 |
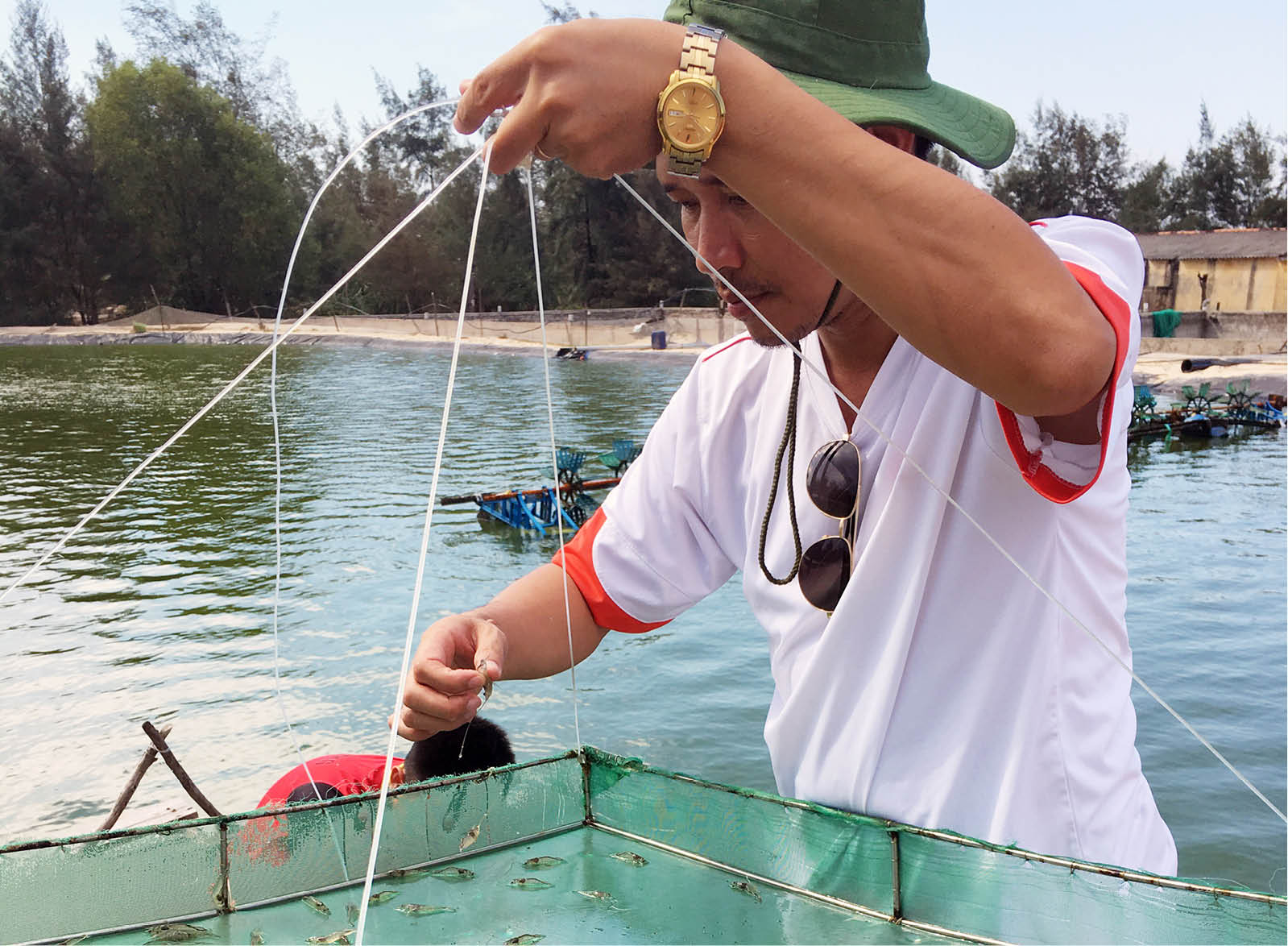
| Research staff inspect farmed shrimp |
Antibiotic abuse, environmental pollution
In the past few years, white-leg shrimp farming on coastal sand in Hue city in particular and Vietnam in general has been facing many difficulties and challenges. In particular, persistent diseases are considered the main cause of shrimp farming losses. From hundreds of hectares of shrimp ponds with an average of two crops per year, most of them have been abandoned for several years now. "For the past 2-3 years, every crop has been a loss due to diseases, people have not been able to reinvest so they have had to abandon their ponds," said Mr. Vo Khang in Phong Quang ward (merged from Phong Hai ward, Quang Cong, Quang Ngan).
