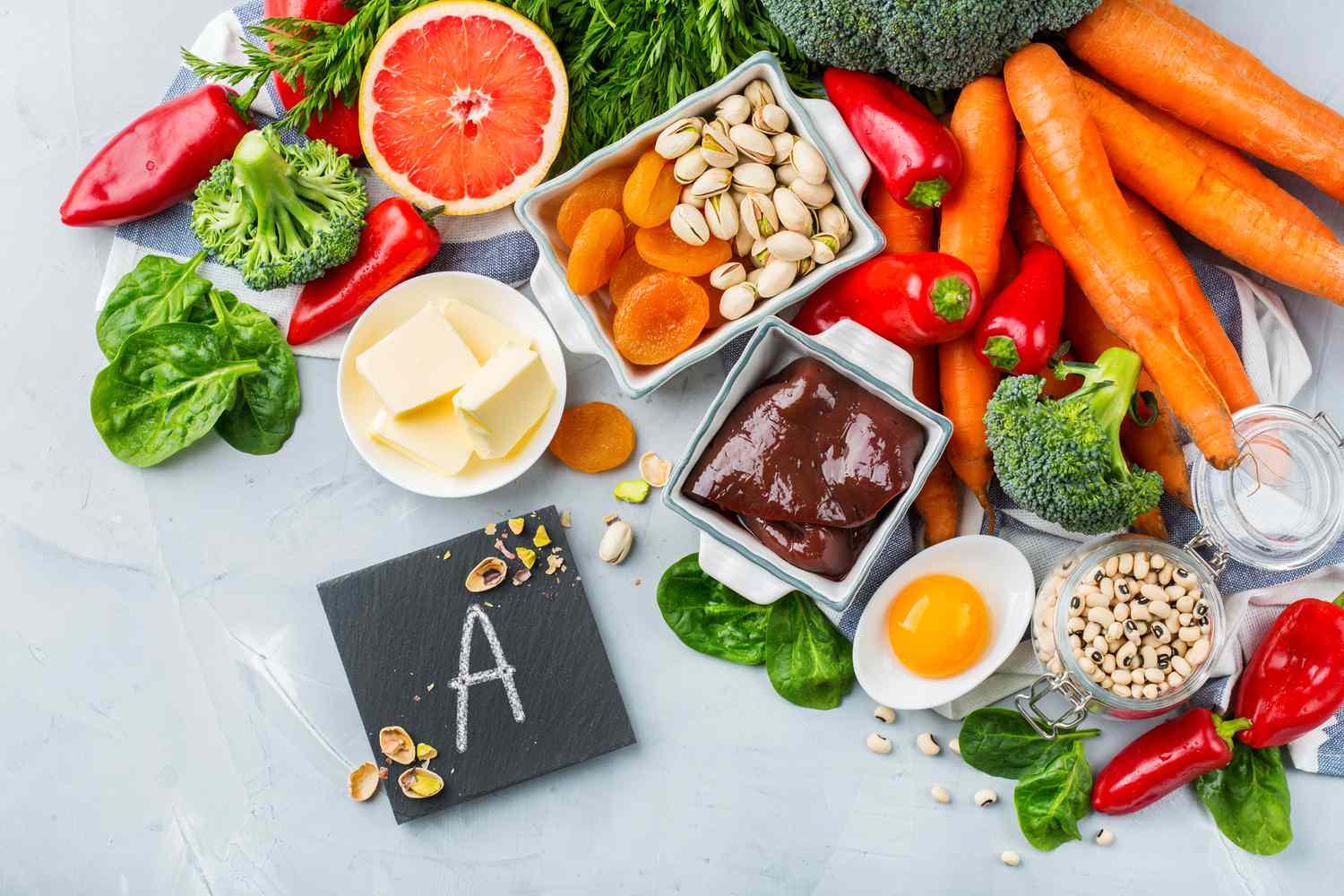

Foods rich in vitamin A are good for health.
Nutritionists recommend that using foods rich in vitamin A in daily meals is the safest and most effective way to supplement vitamin A. When we have applied a nutritious diet and increased foods rich in vitamin A, we should not arbitrarily take vitamin A supplements without a doctor's prescription because it can cause poisoning and many other harmful effects to health.
Source






































































































Comment (0)