According to the Department of Agriculture and Environment, although shrimp farming on coastal sand has become a trend, it is still developing spontaneously. Most of the farming areas take water from the sea directly into the ponds, then discharge the used water directly into the sea without environmental treatment. When shrimp are sick, people still discharge untreated water, causing the disease to spread rapidly. This is a matter of concern because it can lead to bad consequences for the shrimp farmers themselves, affecting the ecological environment.
Associate Professor, Dr. Mac Nhu Binh, Deputy Head of the Faculty of Aquaculture, University of Agriculture and Forestry, Hue University, said that currently, the use of antibiotics to treat diseases in shrimp is very popular. However, antibiotics are no longer effective in treating bacterial infections in aquatic animals, due to the increasing number of drug-resistant bacteria strains. In this situation, new research and treatment methods are needed, in which one of the highly appreciated trends is nanotechnology.
Studies have shown that nano drug delivery systems, with nanometer size, are capable of overcoming the biological barriers of the host body and dealing with the drug resistance mechanism of pathogens. Based on the properties of advanced materials, the drug release process can also be controlled, concentrated in areas with pathogens to help improve the effectiveness of the drug, minimizing side effects on the host body.
Advantages of nanotechnology
The Faculty of Aquaculture, University of Agriculture and Forestry, Hue University has built a shrimp farming model using nanotechnology with an area of 3,000m2, bringing efficiency, opening up new opportunities for shrimp farming in particular and aquaculture in general in Hue city and the whole country.
Dr. Mac Nhu Binh discussed that the above model serves the research to apply nanotechnology to bring antibiotics into white-leg shrimp farming to prevent and treat common diseases caused by bacteria in shrimp. The process of implementing the model shows that the application of nanotechnology contributes to limiting the use of antibiotics as well as reducing the amount of residual antibiotics compared to conventional antibiotic use methods. From there, the effectiveness of using new materials can be evaluated, as a basis for wide application in shrimp farming in particular and aquaculture in general.
Nanotechnology is currently being widely researched and applied to remove pollutants in water. Nanomaterials in the form of activated materials such as carbon, aluminum, with carriers such as zeolite, bentonite and iron-containing compounds can be used to create aerobic and anaerobic filter membranes to remove ammonia, nitrite. Nanoparticles with high antibacterial activity such as nano silver, nano zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, copper and iron are the most commonly researched objects.
Using these nanoparticles in the treatment of aquaculture water environment helps eliminate pathogens and sources of disease that are harmful to aquaculture, including bacteria and viruses that cause diseases in aquaculture such as shrimp, fish, mollusks, etc.; at the same time, cleans impurities in the water environment. Using nanoparticles to treat the environment will increase water quality, almost completely eliminate pathogens as well as toxic substances for aquaculture, minimizing the use of antibiotics and toxic environmental treatment substances. On the other hand, when the aquaculture environment is infected, using nanoparticles to treat the aquaculture environment with the advantage of fast and strong activity will quickly clean the environment and help prevent the spread of disease in the farming area.
The Faculty of Aquaculture, University of Agriculture and Forestry, Hue University is continuing to research a shrimp farming model applying nanotechnology to contribute to the sustainable and effective farming of white-leg shrimp on coastal sand.
Source: https://huengaynay.vn/kinh-te/ung-dung-cong-nghe-nano-trong-nuoi-tom-tren-cat-155872.html


![[Photo] 60th Anniversary of the Founding of the Vietnam Association of Photographic Artists](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764935864512_a1-bnd-0841-9740-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the VinFuture 2025 Award Ceremony](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764951162416_2628509768338816493-6995-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)













































































































Comment (0)